Microbes in Human Welfare
Microbes In Human Welfare PDF Notes, Important Questions and Synopsis
SYNOPSIS
- Microbes in Household Products
Lactic acid bacteria (LAB)
- Curd from milk
- Fermentation of idli and dosa dough
Propionibacterium shermanii
- Production of Swiss cheese
- Microbes in Industrial Products:
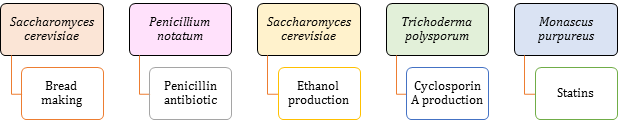
-
Antibiotic is a chemical substance which is obtained as a metabolic product from one living organism and has an inhibitory effect on another living organism.
-
Masses of bacteria associated with fungal filaments to form mesh-like structures are called flocs.
-
Sewage is the municipal waste water containing large amounts of organic matter and microbes.
-
Difference between Primary Treatment and Secondary Treatment of Sewage
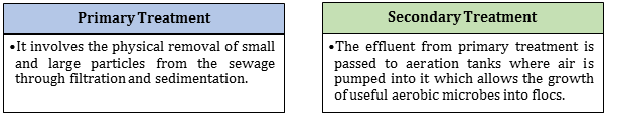
-
Biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) refers to the amount of oxygen which would be consumed if all the organic matter in one litre of water was oxidised by bacteria.
-
Biogas is a mixture of gases produced during the decay of biomass in the absence of oxygen.
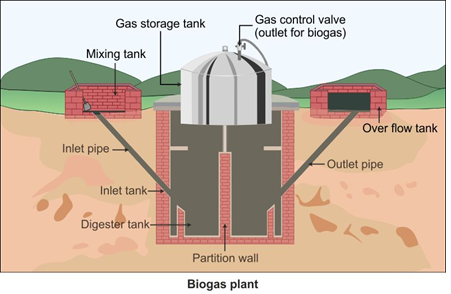
-
Bacteria which grow anaerobically on cellulosic material and produce a large amount of methane along with CO2 and H2 are collectively called methanogens.
-
Biological control is the control of destructive insects with the utilisation of other insects.
-
The soil bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis acts as a biopesticide.
-
Integrated pest management (IPM) aims at the minimum use of pesticides to prevent agrochemical pollution and to adopt natural methods of pest control.
-
Biofertilisers are organisms which can bring about soil nutrient enrichment.
-
Mycorrhiza is the symbiotic association of fungal hyphae and the roots of higher plants.
-
Cyanobacteria are autotrophic microbes which can fix atmospheric nitrogen. Examples: Anabaena, Nostoc, Oscillatoria
Related Chapters
- The Living World
- Biological Classification
- Plant Kingdom
- Animal Kingdom
- Morphology of Flowering Plants
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants
- Structural Organisation in Animals
- Cell : The Unit of Life
- Biomolecules
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division
- Transport in Plants
- Mineral Nutrition
- Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
- Respiration in Plants
- Plant Growth and Development
- Digestion and Absorption
- Breathing and Exchange of Gases
- Body Fluids and Circulation
- Excretory Products and their Elimination
- Locomotion and Movement
- Neural Control and Coordination
- Chemical Coordination and Integration
- Reproduction in Organisms
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
- Human Reproduction
- Reproductive Health
- Principles of Inheritance and Variation
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance
- Evolution
- Human Health and Disease
- Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production
- Biotechnology : Principles and Processes
- Biotechnology and its Applications
- Organisms and Populations
- Ecosystem
- Biodiversity and Conservation
- Environmental Issues

