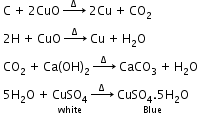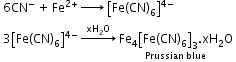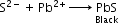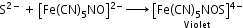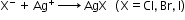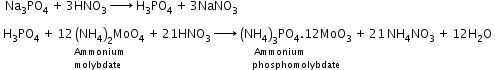Principles Related to Practical Chemistry
Principles Related to Practical Chemistry PDF Notes, Important Questions and Synopsis
SYNOPSIS
- Qualitative analysis of organic compounds:Analysis involving detection of all elements present in an organic compound.
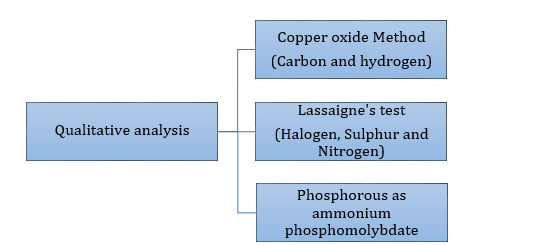
- Detection of carbon and hydrogen by the copper oxide test
- Qualitative analysis (Detection of elements):
- Detection of nitrogen, halogen and sulphur by Lassaigne’s test
|
|
|
|
|
- Qualitative Analysis of Inorganic Compounds:
Identification of acidic radicals (anions):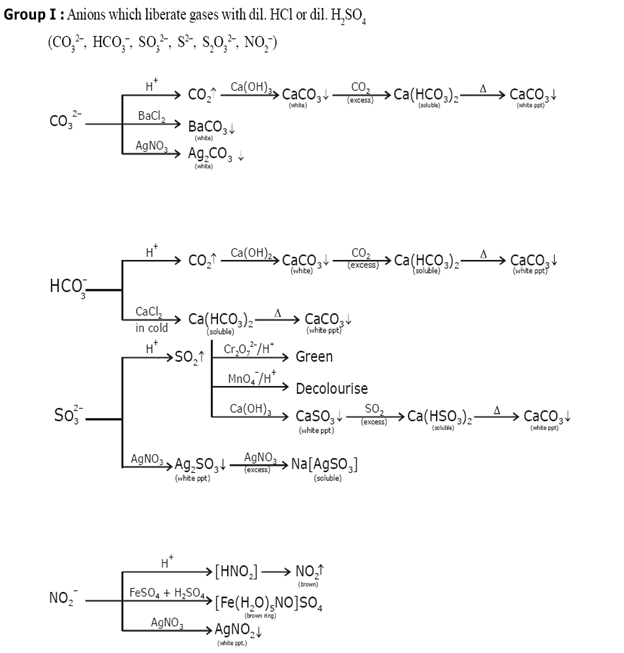
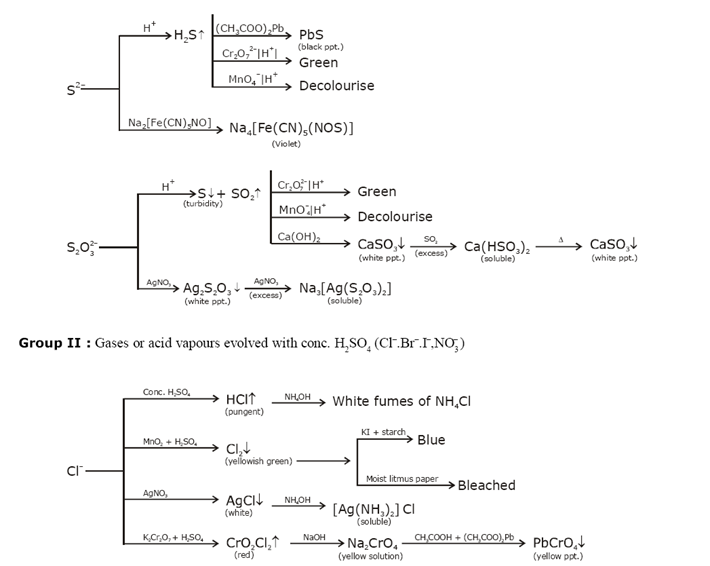
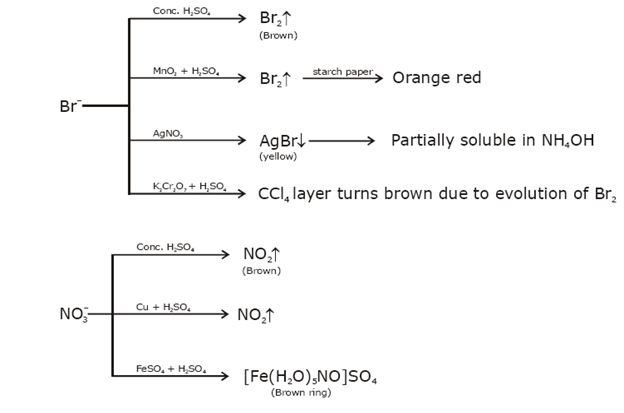
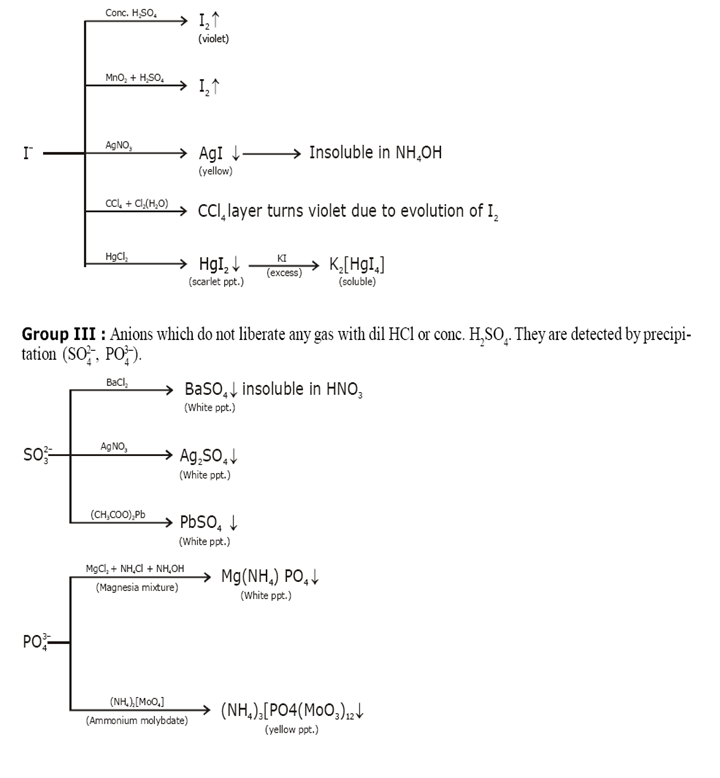
Identification of basic radicals (cations):
Group I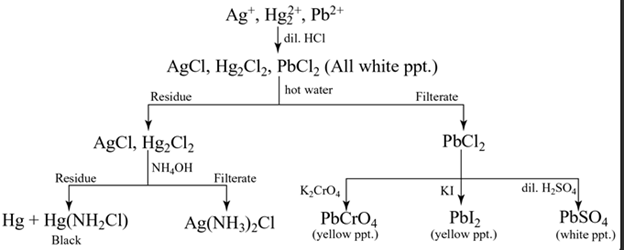
Group II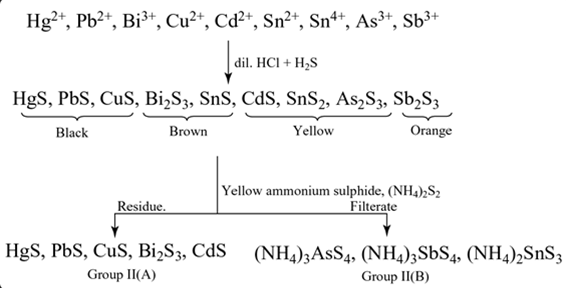
Group II(a)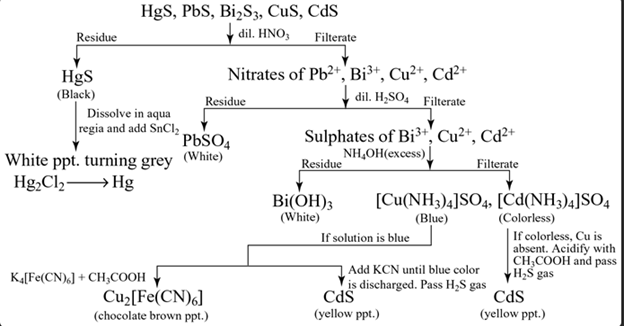
Group II(b)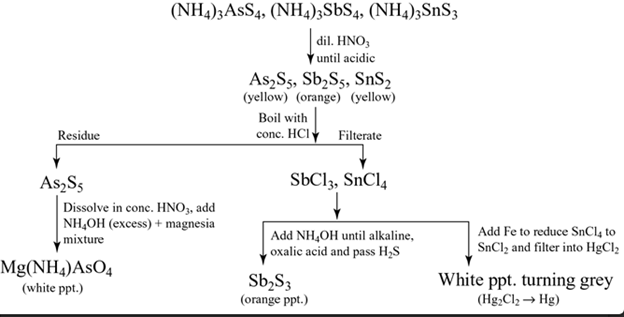
Group III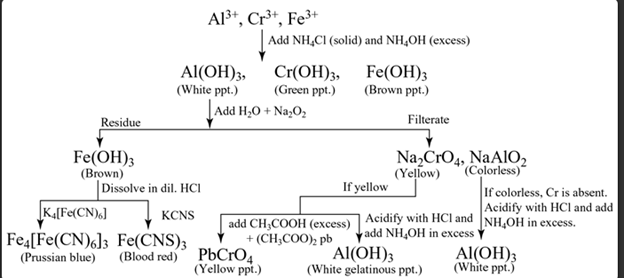
Group IV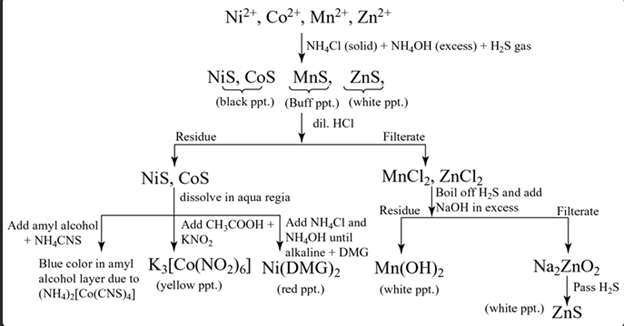
Group V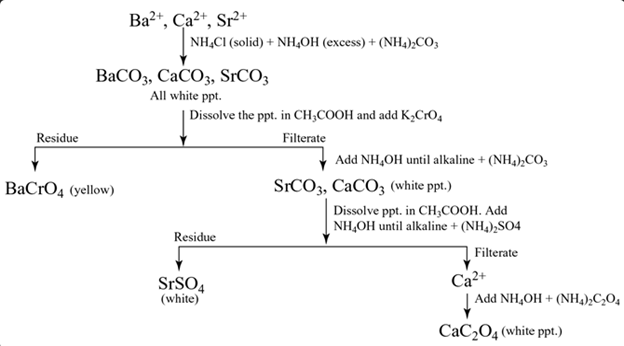
Group VI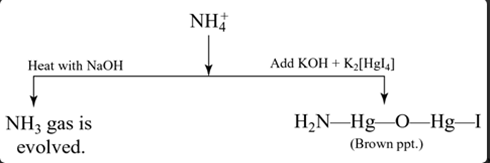
Download complete content for FREE 
JEE Main - Chemistry
Asked by g_archanasharma | 17 Mar, 2019 11:54: AM
Related Chapters
- Some Basic Concepts in Chemistry
- States of Matter
- Atomic Structure
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
- Chemical Thermodynamics
- Solid State
- Solutions
- Equilibrium
- Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry
- Chemical Kinetics
- Surface Chemistry
- Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Metals
- Hydrogen
- s-Block Element (Alkali and Alkaline Earth Metals)
- p-Block Elements
- d - and f - Block Elements
- Co-ordination Compounds
- Environmental Chemistry
- Purification and Characterisation of Organic Compounds
- Some Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry
- Hydrocarbons
- Organic Compounds Containing Halogens
- Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen
- Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen
- Polymers
- Biomolecules
- Chemistry in Everyday Life