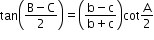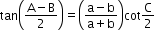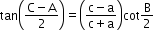Trigonometry
Trigonometry PDF Notes, Important Questions and Synopsis
SYNOPSIS
- If the direction of rotation is anticlockwise, then the angle is said to be positive. If the direction of rotation is clockwise, then the angle is negative.
Positive angle — anticlockwise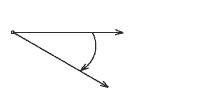
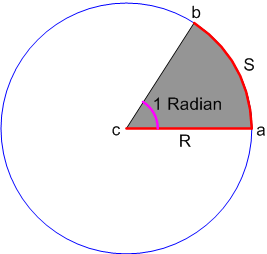
Negative angle - clockwise - The angle subtended at the centre by an arc of length 1 unit in a unit circle is said to have a measure of 1 radian.
- Even function: A function f(x) is said to be an even function if
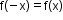 for all x in its domain.
for all x in its domain. - Odd function: A function f(x) is said to be an odd function if
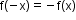 for all x in its domain.
for all x in its domain. -
Cosine is an even function and sine is an odd function.
cos(−x) = cos x
sin(−x) = −sin x -
Signs of trigonometric functions in various quadrants:
I
II
III
IV
sin x
+
+
–
–
cos x
+
–
–
+
tan x
+
–
+
–
cosec x
+
+
–
–
sec x
+
–
–
+
cot x
+
–
+
–
- In quadrants, where the y-axis is positive (i.e. I and II), sine is positive, and in quadrants where the x-axis is positive (i.e. I and IV), cosine is positive.
- A simple rule to remember the sign of the trigonometric ratios in all the four quadrants is the phrase-All Silver Tea Cups.
-
A function ‘f’ is said to be a periodic function if there exists a real number T > 0 such that
f(x + T) = f(x) for all ‘x’. ‘T’ is the period of the function. -
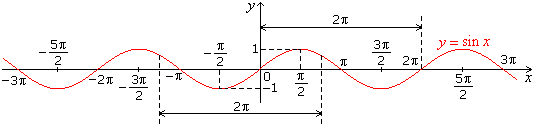
sin(2Π + x) = sin x, so the period of sine is 2Π. Period of its reciprocal is also 2Π.
-
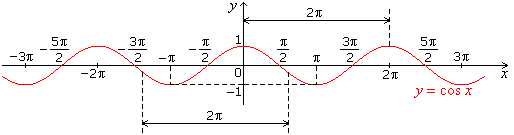
cos(2Π + x) = cos x, so the period of cosine is 2Π. Period of its reciprocal is also 2Π.
-
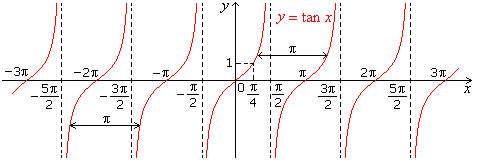
tan(Π + x) = tan x. Period of tangent and cotangent function is Π.
-
The graph of cos x can be obtained by shifting the sine function along the x-axis by the factor
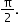
-
The tan function differs from sine and cosine functions in two ways:
- Function tan is not defined at the odd multiples of Π/2.
- The tan function is not bounded.
-
Function
Period
y = sin x
2Π
y = sin (ax)
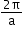
y = cos x
2Π
y = cos (ax)
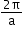
y = cos 3x
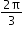
y = sin 5x
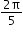
-
For a function of the form y = k f(ax + b), the range will be ‘k’ times the range of function x, where k is any real number.
- If f(x) = sine function in the above form, the range will be equal to [−k, k].
- If f(x) = cosine function in the above form, the range will be equal to R−[−k, k].
- If the function is of the form ‘k sec (ax + b)’ or ‘k cosec (ax + b)’, the period is equal to the period of function ‘f’ divided by ‘a’.
- The position of the graph of y = k f(ax + b) is ‘b’ units to the right or left of y = f(x) depending on whether b < 0 or b > 0.
-
The solutions of a trigonometric equation for which 0 ≤ x ≤ 2Π are called principal solutions.
-
The expression involving an integer ‘n’ which gives all the solutions of a trigonometric equation is called the general solution.
-
The numerically smallest value of the angle (in degree or radian) satisfying a given trigonometric equation is called the principal value. If there are two values, one positive and the other negative, which are numerically equal, then the positive value is taken as the principal value.
-
Trigonometric equations:
No.
Equations
General solution
Principal value
1
sin θ = 0
θ = np, nÎZ
θ = 0
2
cos θ = 0
θ = (2n + 1)p/2, nÎZ
θ = p/2
3
tan θ = 0
θ = np
θ = 0
4
sin θ = sin α
θ = np + (–1)ⁿ α, nÎZ
θ = α
5
cos θ = cos α
θ = 2np ± α, nÎZ
θ = 2α, α > 0
6
tan θ = tan α
θ = np + α, nÎZ
θ = α
7
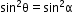
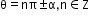
8
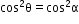
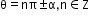
9
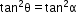
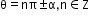
- Sine rule:
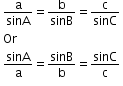
- Law of cosine:

- Napier’s analogy (Law of tangents):
- Area of a triangle having sides a, b and c is given by
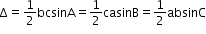
- Graphs of standard trigonometric functions:
- Graph of sin x
- Graph of cos x
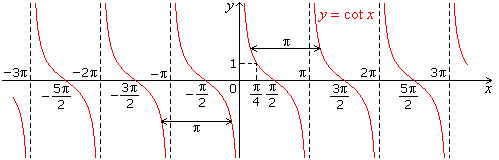
- Graph of tan x
- Graph of sec x
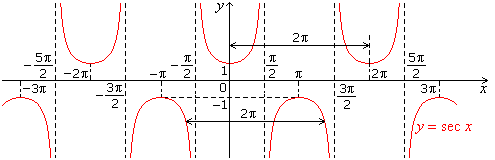
- Graph of cosec x
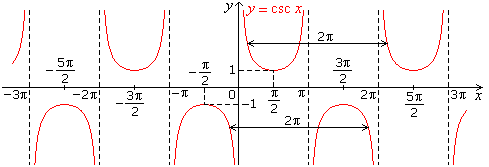
- Graph of cot x
- Graph of sin x
- If f is one-to-one and onto (bijection), then there exists an inverse of a function f denoted by
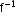 such that
such that 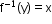 .
. - Inverse trigonometric functions map real numbers back to angles.
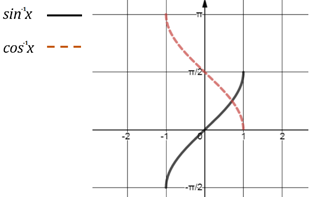
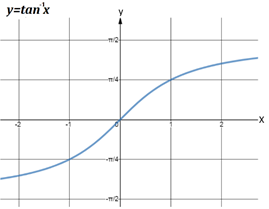
- Graphs of inverse trigonometric functions:
Related Chapters
- Sets, Relations and Functions
- Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations
- Matrices and Determinants
- Permutations and Combinations
- Mathematical Induction
- Binomial Theorem and its Simple Applications
- Sequences and Series
- Limit, Continuity and Differentiability
- Integral Calculus
- Differential Equations
- Co-ordinate Geometry
- Three Dimensional Geometry
- Vector Algebra
- Statistics and Probability
- Mathematical Reasoning