Atomic Structure
Atomic Structure PDF Notes, Important Questions and Synopsis
SYNOPSIS
Dalton’s atomic theory:
Dalton’s atomic theory is based on the law of conservation of mass and the law of definite proportions. He also proposed the law of multiple proportions.
Thomson’s model of atom:
- It is also known as watermelon model or plum pudding model.
- According to this model, the atom is a positive sphere in which negative charges are distributed.
Rutherford alpha scattering experiment:
- This experiment was performed to understand the structure of an atom.
- This model concludes that most of the part of an atom is empty and each atom consists of a heavy positively charged nucleus.
|
Particle |
Mass (amu) |
Charge |
Discoverer |
|
Electron |
1.0073 |
+1 |
JJ Thomson |
|
Proton |
1.0087 |
0 |
Goldstein |
|
Neutron |
0.0005 |
−1 |
Chadwick |
Bohr’s model of atom:
- Electrons orbit the nucleus in orbits which have a set size and energy.
- The lowest energy is found in the smallest orbit.
- Radiation is absorbed or emitted.
Electromagnetic radiation:
- Wavelength: It is the distance between successive points of equal phases of a wave.
- Frequency: It is the number of cycles or oscillations or vibrations of wave motion in unit time.
- Velocity: It is the distance travelled by the wave in one second.
- Wave number: It is defined as the number of waves in unit wavelength.
Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle:
The uncertainty principle says that we cannot measure the position and momentum of the particle with absolute precision.
Bohr–Sommerfield model:
- According to this model, the path of an electron around the nucleus is an ellipse with the nucleus at one of its foci.
- The angular momentum of an electron in a closed elliptical path is also quantised.
Orbital:
An orbital is a three-dimensional region in which the probability of finding an electron is maximum.
Quantum numbers:
Principal quantum number:
- It is denoted by n.
- n = 1, 2, 3, 4 … ∞
- n = 1 K shell; n = 2 L shell
- n = 3 M shell; n = 4 N shell
- As the value of ‘n’ increases, the energy of the electron increases.
Azimuthal or angular quantum number:
- It is denoted by l.
- The values of l are from 0 to (n-1)
- l = 0 s subshell; l = 1 p subshell
- l = 2 d subshell; l = 3 f subshell
- The value of ‘l’ signifies the shape and energy level of subshells in a major energy shell.
Magnetic quantum number:
- It is denoted by ml.
- The values of ml lie from –l to +l.
- The values of ml signify the possible number of orientations of subshells.
Spin quantum number:
- It is denoted by ms.
- The values of ms are +1/2 and −1/2.
- The values of ms signify the direction of rotation or the spin of an electron in its axis during motion.
|
Subshell |
Shape of orbital |
|
s |
Spherical |
|
p |
Dumbbell |
|
d |
Double dumbbell |
|
f |
Diffused shape |
Pauli’s exclusion principle:
- It is impossible for two electrons of an atom to have all its four quantum numbers same.
- Maximum number of electrons in a shell can be 2n2.
- Maximum number of electrons in a subshell can be 2 only.
Aufbau principle:
- Orbitals with lower energy level are filled first.
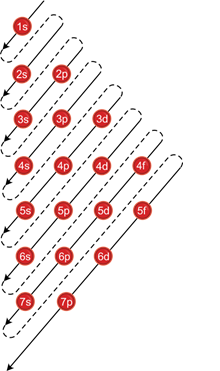
(n+l) rule:
- The subshell with lower values of (n+l) possesses lower energy.
- If (n+l) for two orbitals are the same, the one with lower value of n possesses lower energy and should be filled first.
Paramagnetism:
A substance whose molecules, ions or atoms have unpaired electrons is paramagnetic.
Diamagnetism:
Molecules, ions or atoms having no unpaired electrons are diamagnetic.
Related Chapters
- Some Basic Concepts in Chemistry
- States of Matter
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
- Chemical Thermodynamics
- Solid State
- Solutions
- Equilibrium
- Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry
- Chemical Kinetics
- Surface Chemistry
- Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Metals
- Hydrogen
- s-Block Element (Alkali and Alkaline Earth Metals)
- p-Block Elements
- d - and f - Block Elements
- Co-ordination Compounds
- Environmental Chemistry
- Purification and Characterisation of Organic Compounds
- Some Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry
- Hydrocarbons
- Organic Compounds Containing Halogens
- Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen
- Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen
- Polymers
- Biomolecules
- Chemistry in Everyday Life
- Principles Related to Practical Chemistry