Kinematics
Kinematics PDF Notes, Important Questions and Synopsis
SYNOPSIS
- For motion in a straight line, the position to the right of the origin is taken as positive and that to the left of the origin is taken as negative.
- A body in straight line motion can have the line of path as vertical, horizontal or slanted.
- Path length is defined as the total length of the path traversed by an object.
- Distance: Total path length covered during a given time interval.
- Displacement: Shortest straight line distance between the initial and final position.
- Path length is greater or equal to the magnitude of the displacement between the same points.
- An object is said to be in uniform motion in a straight line if its displacement is equal in equal intervals of time. Otherwise, the motion is said to be non-uniform.
- Average speed: Total distance travelled divided by the total time taken.
- Average velocity: Total displacement divided by the total time taken.
- The average speed of an object is greater or equal to the magnitude of the average velocity over a given time interval.
- The slope of the x–t graph gives the velocity at a given instant.
- The position–time graph of a body in non-uniform motion is curved.
- The velocity–time graph of a body in non-uniform accelerated motion is curved.
- The slope of a v–t graph gives the acceleration at that instant.
- The area between the v–t graph and the time axis gives displacement.
- The steepness of the slope of the position–time graph gives us the magnitude of the velocity and its sign indicates the direction of the velocity.
- If the tangent to the position–time curve slopes upward to the right on the graph, then the velocity is positive.
- If the tangent to the position–time graph slopes downward to the right, then the velocity is negative.
- For one-dimensional motion, the slope of the velocity–time graph at a time gives the acceleration of the object at that time.
- A projectile is an object on which the only force acting is gravity.
- Projectile motion can be thought of as two separate simultaneously occurring components of motion along the vertical and horizontal directions.
- During a projectile’s flight, its horizontal acceleration is zero and its vertical acceleration is −9.8 m/s2.
- The trajectory of a particle in projectile motion is parabolic.
- When a body P moves relative to a body B and B moves relative to A, the velocity of P relative to A is the velocity of P relative to B + velocity of P relative to A.
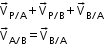
- Motion of a boat in a stream
Let velocities of boat (A) and stream (B) be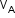 and
and 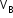 , respectively, with respect to the ground.
, respectively, with respect to the ground.
The velocity of boat (A) with respect to stream (B) is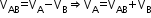
Resultant velocity
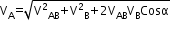
Time to cross the stream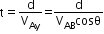
Shortest interval to cross the stream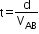
Time is minimum when the denominator is maximum, so at , the time to cross the stream is minimum.
Download complete content for FREE 
NEET - Physics
Asked by cmashudrana | 26 Jul, 2024 10:51: AM
NEET - Physics
Asked by upparmanjunath70 | 19 Jul, 2024 10:26: PM
NEET - Physics
Asked by nk4746870 | 15 Jul, 2024 09:21: PM
NEET - Physics
Asked by dshyamala44 | 08 Jul, 2024 09:05: PM
NEET - Physics
Asked by mnedits01 | 03 Jul, 2024 03:55: PM
NEET - Physics
Asked by musamaria321 | 28 Jun, 2024 08:31: PM
NEET - Physics
Asked by 3s6ng9 | 05 Jun, 2024 11:59: PM
NEET - Physics
Asked by ggovindjakhar | 03 Jun, 2024 08:17: PM
Related Chapters
- Physics and Measurement
- Laws of Motion
- Work, Energy and Power
- Rotational Motion
- Gravitation
- Properties of Solids and Liquids
- Thermodynamics
- Kinetic Theory of Gases
- Oscillations and Waves
- Electrostatics
- Current Electricity
- Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism
- Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents
- Electromagnetic Waves
- Optics
- Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation
- Atoms and Nuclei
- Electronic Devices
- Communication Systems



