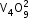d - and f - Block Elements
d and f Block Elements PDF Notes, Important Questions and Synopsis
SYNOPSIS
D-Block Elements:
The general electronic configuration of d-block elements is (n-1) d1-10 ns0-2, where n is the outermost shell.
Different oxidation states of the first transition series:
|
Element |
Outer electronic configuration |
Oxidation states |
|
Sc |
3d14s2 |
+3 |
|
Ti |
3d24s2 |
+2, +3, +4 |
|
V |
3d34s2 |
+2, +3, +4, +5 |
|
Cr |
3d54s1 |
+2, +3, (+4), (+5), +6 |
|
Mn |
3d54s2 |
+2, +3, +4, (+5), +6, +7 |
|
Fe |
3d64s2 |
+2, +3, (+4), (5), +6, +7 |
|
Co |
3d74s2 |
+2, +3, (+4) |
|
Ni |
3d84s2 |
+2, +3, +4 |
|
Cu |
3d104s1 |
+1, +2 |
|
Zn |
3d104s2 |
+2 |
Characteristics of Oxides and Some lons of V and Cr
|
|
|||||
|
Oxidation State |
Oxide/Hydroxide |
Behaviour |
Ion |
Name of Ion |
Colour of Ion |
|
+2 |
VO |
Basic |
V2+ |
vanadium (II) (vanadous) |
violet |
|
+3 |
V2O5 |
basic |
V3+ |
vanadium (III) (vanadic) |
green |
|
+4 |
VO2 |
amphoteric |
VO2+
|
oxovanadium (IV) (vanadyl)
hypovanadate (vanadate) |
blue |
|
+5 |
V2O5 |
amphoteric |
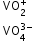 |
dioxovanadium (V) orthovanadate |
brown |
|
+2 |
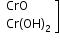 |
basic |
Cr2+ |
Chromium (II) (chromous)
|
yellow colourless |
|
+2 |
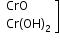 |
basic |
Cr2+ |
Chromium (II) (chromous) |
light blue
light blue |
|
+3 |
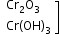 |
amphoteric |
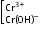 |
Chromium (III) chromic chromite |
violet
green |
|
+5 |
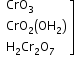 |
acidic |
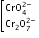 |
Chromate
dichromate |
yellow
orange |
Magnetic Properties:
- Paramagnetic substances: Substances which are attracted by the magnetic field are called paramagnetic substances.
- Diamagnetic substances: Substances which are repelled by the magnetic field are called diamagnetic substances. The spin only magnetic moment can be calculated from the relation:
where n is the number of unpaired electrons and is magnetic moment in Bohr magneton (BM) units.
d-Block metal compounds:
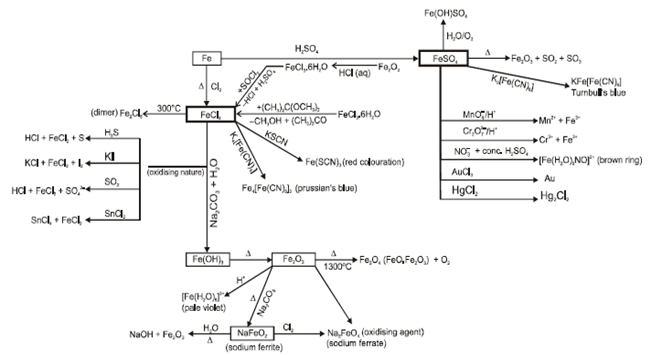
- Hydrated ferrous sulphate (FeSO4.7H2O), ferric chloride (FeCl3) and iron (III) oxide (Fe2O3):
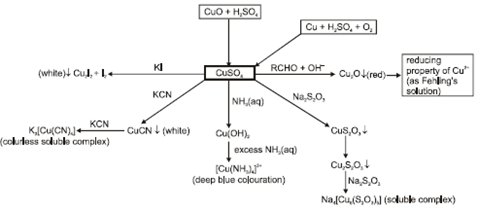
- Hydrated copper sulphate (CuSO4.5H2O):
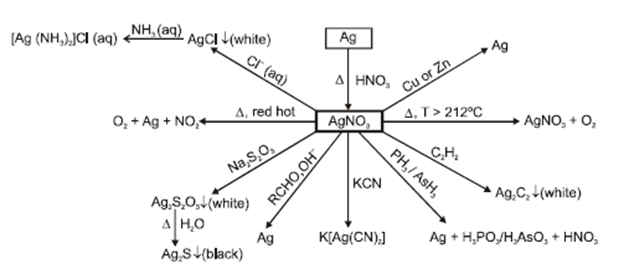
- Silver nitrate (AgNO3):
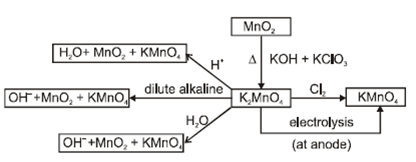
- Potassium permanganate (KMnO4):
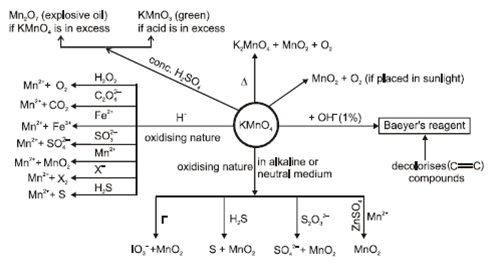
- Potassium dichromate (K2CrO7):
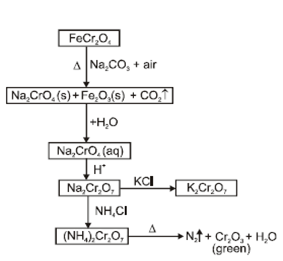
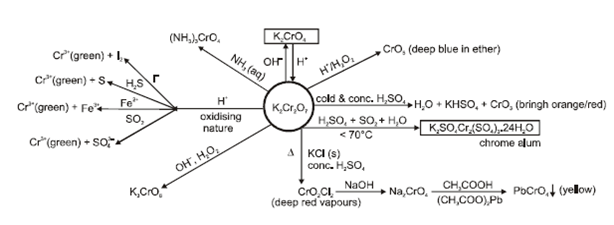
f-Block elements:
- Electronic configuration: (n-2)f1-14(n-1)d0-1ns2
- Lanthanoids: The 14 elements immediately following lanthanum, i.e. cerium (58) to lutetium (71) are called lanthanoids.
- Actinoids: The 14 elements immediately following actinium (89), with atomic numbers 90 to 103 are called actinoids.
- Differences between lanthanoids and actinoids:
Lanthanoids
Actinoids
4f-orbital is progressively filled.
5f-orbital is progressively filled.
Only promethium (Pm) is a radioactive element.
All are radioactive.
Less reactive (than actinoids).
More reactive.
+3 oxidation state is most common along with +2 and +4.
They show +2, +3, +4, +5, +6, +7 oxidation states.
Related Chapters
- Some Basic Concepts in Chemistry
- States of Matter
- Atomic Structure
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
- Chemical Thermodynamics
- Solid State
- Solutions
- Equilibrium
- Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry
- Chemical Kinetics
- Surface Chemistry
- Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Metals
- Hydrogen
- s-Block Element (Alkali and Alkaline Earth Metals)
- p-Block Elements
- Co-ordination Compounds
- Environmental Chemistry
- Purification and Characterisation of Organic Compounds
- Some Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry
- Hydrocarbons
- Organic Compounds Containing Halogens
- Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen
- Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen
- Polymers
- Biomolecules
- Chemistry in Everyday Life
- Principles Related to Practical Chemistry