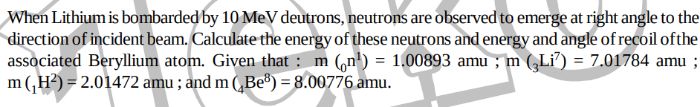Work, Energy and Power
Work, Energy and Power PDF Notes, Important Questions and Synopsis
SYNOPSIS
- Work done by a constant force is
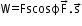
- Work done can be positive, negative or zero.
- Work done by a variable force
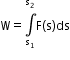
- Work–energy theorem: The work W done by the net force on a particle equals the change in the particle’s kinetic energy.
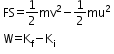
- Gravitational potential energy does not depend on the choice of the reference surface for measuring height.
- Gravitational potential energy:
- Energy possessed by a body changes with height with respect to the surface of the Earth.
- GPE = −WGravitational Force
- Elastic potential energy; When a spring is elongated (or compressed), work is done against restoring force of the spring. This resultant work done is stored in the spring in the form of elastic potential energy.
- Equilibrium
If the forces are conservative, then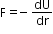
For equilibrium,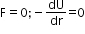
if
if
if
- Law of conservation of mechanical energy:
Total mechanical energy of the system always remains constant in the absence of dissipative forces. - Total mechanical energy of the system equals the sum of potential energy and kinetic energy.
- Conservation and Non-Conservation forces
- A force is said to be of the conservative category if the work done by it in moving a particle from one point to another does not depend on the path taken but depends only on the initial and final positions.
- Work done by a conservative force around a closed path is calculated to be zero. Gravitational force, electric force and spring force are some of the examples of this category.
- If the work done by a force in moving a body from one point to another depends on the path followed, then the force is said to be of the non-conservative category.
- Work done by a non-conservative force around a closed path is cannot be zero. For example, both frictional and viscous forces work in an irreversible manner, and hence, a definite part of energy is lost in overcoming these frictional forces. (Mechanical energy is converted to other energy forms such as heat, sound etc.). Therefore, these forces are of the non-conservative category.
- A force is said to be of the conservative category if the work done by it in moving a particle from one point to another does not depend on the path taken but depends only on the initial and final positions.
- A conservative force is the negative gradient of potential energy function.
F (x) = −DU/Dx - Motion in a Vertical Circle
- A particle of mass m attached to one end of a string and rotated in a vertical circle of radius r with centre O.
The speed of the particle will decrease as the particle travels from the lowest point to the highest point but increases in the reverse direction due to acceleration due to gravity.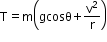
At the highest point,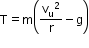 At the lowest point,
At the lowest point, 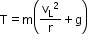
- Body inside a hollow tube
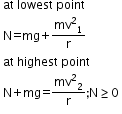
Minimum velocity to complete the circle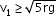
- Power is the rate at which work is done or energy is transformed.
- The unit of power is watt. 1 watt = 1 joule/second. It is a scalar quantity. Dimensions of power =
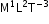
- Linear momentum of an isolated system is always conserved in a collision.
- A collision in which the total kinetic energy of the system is conserved is called elastic.
A collision in which the total kinetic energy of the system is not conserved is called inelastic. - When two bodies collide, stick together and have a common final velocity, the collision is completely inelastic.
Download complete content for FREE 
JEE Main - Physics
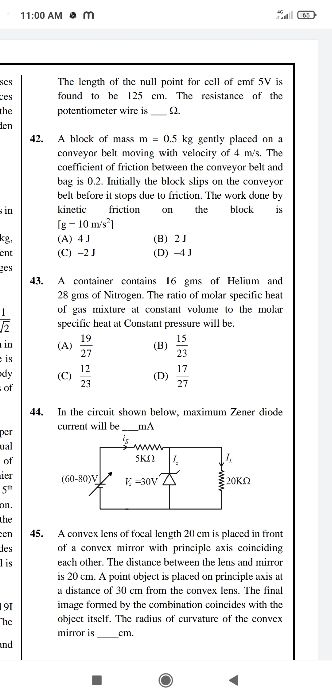
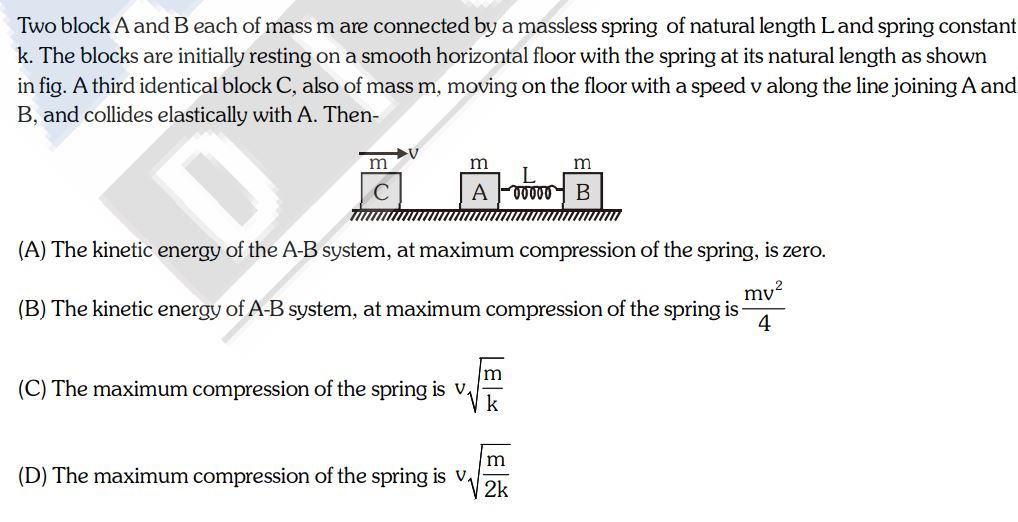
Asked by sarthakbhoskar7630 | 05 Mar, 2024 07:03: PM
JEE Main - Physics
Asked by fekishfaker | 18 Nov, 2023 01:39: PM
JEE Main - Physics
Asked by theavengers0203 | 24 May, 2023 08:40: AM
JEE Main - Physics
Asked by mdowaisraza581 | 16 May, 2023 10:06: PM
JEE Main - Physics
Asked by vishal.vini86 | 22 Apr, 2022 12:06: AM
JEE Main - Physics
Asked by pratham.k | 02 Jun, 2020 12:20: AM
JEE Main - Physics
Asked by Harshhacker2580 | 30 Apr, 2020 01:04: PM
Related Chapters
- Physics and Measurement
- Kinematics
- Laws of Motion
- Rotational Motion
- Gravitation
- Properties of Solids and Liquids
- Thermodynamics
- Kinetic Theory of Gases
- Oscillations and Waves
- Electrostatics
- Current Electricity
- Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism
- Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents
- Electromagnetic Waves
- Optics
- Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation
- Atoms and Nuclei
- Electronic Devices
- Communication Systems