Circles: Area and Perimeter
Circles: Area and Perimeter Synopsis
Synopsis
- The distance around the boundary of the circle is called the perimeter or the circumference of the circle.
- Circumference (perimeter) of a circle = πd or 2πr, where d is he diameter, r is the radius of the circle and
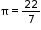 .
.
- Perimeter of a semi circle or protractor = πr + 2r
- Perimeter of a quadrant =

- Distance moved by a wheel in 1 revolution = Circumference of the wheel.
Number of revolutions in one minute =
- The region enclosed inside a circle is called its area.
- Area of a circle = πr2
- Area of a semi-circle =
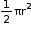
- Area of a quadrant =
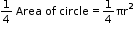
- Circles having the same centre but different radii are called concentric circles.
Area enclosed by two concentric circles = πR2 - πr2 = π(R2 - r2) = π(R + r)(R - r)
Where, R and r are radii of two concentric circles - The part of the circumference between the two end points of the chord is called an arc. In the figure, arc
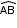 is shown.
is shown. - A diameter of circle divides a circle into two equal arcs, each known as a semi-circle.
- An arc of a circle whose length is less than that of a semicircle of the same circle is called a minor arc.
- An arc of a circle whose length is greater than that of a semicircle of the same circle is called a major arc.
- Length of an arc =
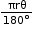
- The region bounded by an arc of a circle and two radii at its end points is called a sector.
If the central angle of a sector is more than , then the sector is called a major sector and if the central angle is less than , then the sector is called a minor sector. - Perimeter of sector of angle θ =
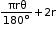
- Area of a sector of angle θ =
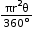
- Area of major sector = πr2 – Area of minor sector
- A chord divides the interior of a circle into two parts, each called a segment.
The segment which is smaller than the portion of semi-circle is called the minor segment and the segment which is larger than the portion of semi-circle is called the major segment. In the circle shown, the yellow portion is the minor segment while the non-shaded portion is the major segment. - Perimeter of segment of angle θ =
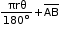
- Area of minor segment = Area of sector - Area of ΔABC
- Area of minor segment can also be written as:
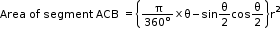
- Area of major segment = Area of the circle – Area of minor segment
Download complete content for FREE 


