Biotechnology : Principles and Processes
Principles and Processes in Biotechnology PDF Notes, Important Questions and Synopsis
SYNOPSIS
- Biotechnology deals with the techniques of using live organisms or enzymes from organisms to produce products and processes useful to humans.
- Genetic engineering is a technique which refers to a change in the genetic material and its introduction into a host organism for changing the phenotype of the host organism.
- Gene cloning is a technique to obtain clones or identical copies of a particular DNA molecule.
- Recombinant DNA technology involves combining DNA from two different organisms to generate recombinant DNA.
- Steps involved in genetically modifying an organism:
- Identification of DNA with desirable genes
- Introduction of the identified DNA into the host
- Maintenance of introduced DNA in the host and transfer of the DNA to its progeny
- Differences between Exonucleases and Endonucleases:

-
A DNA palindrome is a sequence of base pairs which reads the same on the two strands when the orientation of reading is kept the same.
5′ – GAATTC – 3′
3′ – CTTAAG – 5′ -
Restriction enzymes cut the DNA strand a little away from the centre of the palindrome sites, but between the same two bases on the opposite strands leaving the single stranded portions at the ends. These overhanging stretches are called sticky ends.
-
Gel electrophoresis is a technique of separating DNA fragments formed by the action of restriction endonucleases.
-
Plasmids are extra-chromosomal, self-replicating, usually circular, double-stranded DNA molecules.
-
Transformation is a procedure through which a piece of DNA is introduced in a host bacterium.
-
Origin of replication is the sequence from where replication starts and any piece of DNA on linking to this sequence can be made to replicate within the host cells.
-
The method of injecting foreign DNA into the nucleus of an animal cell or a plant cell by using micro-needles or micro-pipettes is called micro-injection.
-
Gene gun is a new technology where vectorless direct gene transfer occurs in organisms.
-
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique used to synthesise multiple copies of the desired gene in vitro within a short span of time.
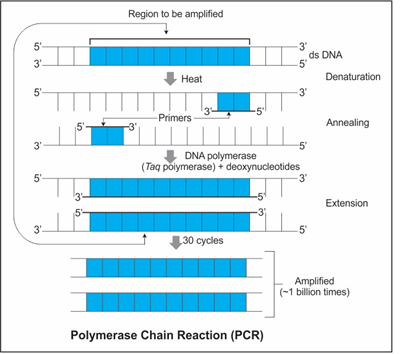
-
Any protein-encoding gene expressed in a heterologous host is called a recombinant protein.
-
Bioreactors are vessels where raw materials are biologically converted to specific products, individual enzymes etc. using microbial plant, animal or human cells.
-
The products formed after completion of biosynthetic phase undergo a series of processes before putting them in the market as a finished product. These processes include separation and purification and are collectively called downstream processing.
Related Chapters
- The Living World
- Biological Classification
- Plant Kingdom
- Animal Kingdom
- Morphology of Flowering Plants
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants
- Structural Organisation in Animals
- Cell : The Unit of Life
- Biomolecules
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division
- Transport in Plants
- Mineral Nutrition
- Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
- Respiration in Plants
- Plant Growth and Development
- Digestion and Absorption
- Breathing and Exchange of Gases
- Body Fluids and Circulation
- Excretory Products and their Elimination
- Locomotion and Movement
- Neural Control and Coordination
- Chemical Coordination and Integration
- Reproduction in Organisms
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
- Human Reproduction
- Reproductive Health
- Principles of Inheritance and Variation
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance
- Evolution
- Human Health and Disease
- Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production
- Microbes in Human Welfare
- Biotechnology and its Applications
- Organisms and Populations
- Ecosystem
- Biodiversity and Conservation
- Environmental Issues

