Some Basic Concepts in Chemistry
Some Basic Concepts in Chemistry PDF Notes, Important Questions and Synopsis
SYNOPSIS
Basic Concepts of Chemistry
Classification of Matter:
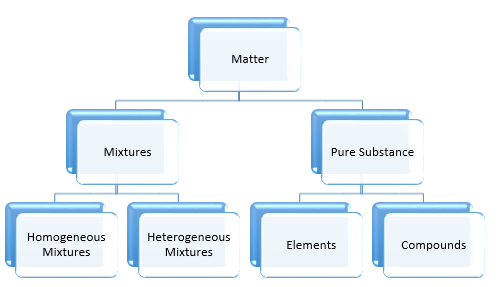
Properties of Matter:
Physical properties: Colour, odour, melting point, boiling point, density
Chemical properties: Acidity, basicity, combustibility
The International System of Units (SI):
|
Physical quantity |
Symbol for quantity |
Name of SI unit |
Symbol for SI unit |
|
Length |
l |
metre |
m |
|
Mass |
m |
kilogram |
kg |
|
Time |
t |
second |
s |
|
Electric current |
I |
ampere |
A |
|
Thermodynamic temperature |
T |
kelvin |
K |
|
Amount of substance |
n |
mole |
mol |
|
Luminous intensity |
Io |
candela |
Cd |
Mass and weight:
- Mass of a substance is the amount of matter present in it, while weight is the force exerted by gravity on an object.
- Thermometer with the Celsius scale is calibrated from 0 to 100.
- The Fahrenheit scale is represented between 32 and 212.
- Negative values of temperature are not possible on the Kelvin scale.
- Significant figures are meaningful digits which are known with certainty.
- Law of conservation of mass: Matter can neither be created nor be destroyed.
- Law of definite proportions: given compound always contains the same proportion of elements by weight.
- Law of multiple proportions: If two elements can combine to form more than one compound, the masses of one element which
combine with a fixed mass of the other element are in the ratio of small whole numbers. - Gay-Lusaac’s law of gaseous volumes: When gases combine or are produced in a chemical reaction, they do so in a simple ratio by volume provided all gases are at the same temperature and pressure.
- Avogadro’s law: Equal volumes of gases at the same temperature and pressure should contain equal number of molecules.
- One atomic mass is defined as mass exactly equal to 1/12th the mass of one carbon-12 atom.
- Molecular mass is the sum of atomic masses of the element present in the molecule.
- The formula mass of a molecule is the sum of the atomic weights of the atoms in the empirical formula of a compound.
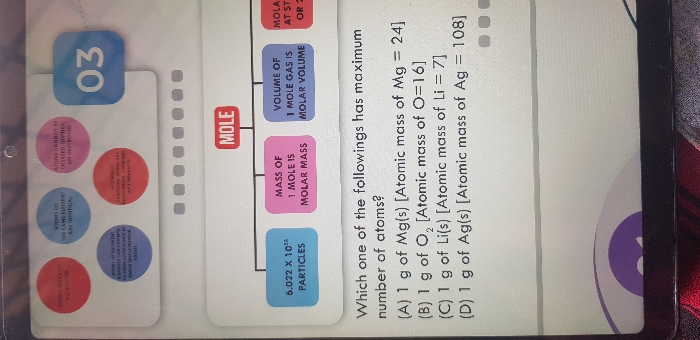
Mole
- One mole is the amount of substance which contains as many particles or entities as there are atoms in exactly 12 g of the C-12 isotope.
- The mass of one mole of a substance in grams.
- An empirical formula represents the simplest whole number ratio of various atoms present in a compound.
- A molecular formula shows the exact number of different types of atoms present in a molecule of a compound.
Stoichiometry
- Stoichiometry deals with the relationship between reactants and products involved in a chemical reaction to determine desired quantitative data.
Limiting reagent
- A limiting reagent in a chemical reaction is a substance which is totally consumed when the reaction is completed.
- Molarity (M): Number of moles of a solute present in per unit volume of solution.
- Molality (m): Number of moles of a solute present in one kilogram of a solvent.
- Normality (N): Number of gram equivalents of a solute present in per unit volume of solution.
- Mole fraction: Ratio of the number of moles of a particular component to the total number of moles of the solution.
- Mass per cent or weight per cent (w/w%): Gram of solute present in 100 gram of solution.
- Volume by volume per cent (v/v%): mL of solute present in 100 mL of solution.
- Weight by volume per cent (w/v%): Gram of solute present in 100 mL of solution.
Related Chapters
- States of Matter
- Atomic Structure
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
- Chemical Thermodynamics
- Solid State
- Solutions
- Equilibrium
- Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry
- Chemical Kinetics
- Surface Chemistry
- Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Metals
- Hydrogen
- s-Block Element (Alkali and Alkaline Earth Metals)
- p-Block Elements
- d - and f - Block Elements
- Co-ordination Compounds
- Environmental Chemistry
- Purification and Characterisation of Organic Compounds
- Some Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry
- Hydrocarbons
- Organic Compounds Containing Halogens
- Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen
- Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen
- Polymers
- Biomolecules
- Chemistry in Everyday Life
- Principles Related to Practical Chemistry