Anatomy of Flowering Plants
Anatomy of Flowering Plants PDF Notes, Important Questions and Synopsis
SYNOPSIS
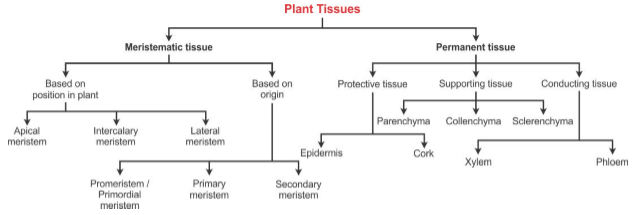
- Classification of Plant Tissues
- Classification of Tissue System
- Differences between Monocotyledonous Stem and Dicotyledonous Stem:
Monocotyledonous Stem
Dicotyledonous Stem
- Hypodermis is sclerenchymatous.
- Hypodermis is collenchymatous.
- Pith is absent.
- Pith is well-developed.
- Phloem parenchyma is absent.
- Phloem parenchyma is present.
- Vascular bundles are scattered.
- Vascular bundles are arranged in a ring.
- Vascular bundles are conjoint and closed.
- Vascular bundles are conjoint and open.
- Differences between Monocotyledonous Root and Dicotyledonous Root:
Monocotyledonous Root
Dicotyledonous Root
- Pericycle gives rise to lateral roots only.
- Pericycle gives rise to cork cambium, parts of the vascular cambium and lateral roots.
- It has a higher number of xylem and phloem.
- It has a limited number of xylem and phloem.
- The xylem is angular or polygonal.
- The xylem is angular or polygonal.
- The pith is larger and well developed.
- The pith is absent or very small and undeveloped.
- Conjunctive tissue is sclerenchymatous.
- Conjunctive tissue is parenchymatous.
- Xylem is polyarch.
- Xylem is usually tetrarch.
- Differences between Monocotyledonous Leaf and Dicotyledonous Leaf:
Monocotyledonous Leaf
Dicotyledonous Leaf
- Isobilateral
- Dorsiventral
- Stomata equally present on both surfaces.
- Stomata usually present on lower surface.
- Stomata have dumb-bell shaped guard cells.
- Stomata have bean-shaped guard cells.
- Mesophyll is undifferentiated.
- Mesophyll is differentiated into palisade and spongy parenchyma.
- Bulliform cells are present.
- Bulliform cells are absent.
-
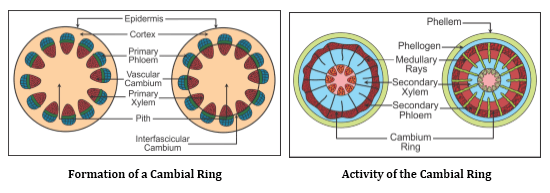
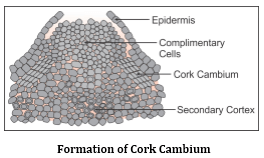
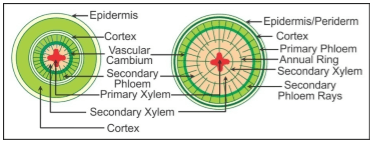
Increase in the girth or thickness of the plant is called secondary growth.
-
Secondary Growth in a Dicot Stem
-
Secondary Growth in a Dicot Stem
Download complete content for FREE 
NEET - Biology
Asked by myindiaisbad | 08 Feb, 2023 05:10: PM
NEET - Biology
Asked by myindiaisbad | 08 Jan, 2023 12:08: AM
NEET - Biology
Asked by spudausa | 31 Dec, 2022 10:34: PM
NEET - Biology
Asked by patra04011965 | 11 Mar, 2022 09:50: AM
NEET - Biology
Asked by ariprashath2001 | 23 Nov, 2020 10:31: AM
NEET - Biology
Asked by abhinavr707 | 31 Mar, 2020 05:07: PM
Related Chapters
- The Living World
- Biological Classification
- Plant Kingdom
- Animal Kingdom
- Morphology of Flowering Plants
- Structural Organisation in Animals
- Cell : The Unit of Life
- Biomolecules
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division
- Transport in Plants
- Mineral Nutrition
- Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
- Respiration in Plants
- Plant Growth and Development
- Digestion and Absorption
- Breathing and Exchange of Gases
- Body Fluids and Circulation
- Excretory Products and their Elimination
- Locomotion and Movement
- Neural Control and Coordination
- Chemical Coordination and Integration
- Reproduction in Organisms
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
- Human Reproduction
- Reproductive Health
- Principles of Inheritance and Variation
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance
- Evolution
- Human Health and Disease
- Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production
- Microbes in Human Welfare
- Biotechnology : Principles and Processes
- Biotechnology and its Applications
- Organisms and Populations
- Ecosystem
- Biodiversity and Conservation
- Environmental Issues