Hydrocarbons
Hydrocarbons PDF Notes, Important Questions and Synopsis
SYNOPSIS
- Alkanes: General formula: CnH2n+2
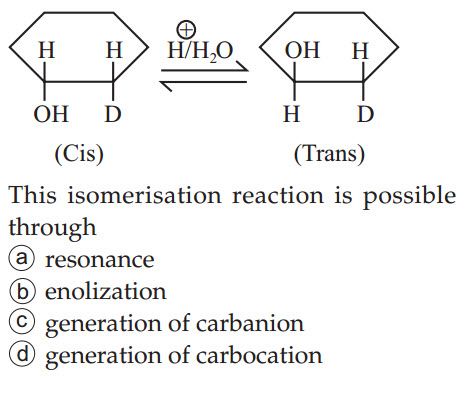
- Preparation of alkanes
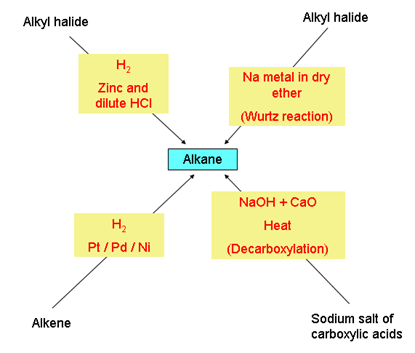
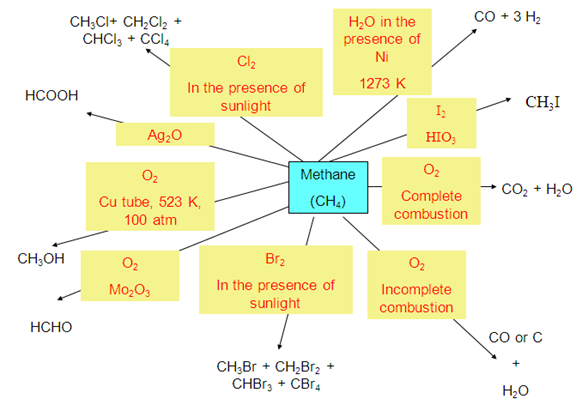
- Chemical properties of alkanes
- Aromatisation:
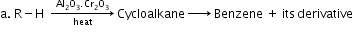
- Cracking (pyrolysis):
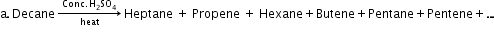
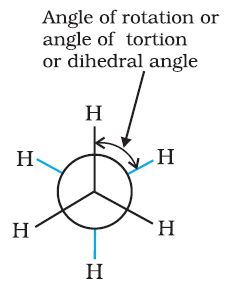
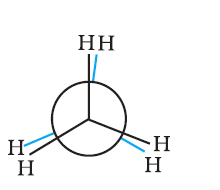
Conformations →
Eclipsed
Staggered
Skew
Conformation in
which hydrogen atoms attached to two carbon atoms are as close to each other as possible
Conformation in which hydrogen atoms are as farther away as possible
Any other intermediate
conformation in between eclipsed and sawhorse
Sawhorse projection
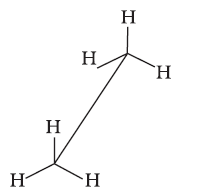
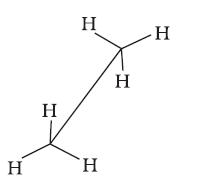
Newman projection
- Preparation of alkanes
- Geometrical isomers of alkenes
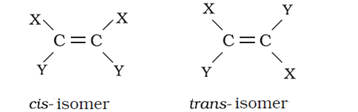
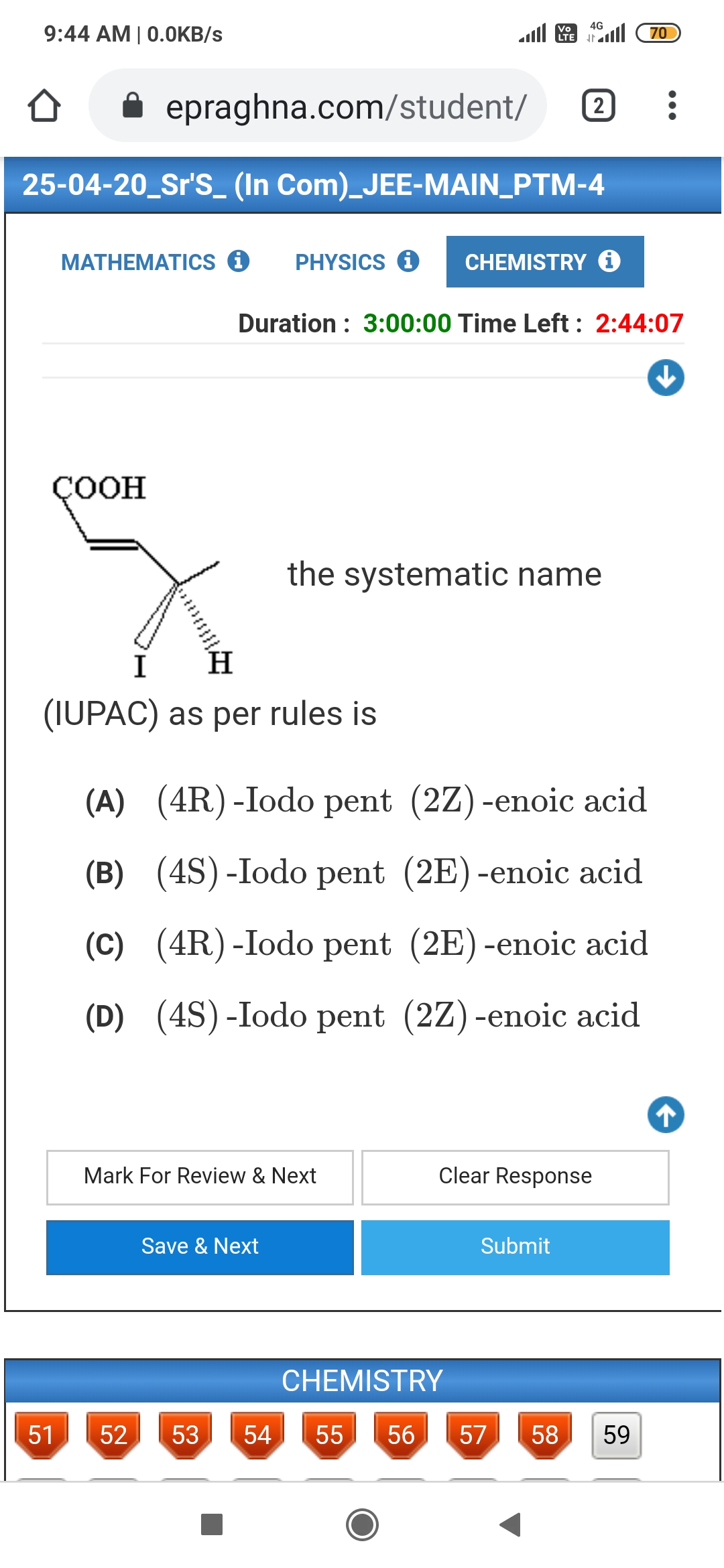
Trans-isomer is non-polar and has zero dipole moment where a cis-isomer is polar.
Cis-isomer has higher boiling points compared to trans-isomer because it is polar.
In case of solids, cis-isomer has a lower melting point than trans-isomer. This is because the trans-isomer is symmetrical and fits well into the crystal lattice.
. Preparation of alkenes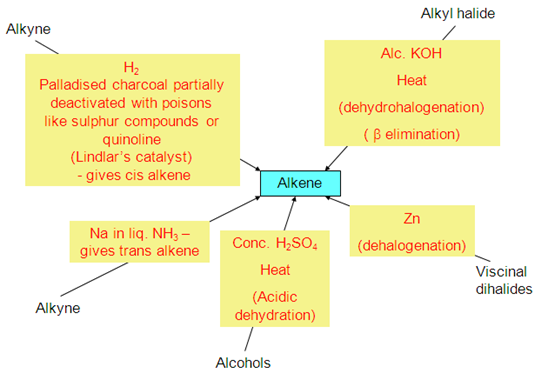
Chemical properties of alkenes
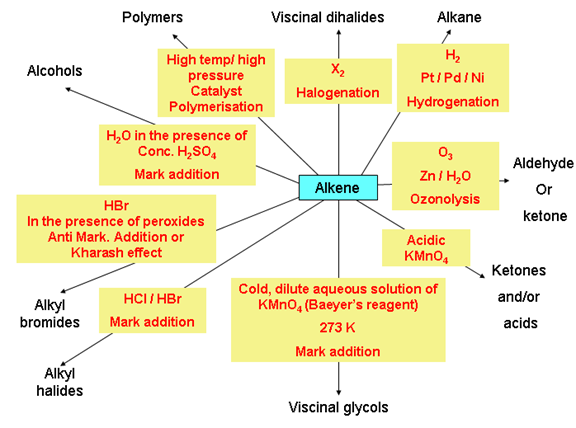
Test for Unsaturation: There are two tests to know whether a compound is unsaturated or not
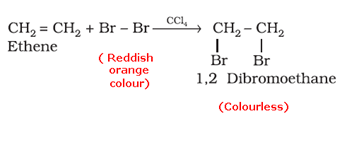
- Bromine water test: When an unsaturated compound is reacted with bromine solution in carbon tetrachloride, the reddish-orange colour of bromine solution in carbon tetrachloride is discharged.
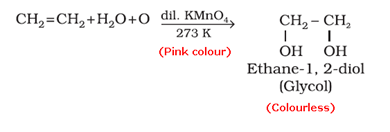
- Baeyer’s reagent test: When an unsaturated compound is reacted with cold, dilute and aqueous solution of potassium permanganate (Baeyer’s reagent), the pink colour of KMnO4 solution is discharged.
- Bromine water test: When an unsaturated compound is reacted with bromine solution in carbon tetrachloride, the reddish-orange colour of bromine solution in carbon tetrachloride is discharged.
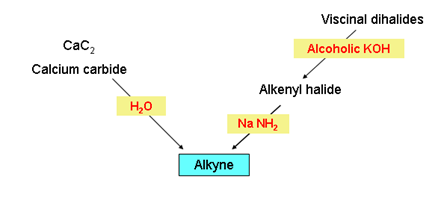
- Preparation of alkynes
Acidic nature of alkynes: Hydrogen atoms of ethyne attached to triple bonded carbon atom are acidic in nature.
Example: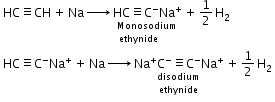
Reason:
Alkyne
Alkene
Alkane
Hybridisation of carbon to which H atom is attached
sp
sp2
sp3
Percentage s character of carbon
50%
(maximum)
66.6%
25%
(minimum)
Electronegativity of carbon atom
Highest
Less than alkyne and more than alkane
Lowest
Extent of attraction of hydrogen atoms of C-H bonds towards C
Highest
Less than alkyne and more than alkane
Lowest
Ease of liberation of H atoms as protons
Highest
Less than alkyne and more than alkane
Lowest
Acidic character
Highest
Less than alkyne and more than alkane
Lowest
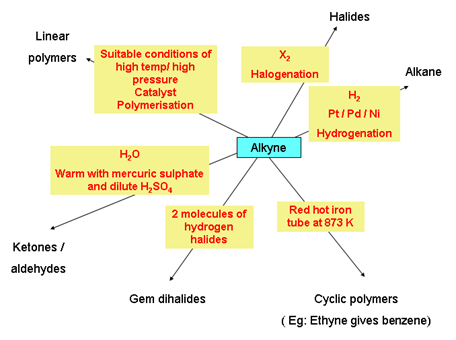
Chemical properties of alkynes
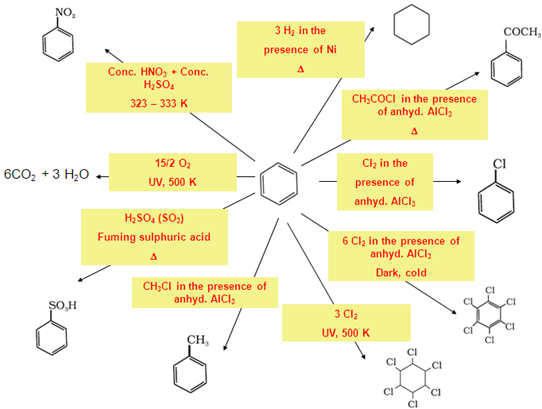
- Benzene:
Conditions for aromaticity
- Planarity: The ring should be planar. In simple words, all the carbons of the ring should be sp2 hybridised.
- Complete delocalisation of the p electrons in the ring: The p electrons should be completely delocalized. In simple words, in the ring alternate single and double bonds should exist.
- Hückel Rule: Presence of (4n + 2) p electrons in the ring where n is an integer (n = 0, 1, 2, . . .).
- Ortho–para directing groups: Groups which direct the incoming group to
ortho and para positions are called ortho–para directing groups.
Activating groups: Groups which increase the electron density at ortho and para positions of the benzene ring.
Examples: –NH2, –NHR, –NHCOCH3, –OCH3, –CH3 and –C2H5.Deactivating groups: Groups which decrease the electron
density at ortho and para positions of the benzene ring.
Example: –X. - Meta directing groups: The groups which direct the incoming group to meta position are called meta directing groups.
Examples: –NO2, –CN, –CHO, –COR, –COOH, –COOR and –SO3H.
Related Chapters
- Some Basic Concepts in Chemistry
- States of Matter
- Atomic Structure
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
- Chemical Thermodynamics
- Solid State
- Solutions
- Equilibrium
- Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry
- Chemical Kinetics
- Surface Chemistry
- Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Metals
- Hydrogen
- s-Block Element (Alkali and Alkaline Earth Metals)
- p-Block Elements
- d - and f - Block Elements
- Co-ordination Compounds
- Environmental Chemistry
- Purification and Characterisation of Organic Compounds
- Some Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry
- Organic Compounds Containing Halogens
- Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen
- Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen
- Polymers
- Biomolecules
- Chemistry in Everyday Life
- Principles Related to Practical Chemistry