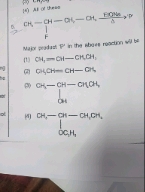
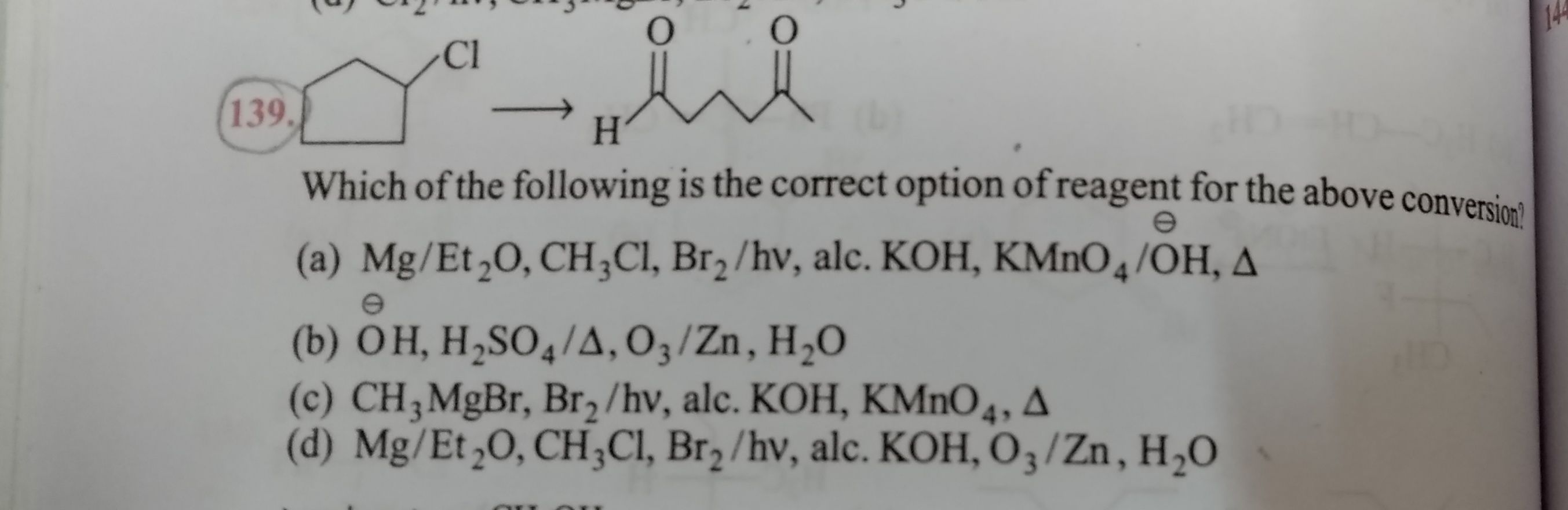
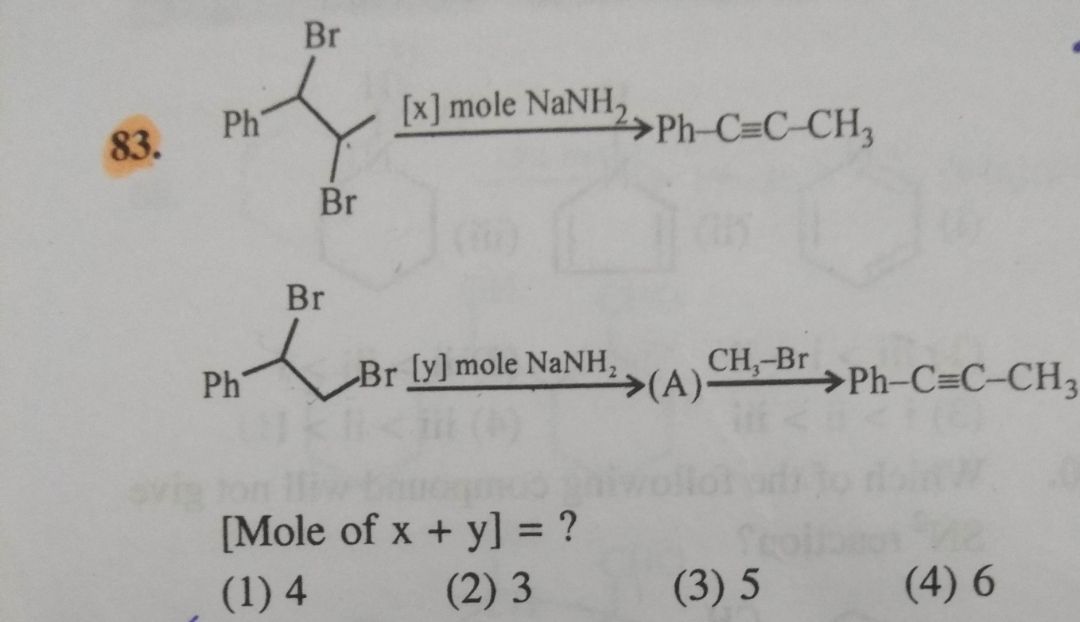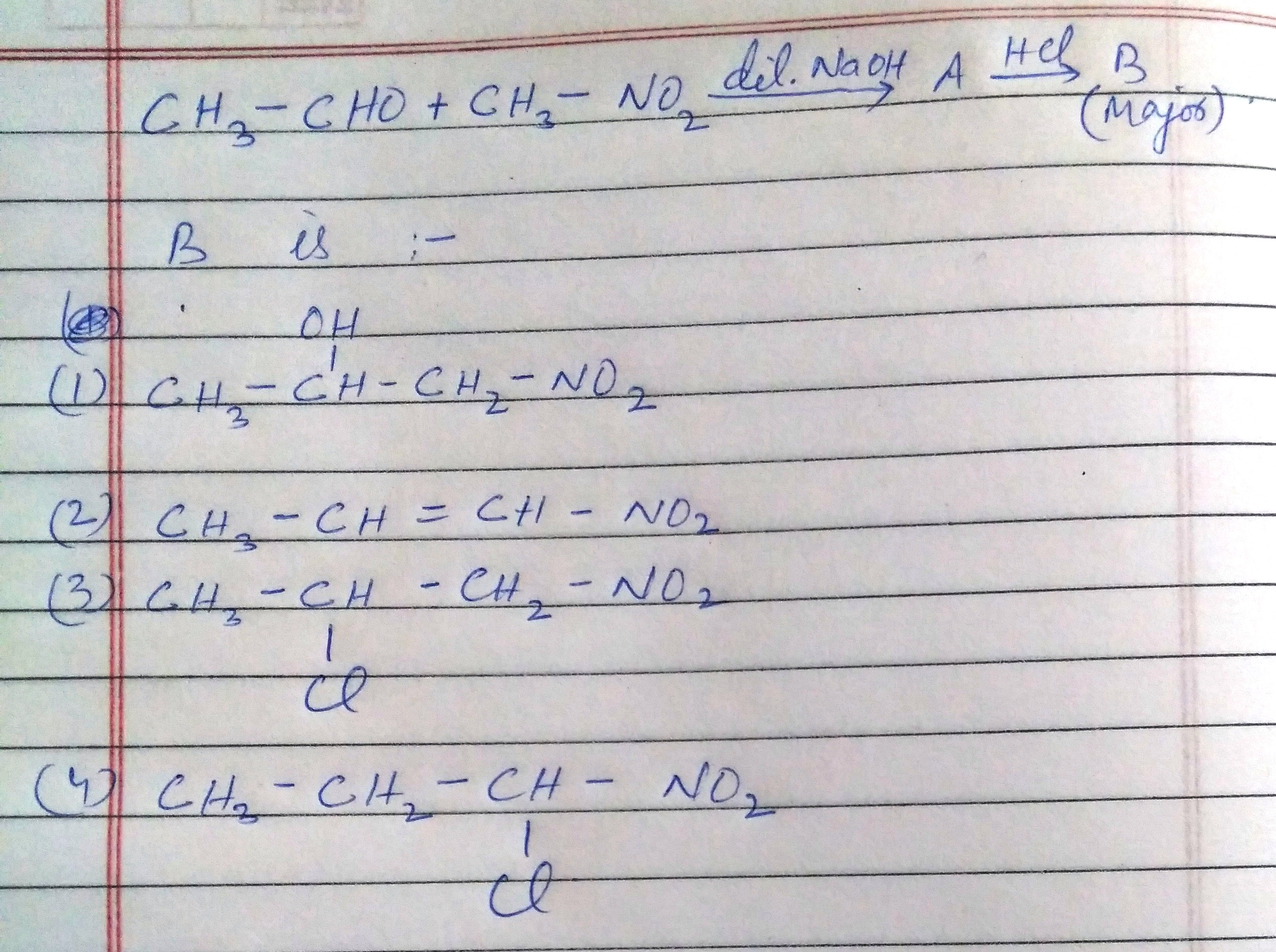Organic Compounds Containing Halogens
Organic Compounds Containing Halogens PDF Notes, Important Questions and Synopsis
SYNOPSIS
The halogen derivative of hydrocarbons are called as halogenated hydrocarbons. The general formula of monohalogenated hydrocarbons is R-X. (X = F, Cl, Br, I and R= alkyl, aryl etc.)
- Haloalkanes (R-X):
- Classification:
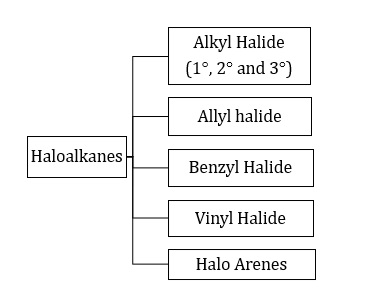
- Preparation:
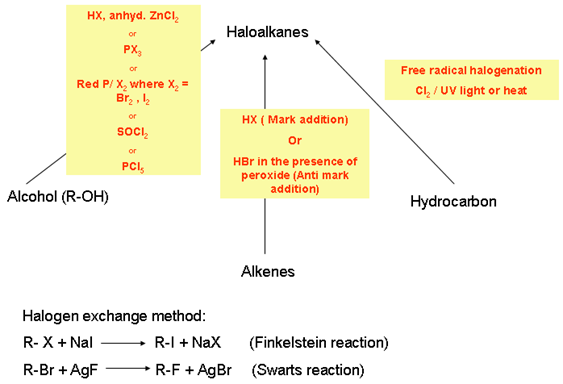
-
General Characteristics:
Bond energy order
C-F > C-Cl > C-Br > C-I
Boiling point order
R-I > R-Br > R-Cl >R-F
Density order
R-I > R-Br > R-Cl
Dipole moment order
CH3Cl > CH3F > CH3Br > CH3I
Stability order
R-F> R-Cl> R-Br>R-I
-
Chemical Characteristics:
- Nucleophilic substitution reactions
There are four types of substitution reactions, their characteristics are given below:
Type
SN1
SN2
SNi
SNAr
Molecularity
Unimolecular
Bimolecular
Unimolecular
Bimolecular
Order
Two-Step
One-step
One-step
Two-Step
Medium
Acidic
Basic
Acidic
Basic
Intermediate
Carbocation
No intermediate
No intermediate
Carbanion
Orientation of product
Racemisation
Inversion
Retention
−
-
Wittigs’ reactions:
The formation of alkene by the action of ylide on carbonyl compounds is known as wittigs’ reaction.
-
Friedal Craft reaction:
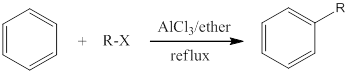
- Classification:
- Haloarenes (Ar-X):
Preparation:- From aromatic hydrocarbons:
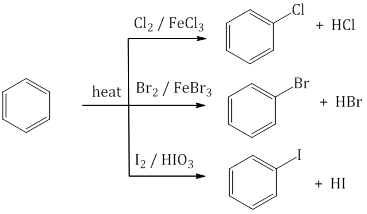
- From diazonium salt:
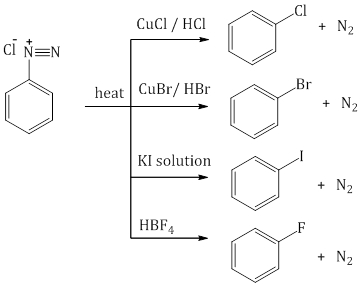
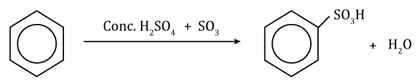
Chemical Reactions of Benzene: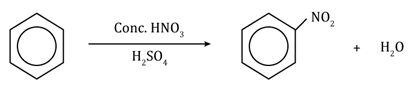
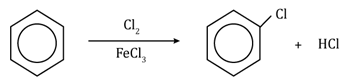
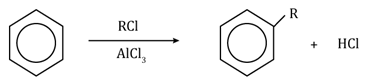
Friedel-Craft’s alkylation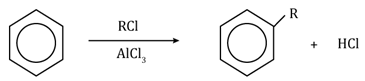
Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution:
In this type of substitution reactions nucleophile attacked to the carbon of benzene ring having substituent. This reaction proceeds via an intermediate σ-complex, the benzenonium carbanion.
e.g.,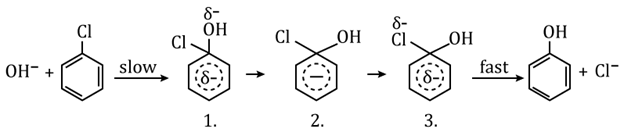
- From aromatic hydrocarbons:
Related Chapters
- Some Basic Concepts in Chemistry
- States of Matter
- Atomic Structure
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
- Chemical Thermodynamics
- Solid State
- Solutions
- Equilibrium
- Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry
- Chemical Kinetics
- Surface Chemistry
- Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Metals
- Hydrogen
- s-Block Element (Alkali and Alkaline Earth Metals)
- p-Block Elements
- d - and f - Block Elements
- Co-ordination Compounds
- Environmental Chemistry
- Purification and Characterisation of Organic Compounds
- Some Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry
- Hydrocarbons
- Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen
- Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen
- Polymers
- Biomolecules
- Chemistry in Everyday Life
- Principles Related to Practical Chemistry