Principles of Inheritance and Variation
Principles of Inheritance and Variation PDF Notes, Important Questions and Synopsis
SYNOPSIS
- Heredity is the transmission of characters from one generation to another through direct genetic descendants.
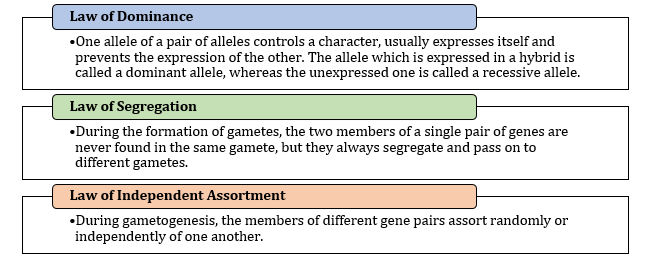
- Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance:
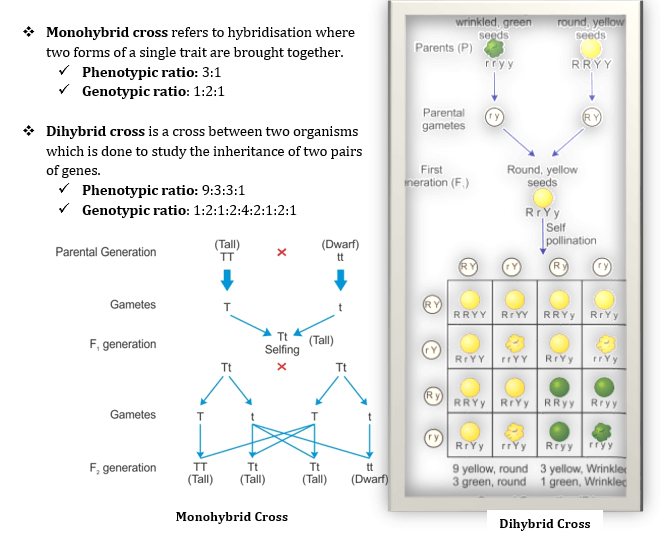
- Punnett square is a graphical representation to calculate the probability of all possible genotypes of offspring in a genetic cross.
- Test cross is a cross between the F1 hybrid and its recessive parent. It confirms the purity of the F1 hybrid, whether it is homozygous or heterozygous.
- Back cross is a cross between the F1 hybrid and one of its parents, which may be dominant or recessive.
- Incomplete dominance occurs when two parents are intercrossed with each other, and the hybrid produced does not resemble either of its parents but is mid-way between the parents.
- Multiple allelism occurs when more than two alleles exist at a given locus of a chromosome. In a given individual, only two of these alleles occur, one derived from each parent.
- Co-dominance is the phenomenon when both alleles of a pair are fully expressed in a heterozygote, so the genes and traits are said to be co-dominant.
- Linkage is the tendency of the genes to remain together during the process of inheritance.
- Differences between complete linkage and incomplete linkage:

- Crossing over is the mutual exchange of segments of non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes during the process of meiosis.
- Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance was proposed by Walter Sutton and Theodor Boveri. Sutton combined the knowledge of chromosomal segregation with Mendelian principles and called it the chromosomal theory of inheritance.
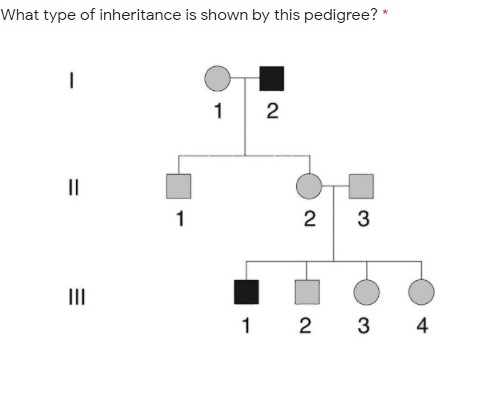
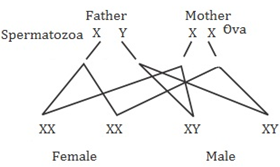
- Sex Determination in Humans:
- Mutation is an abrupt and discontinuous process where a gene or a chromosome undergoes heritable change in its structure or number.
- Ways of Chromosomal Mutation:
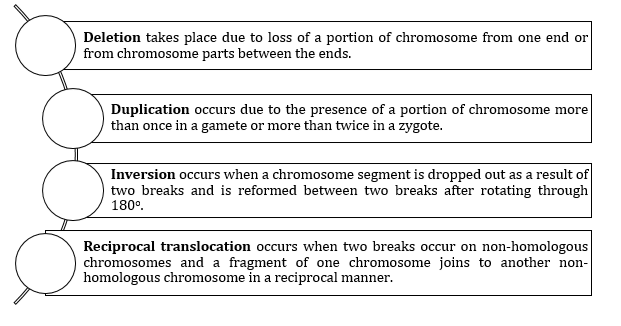
- Mendelian disorders are determined by alteration or mutation in a single gene.

- Aneuploidy is a condition where an organism possesses fewer or extra chromosomes than the normal genome number of the species; e.g. (2N – 1) or (2N + 1), where N is the haploid chromosome number.
- Chromosomal disorders are caused by the absence or excess or abnormal arrangement of one or more chromosomes.

Download complete content for FREE 
NEET - Biology
Asked by prakhart.278 | 05 Jan, 2023 01:44: PM
NEET - Biology
Asked by 8709096763raj | 29 Mar, 2022 10:00: PM
NEET - Biology
Asked by dhruvbaptu02 | 05 Sep, 2021 01:29: PM
NEET - Biology
Asked by patra04011965 | 06 Aug, 2021 08:50: PM
NEET - Biology
Asked by 7085ankitsingh10a | 19 May, 2021 10:45: AM
NEET - Biology
Asked by sweety.agariya1010 | 20 Jan, 2021 08:05: PM
NEET - Biology
Asked by patra04011965 | 18 Jun, 2020 09:10: PM
NEET - Biology
Asked by m.shajahan1991 | 18 Jun, 2020 03:56: PM
NEET - Biology
Asked by arnavvidudala20050 | 24 Apr, 2020 10:40: AM
NEET - Biology
Asked by dr_pradip27121972 | 22 Apr, 2020 03:04: PM
Related Chapters
- The Living World
- Biological Classification
- Plant Kingdom
- Animal Kingdom
- Morphology of Flowering Plants
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants
- Structural Organisation in Animals
- Cell : The Unit of Life
- Biomolecules
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division
- Transport in Plants
- Mineral Nutrition
- Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
- Respiration in Plants
- Plant Growth and Development
- Digestion and Absorption
- Breathing and Exchange of Gases
- Body Fluids and Circulation
- Excretory Products and their Elimination
- Locomotion and Movement
- Neural Control and Coordination
- Chemical Coordination and Integration
- Reproduction in Organisms
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
- Human Reproduction
- Reproductive Health
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance
- Evolution
- Human Health and Disease
- Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production
- Microbes in Human Welfare
- Biotechnology : Principles and Processes
- Biotechnology and its Applications
- Organisms and Populations
- Ecosystem
- Biodiversity and Conservation
- Environmental Issues