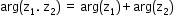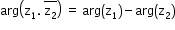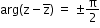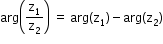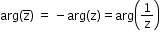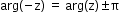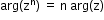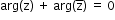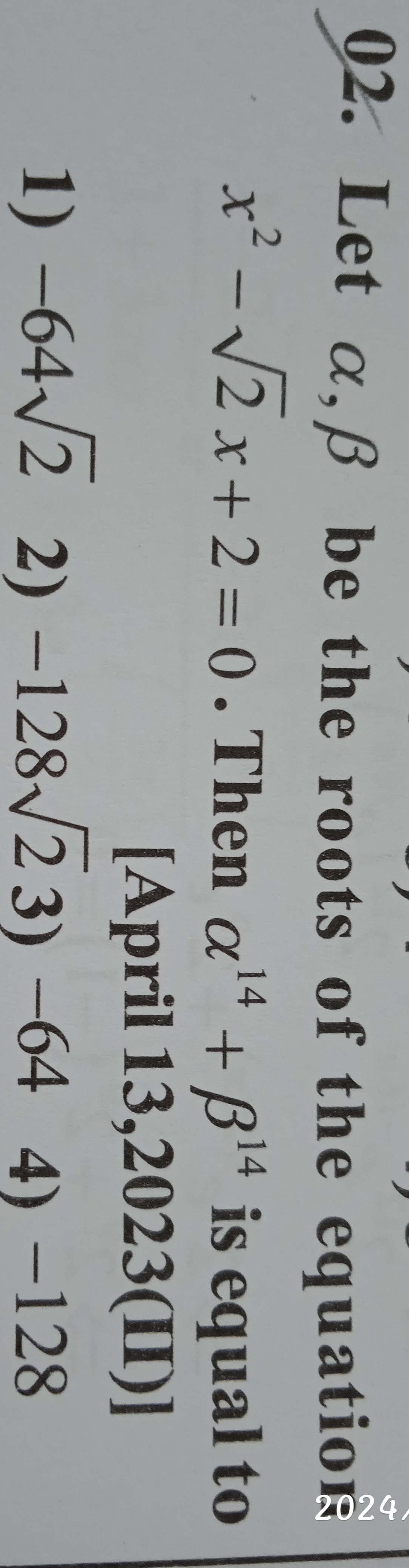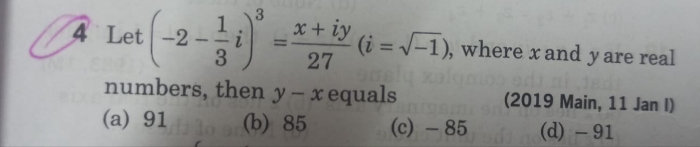Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations
Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations PDF Notes, Important Questions and Synopsis
SYNOPSIS
- A number of the form x + iy, where x, y Î ℝ and
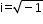 (i is iota), is called a complex number.
(i is iota), is called a complex number.
It is denoted by z, and a set of complex numbers is denoted by ℂ.
x = real part or Re(z), y = imaginary part or Im(z) -
Complex conjugate
Argument
Magnitude
If z = x + iy, then the conjugate of z is
= x - iyamp(z) = arg(z) = q =
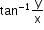
General argument: 2nπ + θ, n ϵ ℕ
Principal argument: -π < θ ≤ π
Least positive argument: 0 < θ ≤ 2πz = x + iy
|z|=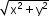
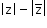
- Representation of Complex Number
Polar Representation
Exponential Form
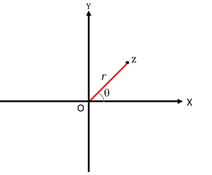
Vector Representation
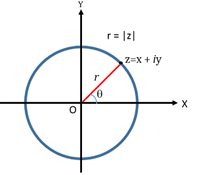
x = r cos θ, y = r sin θ
z = r eiθ
(where = cos eiθ + I sin θ)
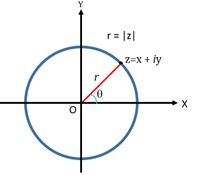
z = x + iy is considered a position vector of point p
- Square roots of a complex number
Let z = x + iy, then square root of z is
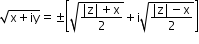 ,for y>0
,for y>0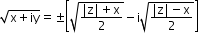 , for y<0
, for y<0 - Properties of the argument of a Complex Number:
- arg(any real positive number) = 0
- arg(any real negative number) = π
- Inequalities
I. Triangle inequalities
1. |z1 ± z2| £ | z1| ± | z2|
2. |z1 ± z2| ³ | z1| - | z2|
II. Parallelogram inequalities
| z1 + z2|2+ | z1 - z2|2 = 2 [|z1|2+| z2|2]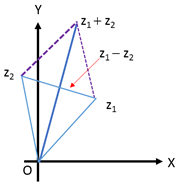
- If ABC is an equilateral triangle having vertices z1, z2, z3, then
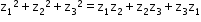 or
or 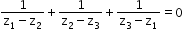
- If z1, z2, z3, z4 are vertices of a parallelogram, then z1 + z3 = z2 + z4.
- If z1, z2, z3 are affixes of the points A, B and C in the Argand plane, then
i. ÐBAC =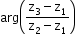
ii. 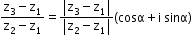 , where α = ÐBAC
, where α = ÐBAC - The equation of a circle whose centre is at a point having affix z0 and radius R = |z - z0|.
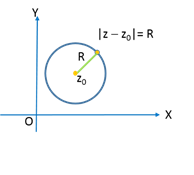
- If a, b are positive real numbers, then.
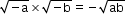
- Integral powers of iota
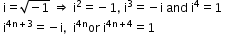
Hence,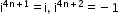
Quadratic Equations
- An equation of the form
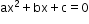 is called a quadratic equation, where a, b, c are real numbers and a ≠ 0.
is called a quadratic equation, where a, b, c are real numbers and a ≠ 0. - Values of the variable which satisfies the quadratic equation are called its roots.
-
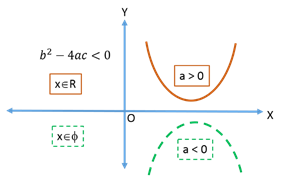
Nature of Roots
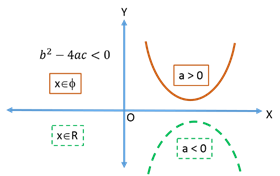
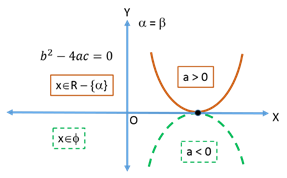
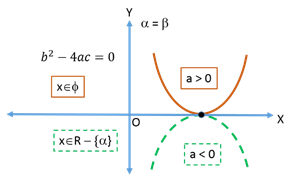
Let f(x) =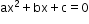 be the quadratic equation, the discriminant D =
be the quadratic equation, the discriminant D = 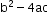 .
.If a > 0
If a < 0
1.
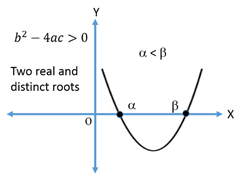
1.
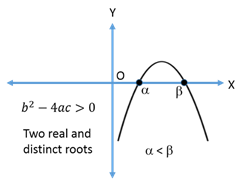
2.
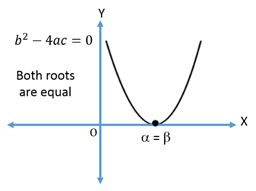
2.
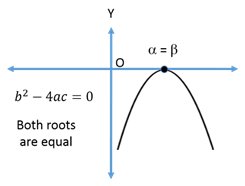
3.
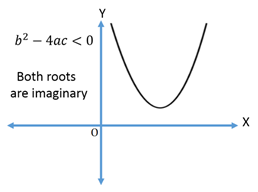
3.
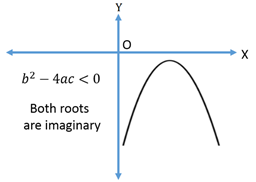
-
Let α, β be the roots of the quadratic equation
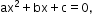 then
theni. Roots are given by the quadratic formula:
formula:
a, b =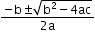
ii. Relation between roots and coefficients:
1. Sum of the roots =a+b = -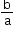
2. Product of the roots = a×b =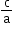
Note: Quadratic equation can be rewritten as
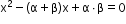 .
. -
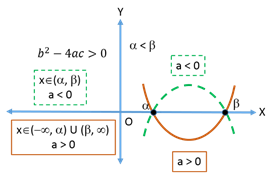
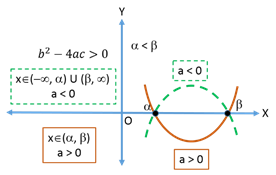
Quadratic inequalities
Let y =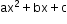 be the quadratic polynomial. There are two inequalities:
be the quadratic polynomial. There are two inequalities: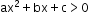
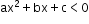
Related Chapters
- Sets, Relations and Functions
- Matrices and Determinants
- Permutations and Combinations
- Mathematical Induction
- Binomial Theorem and its Simple Applications
- Sequences and Series
- Limit, Continuity and Differentiability
- Integral Calculus
- Differential Equations
- Co-ordinate Geometry
- Three Dimensional Geometry
- Vector Algebra
- Statistics and Probability
- Trigonometry
- Mathematical Reasoning