Neural Control and Coordination
Neutral Control and Coordination PDF Notes, Important Questions and Synopsis
SYNOPSIS
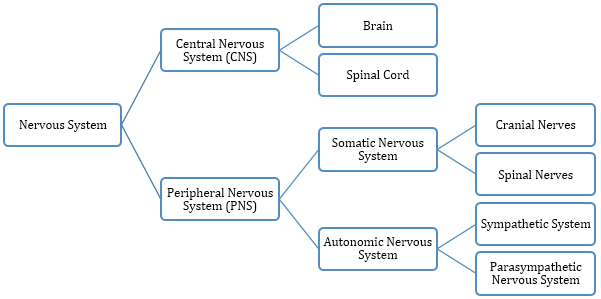
- Human Nervous System
- Neurons and their Types
Types of Neurons
Basis their function
Basis the number of nerve processes -
Sensory neurons
-
Association neurons
-
Motor neurons
- Unipolar neuron
- Bipolar neuron
- Multi-polar neuron
-
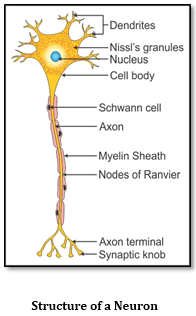
- Types of Axons
Myelinated Axons
Non-myelinated Axons
- Schwann cell covering the axons forms the myelin sheath.
- Schwann cell covering the axons does not form the myelin sheath.
- They contain nodes of Ranvier.
- They are continuous.
- Found in the spinal and cranial nerves.
- Found in ANS and somatic nervous system.
-
Conduction of Nerve Impulse
- A nerve impulse is conducted across the length of a nerve fibre in an organised manner.
- On the nerve fibre during the conduction of an impulse, a region is always depolarised and a region next to it will be polarised.
- To send the impulse forward, the depolarised region repolarises and the polarised region depolarises. This is repeated across the length of the nerve fibre which helps in the conduction of impulse
- Transmission on Nerve Impulse
- A synapse is formed by the membranes of the pre-synaptic neuron and the post-synaptic neuron.
- There are two kinds of synapses—electrical synapse and chemical synapse.

- Involuntary actions in response to external or internal stimuli are termed reflex actions.
- The path travelled by the impulse during a reflex action is called a reflex arc.
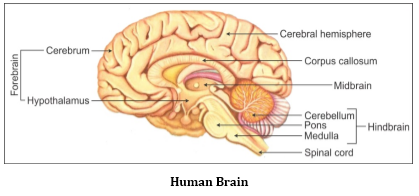
Stimulus → Receptor in the sense organ → Afferent (sensory) nerve fibre → CNS (spinal cord) → Efferent (motor) nerve fibre → Muscle/gland → Response - Function of Parts of the Human Brain
Cerebrum
Centre of intelligence, memory, consciousness, will power and voluntary actions
Thalamus
Relays motor and sensory impulses to the cerebrum
Hypothalamus
Contains the centres which control body temperature, blood pressure and homeostasis
Midbrain
Controls the movement of the head and eye
Cerebellum
Coordinates muscular activity and the balance of the body
Pons varolii
Coordinates between the two lobes of the cerebellum
Medulla oblongata
Controls the activities of the internal organs, heartbeat and breathing
- Mechanism of Vision
- Light rays reflected from the object enter the eyes through transparent structures.
- The light energy produces chemical changes in rods and cones which send the nerve impulse.
- This nerve impulse is sent to the cerebrum through the optic nerve. The cerebrum gives the sensation of sight.
- Photosensitive compounds like opsin and retinal generate potential differences in photoreceptor cells.
- The brain interprets the inverted image on the retina, and the object is seen upright.
- Mechanism of Hearing
- The pinna collects sound waves and conducts them through the external auditory canal. They finally strike the eardrum and the vibration is set.
- The Eustachian tube equalises the air pressure on either side of the eardrum allowing it to vibrate freely.
- The vibrating eardrum sets the three ear ossicles into vibration. The vibration of the first two ossicles, i.e. malleus and incus, magnifies the vibration in the stapes.
- The stapes transmits the vibration to the membrane of the oval window which sets the fluid in the cochlea into vibration.
- The vibrating movement in the fluid stimulates hair-like processes of sense cells of the cochlea and the impulses are transmitted to the brain via the auditory nerve.
Download complete content for FREE 
NEET - Biology
Asked by ghoshanirban2103 | 12 Mar, 2024 08:29: AM
NEET - Biology
Asked by raghudhaygude80 | 09 Nov, 2023 06:59: PM
NEET - Biology
Asked by sengenianbarasan | 30 Oct, 2023 11:18: AM
NEET - Biology
Asked by pagidinikhilesh | 03 Apr, 2022 11:07: AM
Related Chapters
- The Living World
- Biological Classification
- Plant Kingdom
- Animal Kingdom
- Morphology of Flowering Plants
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants
- Structural Organisation in Animals
- Cell : The Unit of Life
- Biomolecules
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division
- Transport in Plants
- Mineral Nutrition
- Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
- Respiration in Plants
- Plant Growth and Development
- Digestion and Absorption
- Breathing and Exchange of Gases
- Body Fluids and Circulation
- Excretory Products and their Elimination
- Locomotion and Movement
- Chemical Coordination and Integration
- Reproduction in Organisms
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
- Human Reproduction
- Reproductive Health
- Principles of Inheritance and Variation
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance
- Evolution
- Human Health and Disease
- Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production
- Microbes in Human Welfare
- Biotechnology : Principles and Processes
- Biotechnology and its Applications
- Organisms and Populations
- Ecosystem
- Biodiversity and Conservation
- Environmental Issues