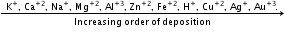Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry
Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry PDF Notes, Important Questions and Synopsis
SYNOPSIS
|
Electrochemical cell |
Galvanic cell |
|
This cell converts electrical energy to chemical energy. |
This cell converts chemical energy to electrical energy. |
|
It requires a source of external energy. |
It is a source of energy. |
|
It has a cathode as the negative electrode. |
It has a cathode as the positive electrode. |
|
It has an anode as the positive electrode. |
It has an anode as the negative electrode. |
Electrode potential:
For any electrode → oxidation potential (OP) = −Reduction potential (RP)
Ecell = RP of the cathode – RP of the anode
Ecell = RP of the cathode + OP of the anode
E°cell is always a +ve quality and the anode will be an electrode of low RP.
- Greater the SRP value, greater will be the oxidising power.
- Concentration cell: A cell in which both electrodes are made of the same material.
For all concentration cells, E°cell = 0. - Electrolyte concentration cell:
Example: Zn(s) / Zn2+ (c1) || Zn2+(c2) / Zn(s)
- Metal–metal ion electrode
Example: M(s)/Mn+
Mn++ ne→M(s) - Gas–ion electrode
Pt/H2(Patm)/Hn+(XM) as a reduction electrode. - Oxidation –reduction electrode
Example: Pt/Fe2+ , Fe3+
As a reduction electrode: AgCl(s)+e → Ag((s) +Cl - Metal-metal insoluble salt electrode
Example: Ag/AgCl,Cl-
As a reduction Electode: AgCl(s) + e → Ag(s) +Cl-
- Electrolysis:
- Similarly, the anion which is a stronger reducing agent (low value of SRP) is liberated first at the anode.
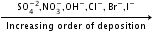
Faraday’s law of electrolysis:
First law:
The mass of an atom or ion oxidised or reduced at either electrode (during electrolysis) is directly proportional to the quantity of electricity passed through the electrolyte.
Second law:
When the same quantity of electricity is passed through different electrolytes, the mass of substances deposited is proportional to their respective chemical equivalent or equivalent weight.
Conductance:
- Conductance is the property of a conductor which facilitates the flow of electricity through it.
- Specific conductors or conductivity: Conductance of a solution of definite dilution enclosed in a cell having two electrodes of unit area separated by 1 cm.
- Equivalent conductance: Conductance of all the ions produced by 1 gram equivalent of an electrolyte in a given solution.
- Molar conductance: Conductance of all the ions produced by ionisation of 1 g mole of an electrolyte when present in V mL of solution.
Kohlrausch’s law: Equivalent conductivity of an electrolyte at infinite dilution is equal to the sum of conductances of the anions and cations.
Ionic mobility: Distance travelled by the ion per second under the potential gradient of 1 volt per cm. Its unit is cm2S-1V-1.
Battery: A battery consists of two or more voltaic cells connected in series.
- Primary batteries:
- In primary batteries, the reaction occurs only once and cannot be reused again.
Examples:
Leclanché cell: A zinc container acts as the anode, and the cathode is a carbon (graphite) rod surrounded by powdered manganese dioxide and carbon.
Anode: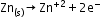
Cathode: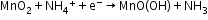
Mercury cell: It consists of zinc and mercury amalgam as the anode and a paste of HgO and carbon as the cathode.
- In primary batteries, the reaction occurs only once and cannot be reused again.
- Secondary batteries are portable voltaic cells which are rechargeable.
- The most important secondary cell is the lead storage battery commonly used in automobiles and invertors.
Anode: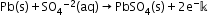
Cathode: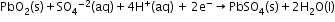
Overall reaction: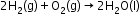
- In corrosion, a metal is oxidised by loss of electrons to oxygen and the formation of oxides.
- It is an electrochemical phenomenon.
- Corrosion of iron:
Oxidation: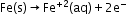
Reduction:
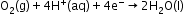
- Atmospheric oxidation:
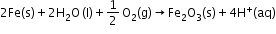
Related Chapters
- Some Basic Concepts in Chemistry
- States of Matter
- Atomic Structure
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
- Chemical Thermodynamics
- Solid State
- Solutions
- Equilibrium
- Chemical Kinetics
- Surface Chemistry
- Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Metals
- Hydrogen
- s-Block Element (Alkali and Alkaline Earth Metals)
- p-Block Elements
- d - and f - Block Elements
- Co-ordination Compounds
- Environmental Chemistry
- Purification and Characterisation of Organic Compounds
- Some Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry
- Hydrocarbons
- Organic Compounds Containing Halogens
- Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen
- Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen
- Polymers
- Biomolecules
- Chemistry in Everyday Life
- Principles Related to Practical Chemistry