Organisms and Populations
Organisms and Populations PDF Notes, Important Questions and Synopsis
SYNOPSIS
- Ecology is a branch of biology which deals with the inter-relationships among organisms and interactions between organisms and their environment.
- Homeostasis is a self-regulatory mechanism to maintain the internal environment constant despite changes in the external environment.
- Regulators are organisms which maintain their homeostasis by physiological means to ensure constant body temperature and osmotic concentration irrespective of the fluctuations in the external environment; for example, birds and mammals.
- Conformers are organisms which cannot maintain a constant internal environment; for example, fish and reptiles.
- Adaptation is the development of certain features in an organism in response to a particular environment which may improve its chances of survival and reproduction in the habitat.
- Differences between Hibernation and Aestivation
-
Population is defined as a group of organisms of the same kind at a particular time which occupy a particular space.
-
Population density is defined as the number of individuals present in a unit area at a given time.
-
Factors Affecting Population Density
-
Natality is the increase in the number of individuals in a population under the given environmental conditions.
-
Mortality is the loss of individuals due to death in a population under the given environmental conditions.
-
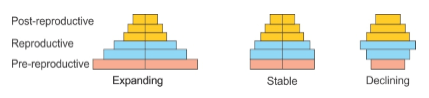
Age Pyramids for Human Population
-
Population growth can be measured as an increase in the size of a population over a period of time.
-
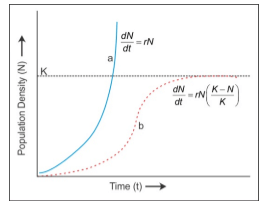
Population exhibits a characteristic pattern of increase known as the population growth curve.
-
Exponential (J-shaped) growth curve: When the resources are not limiting the growth, the plot is exponential (curve a).
-
Logistic (S-shaped) growth curve: When responses are limiting the growth, the plot is logistic (curve b).
-
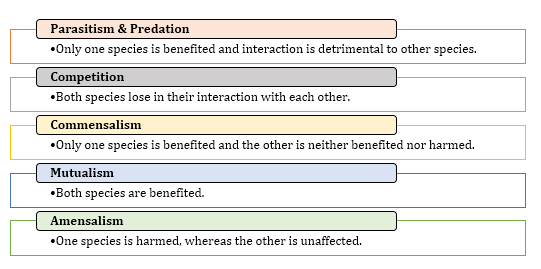
The interaction of populations of two or more different species is known as population interaction.
-
Gauss gave the competitive exclusion principle which states that two closely related species competing for the same resources cannot co-exist indefinitely and the competitively inferior one will be eliminated eventually.
Related Chapters
- The Living World
- Biological Classification
- Plant Kingdom
- Animal Kingdom
- Morphology of Flowering Plants
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants
- Structural Organisation in Animals
- Cell : The Unit of Life
- Biomolecules
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division
- Transport in Plants
- Mineral Nutrition
- Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
- Respiration in Plants
- Plant Growth and Development
- Digestion and Absorption
- Breathing and Exchange of Gases
- Body Fluids and Circulation
- Excretory Products and their Elimination
- Locomotion and Movement
- Neural Control and Coordination
- Chemical Coordination and Integration
- Reproduction in Organisms
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
- Human Reproduction
- Reproductive Health
- Principles of Inheritance and Variation
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance
- Evolution
- Human Health and Disease
- Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production
- Microbes in Human Welfare
- Biotechnology : Principles and Processes
- Biotechnology and its Applications
- Ecosystem
- Biodiversity and Conservation
- Environmental Issues