Evolution
Evolution PDF Notes, Important Questions and Synopsis
SYNOPSIS
- Theories for the Origin of Life:
Theory of Biogenesis
The main concept of biogenesis states that ‘Life originates from pre-existing life’.
Theory of spontaneous generation
This theory states that life originated from non-living things in a spontaneous manner.
Oparin-Haldane theory
Oparin-Haldane suggested that life comes into existence as a result of chemical evolution which took place on the primordial earth under the impact of certain favourable conditions which no longer exist.
Big Bang theory
The Big Bang theory states that the whole matter in the beginning of the universe was concentrated in the form of a dense hot fireball. - Urey and Miller demonstrated that the electrical discharges or heat energy can form complex organic substances from a mixture of methane, ammonia, water and hydrogen.
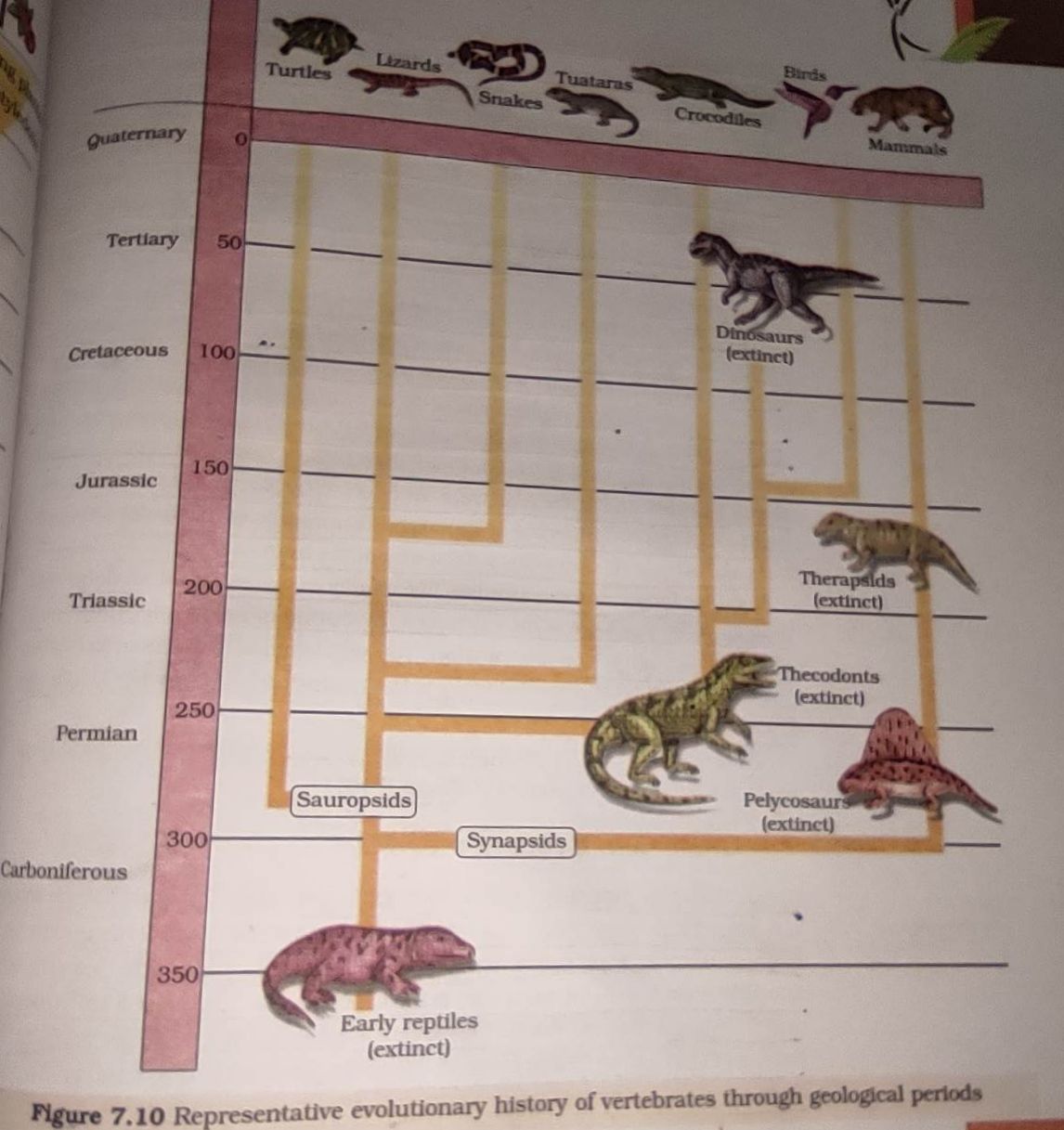
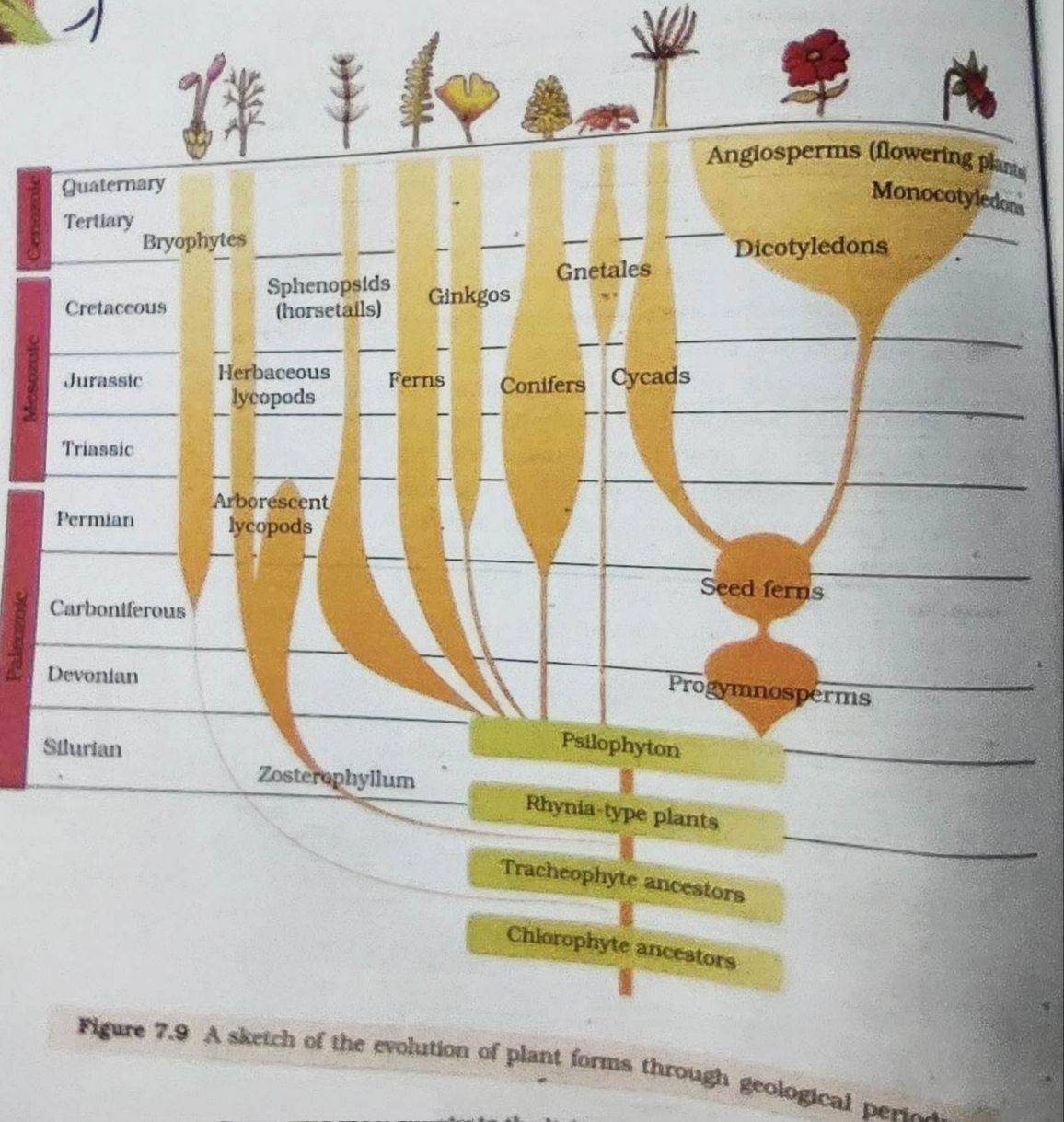
- Evidences of Evolution:
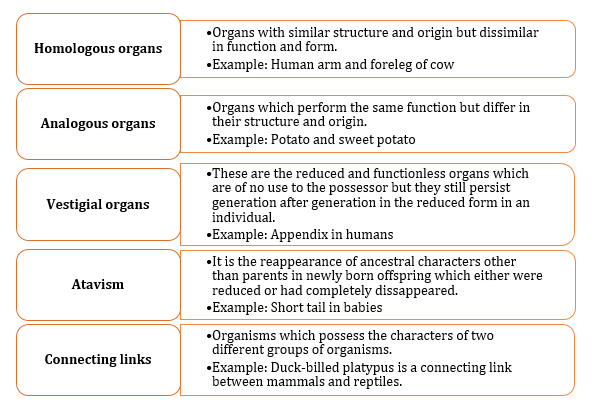
- Differences between Divergent Evolution and Convergent Evolution:
Divergent Evolution
Convergent Evolution
- It is the development of different functional structures from a common ancestral form.
- Homologous organs show divergent evolution.
- It is the development of similar adaptive functional structures in unrelated groups of organisms.
- Analogous organs show convergent evolution.
-
Adaptive radiation is the process of evolution of different species in a given geographical area starting from a point and literally radiating to other geographical areas.
Example: Darwin’s finches and Australian marsupials -
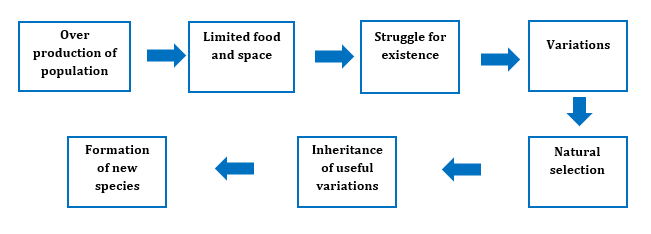
Salient Features of Darwin’s Theory of Evolution:
-
Salient Features of Lamarck’s Theory of Evolution:

-
Hardy-Weinberg Principle:
- Allele frequencies in a population are stable and constant from generation to generation.
- The gene pool remains constant. This is called genetic equilibrium.
- Sum total of all the allelic frequencies is 1.
-
Natural selection is a process in which heritable variations enabling better survival enable the organism to reproduce and leave greater number of progeny.
-
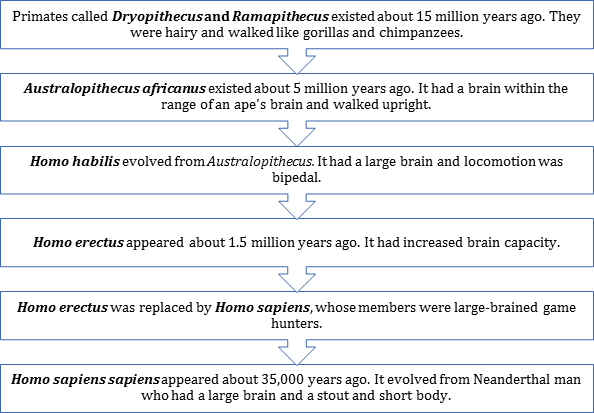
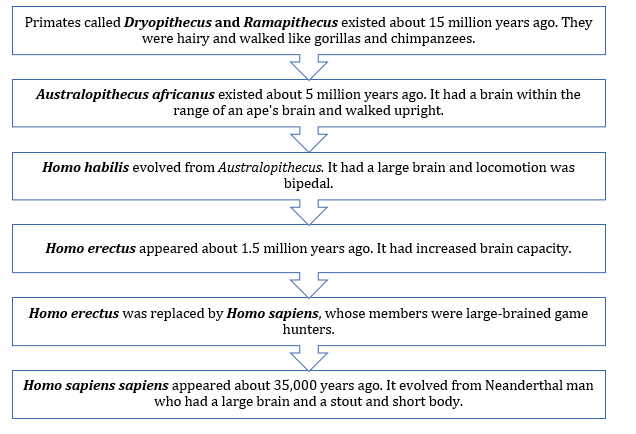
Human Evolution:
Related Chapters
- The Living World
- Biological Classification
- Plant Kingdom
- Animal Kingdom
- Morphology of Flowering Plants
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants
- Structural Organisation in Animals
- Cell : The Unit of Life
- Biomolecules
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division
- Transport in Plants
- Mineral Nutrition
- Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
- Respiration in Plants
- Plant Growth and Development
- Digestion and Absorption
- Breathing and Exchange of Gases
- Body Fluids and Circulation
- Excretory Products and their Elimination
- Locomotion and Movement
- Neural Control and Coordination
- Chemical Coordination and Integration
- Reproduction in Organisms
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
- Human Reproduction
- Reproductive Health
- Principles of Inheritance and Variation
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance
- Human Health and Disease
- Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production
- Microbes in Human Welfare
- Biotechnology : Principles and Processes
- Biotechnology and its Applications
- Organisms and Populations
- Ecosystem
- Biodiversity and Conservation
- Environmental Issues