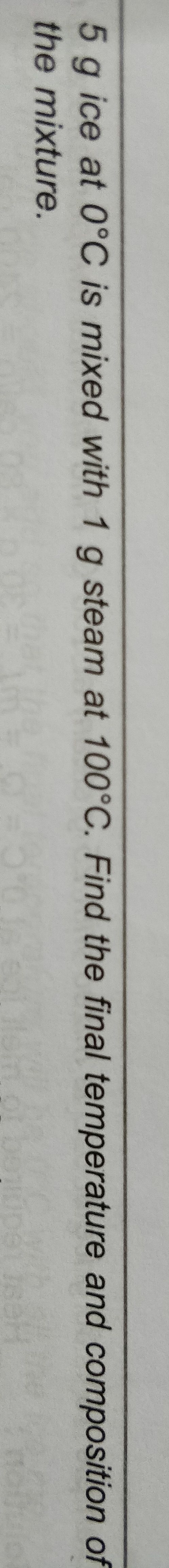Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics PDF Notes, Important Questions and Synopsis
SYNOPSIS
- Thermodynamics deals with the exchange of heat between a body and the surrounding along with other processes accompanying it.
- The nature of heat and its relationship to mechanical work was studied by Joule.
- Thermal equilibrium implies that systems are at the same temperature.
- Internal energy of a system is the sum of kinetic energies and potential energies of the molecular constituents of the system. It does not include the overall kinetic energy of the system.
- Equilibrium states of a thermodynamic system are described by state variables. The value of a state variable depends only on the particular state and not on the path used to arrive at that state.
- Examples of state variables are pressure (P), volume (V), temperature (T) and mass (m). Heat and work are not state variables.
- Zeroth law of thermodynamics: Two systems in thermal equilibrium with a third system are in thermal equilibrium with each other.
- The first law of thermodynamics is based on the principle of conservation of energy.
∆U = ∆Q − P∆V - Efficiency of a heat engine is the ratio of work done by the engine to input heat.
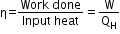
- If all the input heat is converted entirely to heat, then the engine would have an efficiency of 1.
- In a reversible process, both the system and its environment can be returned to their initial states.
- Spontaneous processes of nature are irreversible. The idealised reversible process is a quasi-static process with no dissipative factors such as friction, viscosity etc.
- A quasi-static process is an infinitely slow process such that the system remains in thermal and mechanical equilibrium with the surroundings throughout. In a quasi-static process, the pressure and temperature of the environment can differ from those of the system only infinitesimally.
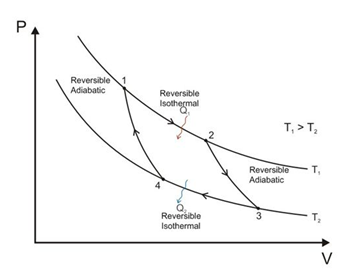
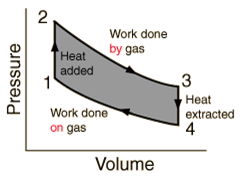
- A heat engine is a device in which a system undergoes a cyclic process resulting in conversion of heat to work.
- The Carnot engine is a reversible engine operating between two temperatures T1 (source) and T2 (sink). The Carnot cycle consists of two isothermal processes connected by two adiabatic processes.
- The efficiency of the Carnot engine is independent of the working substance of the engine. It only depends on the temperatures of the hot and cold reservoirs.
- Efficiency of the Carnot engine is 𝜂 = 1 − TC/TH = 1 − (Temperature of cold reservoir/Temperature of hot reservoir).
- The efficiency of an engine is never more than that of a Carnot engine.
- Heat lost by a hot body = heat gained by a cold body
- Heat can flow from cooler surroundings into a hotter body (e.g. coffee) to make it hotter.
- Kelvin’s statement of the second law of thermodynamics:
No heat engine can convert heat to work with 100% efficiency. - Clausius statement: No process is possible whose sole result is the transfer of heat from a colder body to a hotter body.
- Kelvin’s statement: No process is possible whose sole result is the complete conversion of heat to work.
- Coefficient of performance of a refrigerator is α = QC/W.
- A heat pump is called so because it pumps heat from the cold outdoors (cold reservoir) into the warm house (hot reservoir).
- When Q > 0, heat is added to the system.
When Q < 0, heat is removed from the system.
When W > 0, work is done by the system.
When W < 0, work is done on the system. - Heat engine
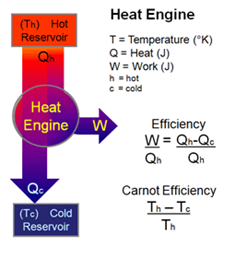
- Work done by a heat engine
Download complete content for FREE 
NEET - Physics
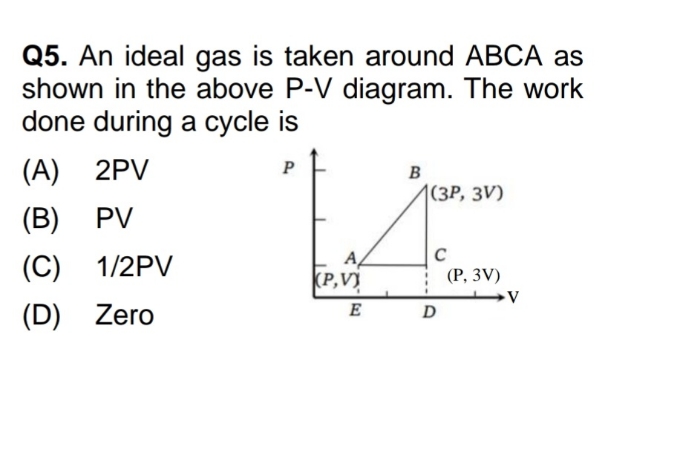
Asked by yadavaradhana9335 | 19 Feb, 2024 04:53: PM
NEET - Physics
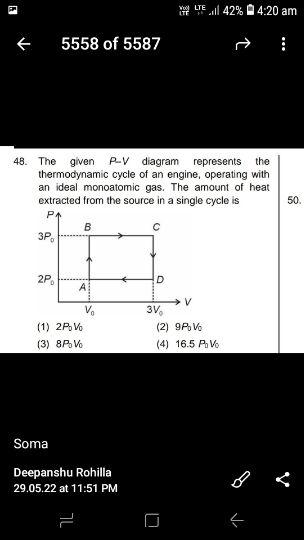
Asked by sujitjana971 | 18 Dec, 2022 05:23: PM
NEET - Physics
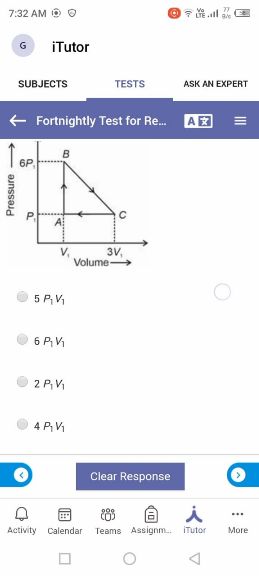
Asked by takshitashu46 | 09 Feb, 2022 06:01: PM
NEET - Physics
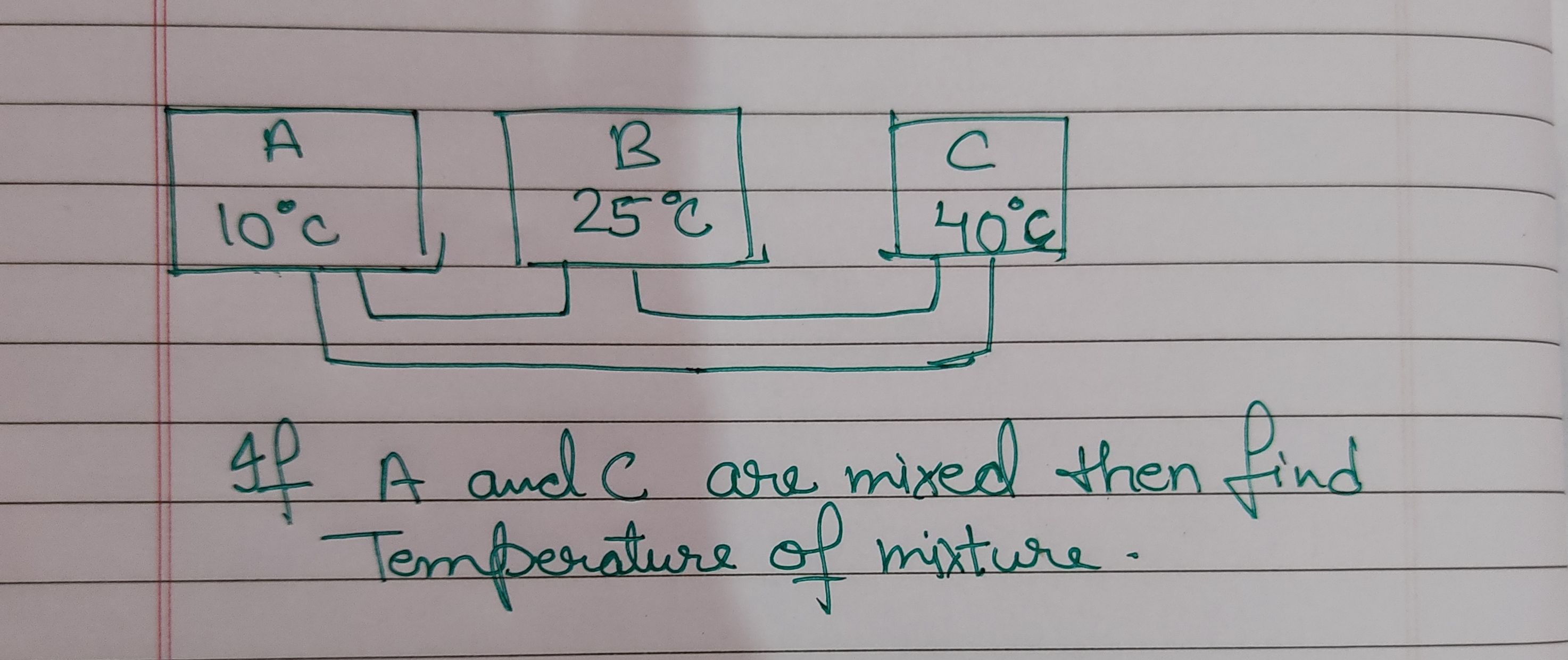
Asked by jhajuhi19 | 18 Aug, 2021 03:21: AM
NEET - Physics
Asked by 22bakugoku | 21 Apr, 2019 05:23: PM
NEET - Physics
Asked by 22bakugoku | 21 Apr, 2019 05:23: PM
Related Chapters
- Physics and Measurement
- Kinematics
- Laws of Motion
- Work, Energy and Power
- Rotational Motion
- Gravitation
- Properties of Solids and Liquids
- Kinetic Theory of Gases
- Oscillations and Waves
- Electrostatics
- Current Electricity
- Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism
- Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents
- Electromagnetic Waves
- Optics
- Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation
- Atoms and Nuclei
- Electronic Devices
- Communication Systems