Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants PDF Notes, Important Questions and Synopsis
SYNOPSIS
- A flower is a compressed shoot which bears nodes and modified floral leaves.
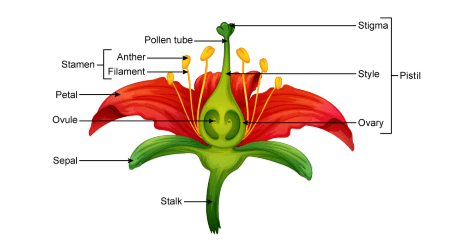
- Parts of a Flower
- Difference between Monoecious and Dioecious Plants
Monoecious Plants
Dioecious Plants
- Plants which bear flowers of both sexes. Example: Maize
- Plants which produce exclusively staminate or pistillate flowers. Example: Date palm
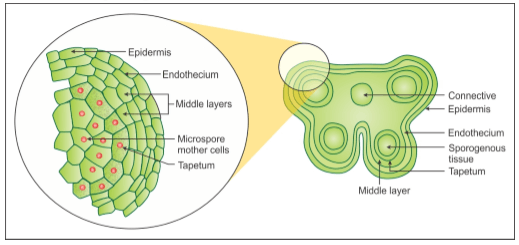
- Structure of Microsporangium
- The process of formation of microspores from a pollen mother cell through meiosis is called microsporogenesis.
-
A monocarpellary gynoecium consists of a single pistil, and a multicarpellary gynoecium has more than one pistil.
-
When more than one pistils are fused together, it is called syncarpous. When the pistils are free, it is called apocarpous.
-
The process of formation of megaspores from the megaspore mother cell is called megasporogenesis.
-
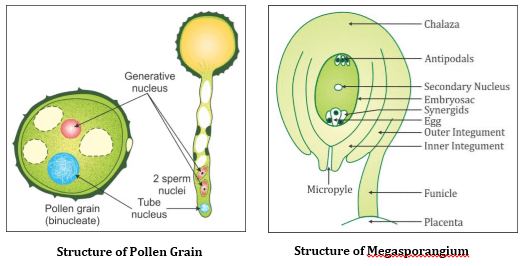
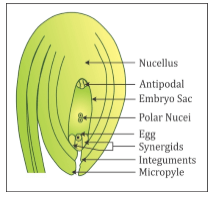
Structure of a Typical Angiosperm Ovule
-
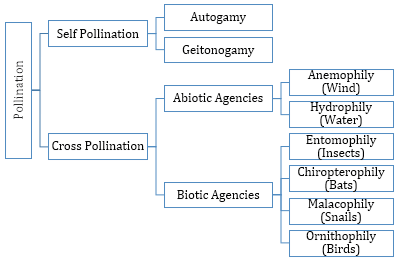
Pollination is the transfer of pollen grains from the anther of a flower to the stigma of the same flower or another flower of the same or different plant of the same species.
-
Types of Pollination
-
Emasculation is the technique in which the anthers of bisexual flowers are removed from the flower bud with the help of forceps before the anther dehisces.
-
If the pollen is of the right type, the pistil accepts the pollen and promotes post-pollination events which leads to fertilisation.
-
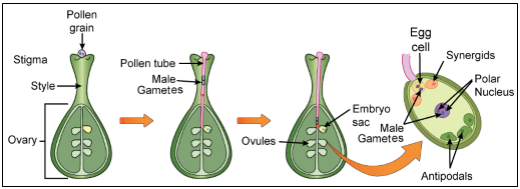
Double Fertilisation in Flowering Plants
-
The endosperm is a highly nutritive tissue formed as a result of triple fusion and provides nourishment to the developing embryo.
-
The zygote gives rise to the proembryo and the globular, heart-shaped mature embryo.
-
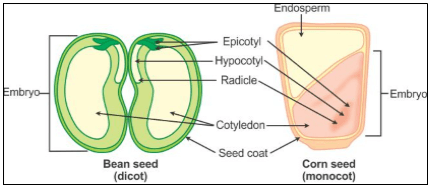
The portion of the embryonal axis above the level of cotyledons is the called the epicotyl, while the cylindrical portion below the level of the cotyledons is called the hypocotyl.
-
The seed is regarded as a fertilised mature ovule which bears an embryonic plant, a protective seed coat and often stored food material.
-
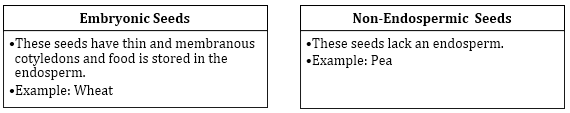
Embryonic Seeds and Non-Endospermic Seeds
-
Structure of Monocotyledonous and Dicotyledonous Seeds
-
A fruit is regarded as a ripened ovary.
-
A true fruit is a fruit which develops only from the ovary, whereas a false fruit is a fruit which develops from any floral part of the flower other than the ovary.
-
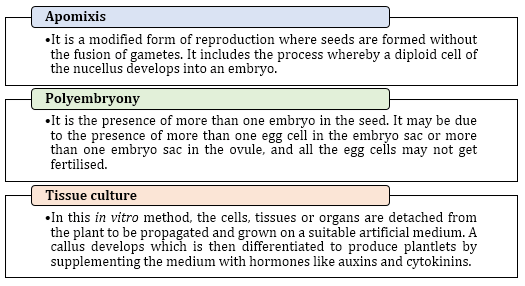
Special Modes of Reproduction
Related Chapters
- The Living World
- Biological Classification
- Plant Kingdom
- Animal Kingdom
- Morphology of Flowering Plants
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants
- Structural Organisation in Animals
- Cell : The Unit of Life
- Biomolecules
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division
- Transport in Plants
- Mineral Nutrition
- Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
- Respiration in Plants
- Plant Growth and Development
- Digestion and Absorption
- Breathing and Exchange of Gases
- Body Fluids and Circulation
- Excretory Products and their Elimination
- Locomotion and Movement
- Neural Control and Coordination
- Chemical Coordination and Integration
- Reproduction in Organisms
- Human Reproduction
- Reproductive Health
- Principles of Inheritance and Variation
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance
- Evolution
- Human Health and Disease
- Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production
- Microbes in Human Welfare
- Biotechnology : Principles and Processes
- Biotechnology and its Applications
- Organisms and Populations
- Ecosystem
- Biodiversity and Conservation
- Environmental Issues