Excretory Products and their Elimination
Excretory Products and Their Elimination PDF Notes, Important Questions and Synopsis
SYNOPSIS
- Excretion is the process by which living organisms get rid of waste substances either totally or partially accumulated during metabolic activities.
- Modes of Excretion in Animals
- Organs of Excretion in Animals
Animal group
Excretory structures
Protozoans
- Contractile vacuole
Sponges
- Body surface
Coelenterates
- Body surface
Platyhelminthes
- Protonephridia or flame cells
Annelids
- Nephridia
Echinoderms
- Tube feet and dermal branchiae
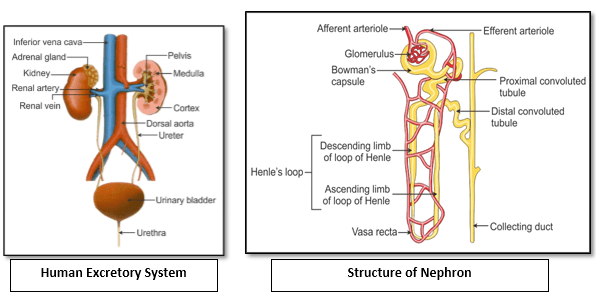
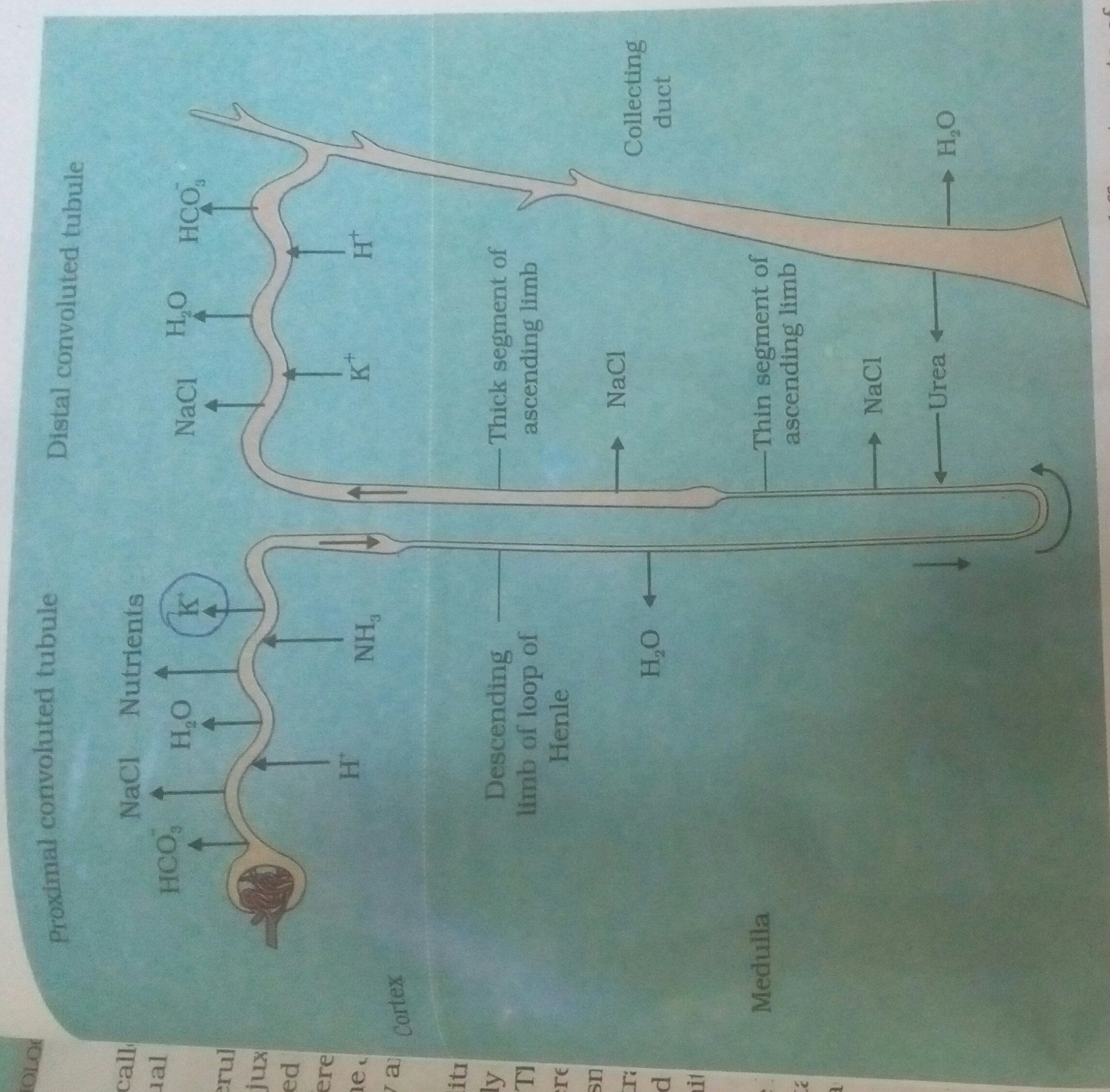
- Urine Formation
-
Counter Current Mechanism
- In the two limbs of the loop of Henle, urine flows in the opposite direction which forms a
- counter current.
- Similarly, the flow of blood in the two limbs of the vasa recta are also in the counter current pattern.
- This system of a liquid flowing in the two limbs in two opposite directions is termed the counter
- current mechanism.
- It helps to maintain the concentration gradient in the renal medulla and hence helps in concentrating urine in the loop of Henle.
- Regulation of Kidney Function
Myogenic Autoregulation
Neural Control Hormonal Control -
When the systemic blood pressure increases, the afferent arteriole narrows down which decreases GFR.
- Nerve fibres of the sympathetic nervous system innervate the blood vessels of the kidneys which decreases GFR.
- Anti-diuretic hormone (ADH)
- Renin
- Atrial natriuretic factor (ANF)
-
-
The process of release of urine is called micturition.
-
Role of Other Excretory Organs
Sweat glands
- Excrete sweat
Lungs
- Remove carbon dioxide and water vapour
Liver
-
Eliminates cholesterol, inactivated products of steroid hormones, vitamins and drugs
Large intestine
- Removes salts such as calcium phosphate
Download complete content for FREE 
NEET - Biology
Asked by sanjukohli05 | 21 Jun, 2022 01:59: PM
NEET - Biology
Asked by ravs5050 | 09 Aug, 2021 11:43: AM
NEET - Biology
Asked by sahilrock811 | 02 May, 2021 08:48: AM
NEET - Biology
Asked by anshika.akk668 | 15 Aug, 2020 05:30: PM
NEET - Biology
Asked by sanjay258147 | 12 May, 2020 12:00: AM
NEET - Biology
Asked by Prashant DIGHE | 03 Feb, 2020 10:19: PM
NEET - Biology
Asked by sumayiah2000 | 27 Jan, 2020 10:19: PM
NEET - Biology
Asked by jhajuhi19 | 23 Dec, 2019 11:30: AM
Related Chapters
- The Living World
- Biological Classification
- Plant Kingdom
- Animal Kingdom
- Morphology of Flowering Plants
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants
- Structural Organisation in Animals
- Cell : The Unit of Life
- Biomolecules
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division
- Transport in Plants
- Mineral Nutrition
- Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
- Respiration in Plants
- Plant Growth and Development
- Digestion and Absorption
- Breathing and Exchange of Gases
- Body Fluids and Circulation
- Locomotion and Movement
- Neural Control and Coordination
- Chemical Coordination and Integration
- Reproduction in Organisms
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
- Human Reproduction
- Reproductive Health
- Principles of Inheritance and Variation
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance
- Evolution
- Human Health and Disease
- Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production
- Microbes in Human Welfare
- Biotechnology : Principles and Processes
- Biotechnology and its Applications
- Organisms and Populations
- Ecosystem
- Biodiversity and Conservation
- Environmental Issues