Ecosystem
Ecosystem PDF Notes, Important Questions and Synopsis
SYNOPSIS
- Ecosystem is the relationship between a biotic community and an abiotic environment.
- Stratification is the vertical distribution of different species occupying different levels.
- Primary production is defined as the amount of biomass or organic matter produced per unit area over a time period by plants during photosynthesis. It is expressed in terms of weight (g–2) or energy (kcal m–2).
- Productivity is the rate of biomass production and is expressed in terms of dry matter produced or energy captured per unit area of land per unit time.
- Gross primary productivity of an ecosystem is the rate of production of organic matter during photosynthesis.
- Net primary productivity is the total amount of energy stored in the plant tissues after utilising some energy for their own metabolic activities through respiration.
- Secondary productivity is defined as the rate of formation of new organic matter by consumers.
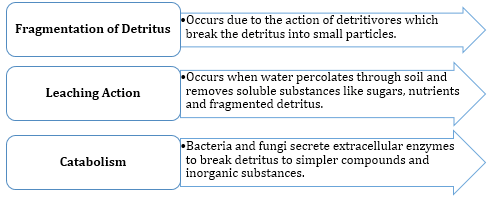
- Decomposition is the process of breakdown of complex organic matter by decomposers to inorganic raw materials like carbon dioxide, water and various nutrients.
- Dead plant remains such as leaves, bark and flowers and dead remains of animals, including faecal matter, constitute detritus.
-
Humification is the formation of a dark-coloured amorphous substance called humus.
-
Mineralisation refers to the formation of minerals during the process of decomposition in the soil.
-
First law of thermodynamics: Energy is neither created nor destroyed but can be transferred from one component to another or transformed from one state to another.
-
Second law of thermodynamics: Every system when left to itself has the tendency towards disorderliness or entropy.
-
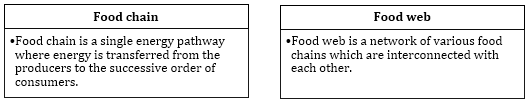
Differences between Food Chain and Food Web
-
Each step in the food chain at which the transfer of food takes place is known as a trophic level.
-
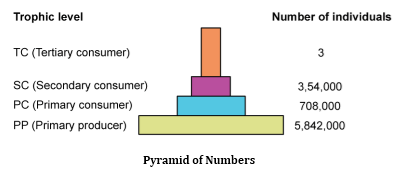
Each trophic level has a certain mass of living material at a particular time called the standing crop.
-
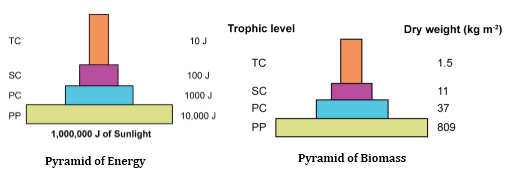
Energy flow in an ecosystem: It is unidirectional and follows the 10% law. According to this law, only 10 percent of energy is transferred from one trophic level to the other; the rest is lost to the atmosphere in the form of heat.
-
Ecological pyramids are graphic representations of certain specific parameters such as number and biomass of energy of a food chain.
-
The gradual and fairly predictable change in the species composition of a given area is called ecological succession.
-
Difference between Hydrarch Succession and Xerarch Succession
Hydrarch succession
Xerarch succession
- It takes place in wetter areas and the successional series progresses from hydric to mesic conditions.
- It takes place in dry areas and the successional series progresses from xeric to mesic conditions.
-
The species which invade a bare area is called a pioneer species.
-
The amount of nutrients, such as carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, calcium etc., present in the soil at any given time is referred to as the standing state.
-
The movement of nutrient elements through the various components of an ecosystem is called nutrient cycling.
Gaseous Cycle
Sedimentary Cycle
- Reservoir – Atmosphere
- Reservoir – Earth’s crust
- Nitrogen cycle, carbon cycle
- Phosphorus cycle, sulphur cycle
Related Chapters
- The Living World
- Biological Classification
- Plant Kingdom
- Animal Kingdom
- Morphology of Flowering Plants
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants
- Structural Organisation in Animals
- Cell : The Unit of Life
- Biomolecules
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division
- Transport in Plants
- Mineral Nutrition
- Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
- Respiration in Plants
- Plant Growth and Development
- Digestion and Absorption
- Breathing and Exchange of Gases
- Body Fluids and Circulation
- Excretory Products and their Elimination
- Locomotion and Movement
- Neural Control and Coordination
- Chemical Coordination and Integration
- Reproduction in Organisms
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
- Human Reproduction
- Reproductive Health
- Principles of Inheritance and Variation
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance
- Evolution
- Human Health and Disease
- Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production
- Microbes in Human Welfare
- Biotechnology : Principles and Processes
- Biotechnology and its Applications
- Organisms and Populations
- Biodiversity and Conservation
- Environmental Issues