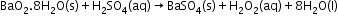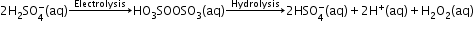Hydrogen
Hydrogen PDF Notes, Important Questions and Synopsis
SYNOPSIS
Symbol- H
Electronic configuration-1s1
Position in Periodic Table- Not fixed (sometimes with alkali metals in IA and sometimes with halogens in VIIA group.
Similarities with alkali metals-
- Electronic Configuration- ns1
- Electropositive character-
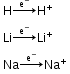
-
Valency- Both hydrogen and alkali metals show electrovalency +1.
-
Oxidation state- Both hydrogen and alkali metals show +1 oxidation state
-
Affinity for non-metal
-
Reducing nature
Similarities with Halogens-
- Nonmetallic character
- Electronic configuration-Both have one electron less than the next inert gas.
- Diatomic nature- H2,F2,Cl2,Br2
- Electronegative nature-
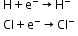
- Ionisation potential- Ionisation position of hydrogen is 13.5eV. The value is nearer to the halogens.
- Similar covalent compound- CH4 and CCl4, SiH4 and SiCl4.
Discovery and Occurrence-
1. Hydrogen was prepared by Henry Cavendish by the action of acids on metals.
2. Lavoisier named it hydrogen.
3. Hydrogen is most abundant element in the universe.
4. Present in sun’s atmosphere, mineral oils, Organic compounds, alkalies.
Isotopes of Hydrogen-
Protium(1H1), Deuterium(1H2), Tritium(1H3)
Preparation of Dihydrogen, H2 –
Laboratory preparation-
- Reaction of granulate zinc with dilute hydrochloric acid
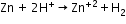
Reaction of zinc with aqueous alkali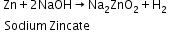
Commercial production-
- Electrolysis of acidified water
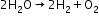
- In production of NaOH and Cl2
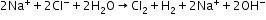
- Reaction of Steam on hydrocarbons
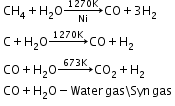
Properties of Dihydrogen, H2 –
Physical properties- Colourless, odourless, tasteless, combustible gas
Chemical properties-
- Reaction with halogens-
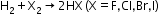
- Reaction with dioxygen-
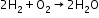
- Reaction with dinitrogen
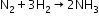
- Reactions with metals
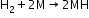
- Reactions with metal ions and metal oxides
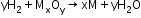
- Reactions with organic compounds
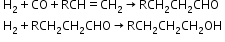
Hydrides-
- Ionic or Saline hydride- NaH,LiH
- Covalent hydride- H2O, NH3,CH3
- Metallic or Non-Stoichiometric(or Interstitial) Hydride- LaH2.87,YbH2.55,VH0.56
Water-
- Colourless, tasteless liquid
- High freezing and High boiling point
- Bond angle in the water molecule is 104.5°.
Structure of Ice
- The crystalline form of water is ice.
- At atmospheric pressure, ice crystallises in the hexagonal form, but at very low temperatures, it condenses to the cubic form.
Chemical Properties of Water-
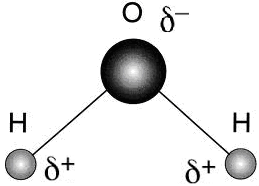
- Amphoteric nature-
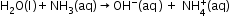
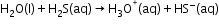
- Redox Reactions Involving Water-
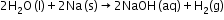
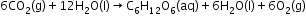
- Hydrolysis Reaction-
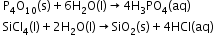
- Hydrates Formation-
Coordinated water-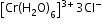
Interstitial water-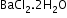
Hydrogen-bonded water-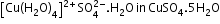
Hard and Soft Water-
- Water free from soluble salts of calcium and magnesium is called soft water. It gives lather with soap.
- Water containing soluble salts of calcium and magnesium in the form of hydrogen carbonate, chlorides and sulphates is called hard water. It does not give lather with soap.
Hardness of Water-
- Temporary hardness
- Permanent hardness
Methods to remove Temporary hardness-
- Boiling:
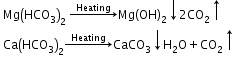
- Clark’s method:
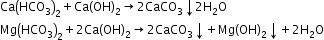
Methods to remove permanent hardness-
- Treatment with washing soda (sodium carbonate):
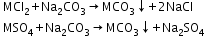
- Calgon’s method:
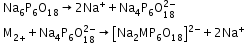
- Ion-exchange method:
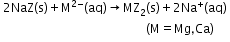
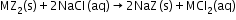
- Synthetic resins method:
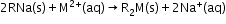
Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2)-
Preparation-
Physical Properties
- In the pure state, H2O2 is a colourless (very pale blue) liquid.
- H2O2 is miscible with water and forms a hydrate H2O2. H2O.
Structure
- It has a non-polar open book (skew) structure.
- The length of the O–H bond is 95 pm, that of the O–O bond is 147.5 pm and the H–O–H bond angle is 111°5.
Chemical properties-
- Oxidising action in acidic medium
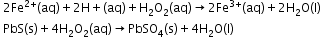
- Reducing action in acidic medium
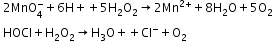
- Oxidising action in basic medium
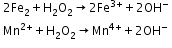
- Reducing action in basic medium
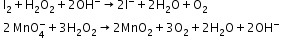
Heavy Water (D2O)-
- It is manufactured by the electrolytic enrichment of normal water. It is used as a moderator in nuclear reactors.
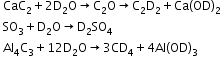
Related Chapters
- Some Basic Concepts in Chemistry
- States of Matter
- Atomic Structure
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
- Chemical Thermodynamics
- Solid State
- Solutions
- Equilibrium
- Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry
- Chemical Kinetics
- Surface Chemistry
- Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Metals
- s-Block Element (Alkali and Alkaline Earth Metals)
- p-Block Elements
- d - and f - Block Elements
- Co-ordination Compounds
- Environmental Chemistry
- Purification and Characterisation of Organic Compounds
- Some Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry
- Hydrocarbons
- Organic Compounds Containing Halogens
- Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen
- Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen
- Polymers
- Biomolecules
- Chemistry in Everyday Life
- Principles Related to Practical Chemistry