Three Dimensional Geometry
Three Dimensional Geometry PDF Notes, Important Questions and Synopsis
SYNOPSIS
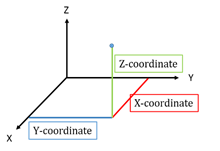
- 3D geometry is a three-dimensional geometry where each point is described in three-dimensional space with three coordinate axes named X, Y and Z.
-
Section Formula:
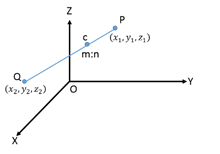
If c is the point which divides a line PQ in the ratio m:n, then the coordinates of c are given by
c =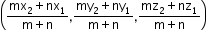 " >
" >
-
Direction Cosines:
The angles α, β and γ made by the directed line L passing through the origin with x, y and z axes respectively are called direction angles.
Cosines of these angles (cos α, cos β and cos γ) are called the direction cosines of line L.
Note: The direction cosines of the directed line not passing through the origin can be obtained by drawing a line parallel to it which passes through the origin.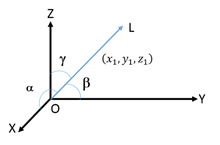
-
Direction Ratios:
If l, m and n are the cosines of the vector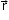 and a, b and c are three numbers such that they are proportional to l, m and n respectively, then a, b and c are called the direction ratios of the vector
and a, b and c are three numbers such that they are proportional to l, m and n respectively, then a, b and c are called the direction ratios of the vector 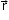 .
.
Also,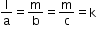
-
For points P(x1, y1, z1) and Q(x2, y2, z2), the direction ratios of line PQ are
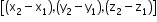 " >.
" >. -
A line is uniquely determined if it passes through
- a given point and parallel to a vector/line having direction cosines
- the two given points
- Two lines having direction cosines l1, m1, n1 and l2, m2, n2 are
- Perpendicular if and only if l1 l2 + m1 m2 + n1 n2 = 0
- Parallel if
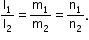
- Two lines having direction ratios a1, b1, c1 and a2, b2, c2 are
- Perpendicular if and only if a1 a2 + b1 b2 + c1 c2 = 0
- Parallel if
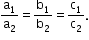
- If two lines intersect at a point, then the shortest distance between them is zero.
- If two lines are parallel, then the shortest distance between them is the perpendicular distance.
- Two lines which are neither parallel nor intersect are called skew lines.
These lines are non-coplanar, i.e. they do not belong to the same 2D plane.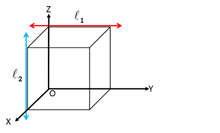
- Angle between two skew lines:
Angle between two skew lines is the angle between two lines which are drawn from any point and parallel to each of the skew lines. - A normal vector, simply called normal, is a vector perpendicular to a surface.
- Plane:
A plane is a surface such that a line joining any two points taken on it lies completely on the surface.
A plane is uniquely determined if- The normal to the plane and its distance from the origin is given.
- It passes through a point and perpendicular to a given direction.
- It passes through three given non-collinear points.
Note: A line containing three collinear points can be a part of many planes.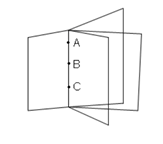
- Angle between two planes is the angle between their normals.
- Planes a1x + b1y + c1z + d2 = 0 and a2x + b2y + c2z +d2 = 0 are
- Perpendicular if a1a2 + b1b2 + c1c2 = 0
- Parallel if
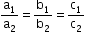
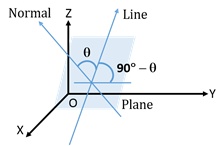
- The angle between a line and a plane is the complement of the angle between a line and the normal to the plane.
- Distance of a point from a plane is the length of the line (perpendicular to the plane) from the plane to the point.
Related Chapters
- Sets, Relations and Functions
- Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations
- Matrices and Determinants
- Permutations and Combinations
- Mathematical Induction
- Binomial Theorem and its Simple Applications
- Sequences and Series
- Limit, Continuity and Differentiability
- Integral Calculus
- Differential Equations
- Co-ordinate Geometry
- Vector Algebra
- Statistics and Probability
- Trigonometry
- Mathematical Reasoning