Biological Classification
Biological Classification PDF Notes, Important Questions and Synopsis
SYNOPSIS
- Different classification systems proposed by scientists:
Classification System
Description
Two Kingdom Classification
- Linnaeus (1758) divided all organisms into two kingdoms—Plantae and Animalia
Three Kingdom Classification
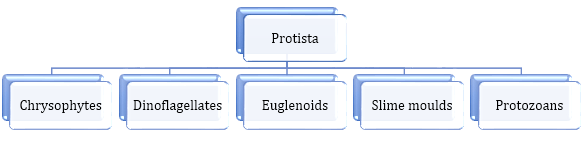
- Haeckel (1866) created a new kingdom Protista having only unicellular eukaryotes.
Four Kingdom Classification
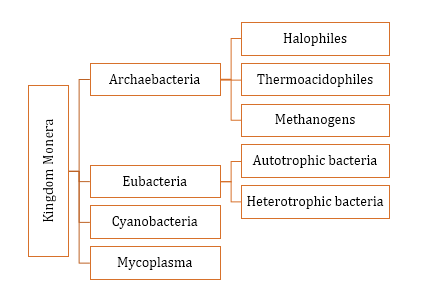
- Copeland (1956) placed prokaryotes under a separate kingdom named Monera.
Five Kingdom Classification
- R.H. Whittaker (1969) classified organisms into five kingdoms—Monera, Protista, Plantae, Fungi and Animalia.
Six Kingdom Classification
- Carl Woese proposed the three domain system—Archae (Archaebacteria), Bacteria (Eubacteria), Eukarya (Plantae, Animalia, Protista, Fungi).
- Classification of Kingdom Protista:
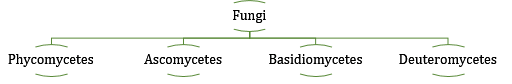
- Classification of Kingdom Fungi:
- Classification of Kingdom Monera:
-
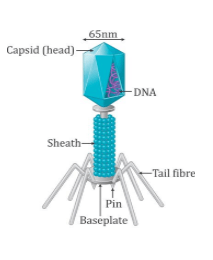
Viruses are non-cellular organisms characterised by an inert crystalline structure outside the living cell.
-
Viroids are infectious RNA particles which lack a protein coat.
-
Prions are infectious proteinaceous agents which lack genetic material.
-
Lichens are the symbiotic association between an alga (phycobiont) and a fungus (mycobiont).
Different classification systems proposed by scientists:
Download complete content for FREE 
NEET - Biology
Asked by patelniharranjan50 | 27 Jan, 2024 08:15: PM
NEET - Biology
Asked by vaibhavsharma6033 | 29 May, 2022 07:18: AM
NEET - Biology
Asked by vipinmathewneduvannoor | 11 Apr, 2022 02:21: PM
NEET - Biology
Asked by debasissen.hal | 01 Sep, 2021 06:55: PM
NEET - Biology
Asked by Kspgulbarga1 | 03 Apr, 2021 06:41: PM
NEET - Biology
Asked by laxmigitte01 | 02 Feb, 2021 09:43: PM
NEET - Biology
Asked by jhajuhi19 | 06 Nov, 2020 09:46: AM
NEET - Biology
Asked by abhaytripathi0401 | 07 Sep, 2020 07:49: PM
NEET - Biology
Asked by himaaslam1595 | 27 Feb, 2020 03:38: PM
Related Chapters
- The Living World
- Plant Kingdom
- Animal Kingdom
- Morphology of Flowering Plants
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants
- Structural Organisation in Animals
- Cell : The Unit of Life
- Biomolecules
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division
- Transport in Plants
- Mineral Nutrition
- Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
- Respiration in Plants
- Plant Growth and Development
- Digestion and Absorption
- Breathing and Exchange of Gases
- Body Fluids and Circulation
- Excretory Products and their Elimination
- Locomotion and Movement
- Neural Control and Coordination
- Chemical Coordination and Integration
- Reproduction in Organisms
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
- Human Reproduction
- Reproductive Health
- Principles of Inheritance and Variation
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance
- Evolution
- Human Health and Disease
- Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production
- Microbes in Human Welfare
- Biotechnology : Principles and Processes
- Biotechnology and its Applications
- Organisms and Populations
- Ecosystem
- Biodiversity and Conservation
- Environmental Issues