Environmental Issues
Environmental Issues PDF Notes, Important Questions and Synopsis
SYNOPSIS
- Pollution is any undesirable change in physical, chemical or biological characteristics of air, land, water or soil.
- Agents which bring about pollution are called pollutants.
- Air pollution is the undesirable change in physico-chemical characteristics of air which adversely affects the functioning of human life.
- Electrostatic precipitators are used to separate particulate matter from polluted air.
- Scrubbers are used in chemical, mining and metallurgical industries to remove gases like SO2, NH3 etc.
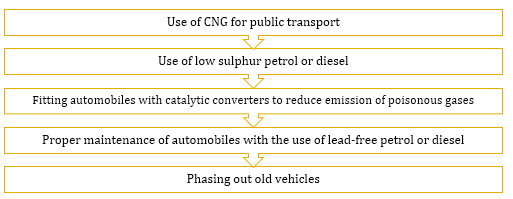
- Steps to Reduce Vehicular Pollution
-
CNG is better than diesel because
- It burns efficiently.
- It is cheaper than petrol/diesel.
- It cannot be adulterated.
- Noise pollution is the unwanted sound dumped into the atmosphere which interferes with human communication, comfort and health.
-
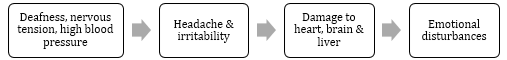
Effects of Noise Pollution
-
Control Methods of Noise Pollution
- Construction of sound barriers and improvement in machines.
- Use of ear protective devices by workers of factories.
- Use of ear plugs or muffs.
- Legislation should not permit anyone to create noise in silent zones.
- Water pollution is the degradation of water due to the addition of harmful substances and deprivation which makes it hazardous, unfit for human use and causes the growth of aquatic biota.
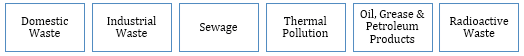
- Sources of Water Pollution
- Biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) is the amount of oxygen required by microorganisms in stabilising biologically degradable matter.
- Biological magnification is the process of concentration of harmful chemicals at each successive trophic level in a food chain.
- Eutrophication is the excessive consumption of dissolved oxygen in water by the rich growth of microorganisms.
- Solid wastes refer to everything which goes out in trash including municipal solid wastes from homes, offices, stores, schools and hospitals.
- Methods to Control Solid Wastes
- Radioactive pollution is related to air, water and soil and is caused by radioactive substances when they disintegrate in nature.
- Radioactive waste is a toxic waste given out by nuclear reactors.
- Greenhouse effect is the phenomenon where global warming occurs due to the increased level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
- Increase in the level of greenhouse gases led to the heating of the Earth leading to global warming.
-
The gradual reduction in the thickness of the ozone layer leads to the ozone hole.
-
Effects of Ultraviolet Radiation
- Snow-blindness cataract
- Ageing of skin, skin cancer
- Mutations in humans
- Soil erosion is the removal of the top, fertile layer of soil which occurs due to over-grazing and depletion of the vegetation cover in semi-arid regions.
- Irrigation without proper drainage of water leads to waterlogging in soil.
- Deforestation is the conversion of forested areas to non-forested ones.
- Reforestation is the process of restoring a forest which once existed but was removed at some point of time in the past.
- Slash and burn agriculture, commonly called Jhum cultivation, is a process in which farmers cut down the trees of the forest and burn the plant remains. The ash is used as a fertiliser and the land is used for farming or cattle grazing.
Download complete content for FREE 
NEET - Biology
Asked by ishitajain639 | 26 Jul, 2020 09:36: AM
NEET - Biology
Asked by sumayiah2000 | 26 Mar, 2020 01:24: AM
Related Chapters
- The Living World
- Biological Classification
- Plant Kingdom
- Animal Kingdom
- Morphology of Flowering Plants
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants
- Structural Organisation in Animals
- Cell : The Unit of Life
- Biomolecules
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division
- Transport in Plants
- Mineral Nutrition
- Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
- Respiration in Plants
- Plant Growth and Development
- Digestion and Absorption
- Breathing and Exchange of Gases
- Body Fluids and Circulation
- Excretory Products and their Elimination
- Locomotion and Movement
- Neural Control and Coordination
- Chemical Coordination and Integration
- Reproduction in Organisms
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
- Human Reproduction
- Reproductive Health
- Principles of Inheritance and Variation
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance
- Evolution
- Human Health and Disease
- Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production
- Microbes in Human Welfare
- Biotechnology : Principles and Processes
- Biotechnology and its Applications
- Organisms and Populations
- Ecosystem
- Biodiversity and Conservation