Binomial Theorem
Binomial Theorem Synopsis
Synopsis
- Introduction to Binomial Expansion
• A binomial expression is an algebraic expression having two terms. For example, (a + b), (a - b) etc.
• The expansion of a binomial for any positive integral exponent ‘n’ is given by the binomial theorem. The binomial theorem says that
(x + y)n = xn + nC1xn-1y + nC2xn-2y2 + ---- + nCrxn-ryr + ----- + nCn-1xyn-1 + nCnyn
• In summation notation,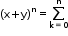 nCkxn-kyk
nCkxn-kyk - Properties of Binomial Expansion
• In the binomial expansion of (x + y)n the number of terms is (n + 1) i.e. one more than the exponent.
• The exponent of ‘x’ goes on decreasing by unity and that of ‘y’ increases by unity. Exponent of ‘x’ is ‘n’ in the first term, (n - 1) in the second term, and so on ending with zero in the last term.
• The sum of the indices of ‘x’ and ‘y’ is always equal to the index of the expression.
• Replacing a by –a in the expansion of (x + y)n, we have
(x – y)n = [x + (-y)]n
(x – y)ⁿ = nC0xn - nC1xn-1y + nC2xn-2y2 - nC3xn-3y3 + … + (-1)n nCnyn
In summation notation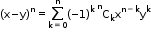
• (x + y)n + (x - y)n = 2[nC0xny0 + nC2xn-2y2 + nC4xn-4y4 + ...]
and
(x + y)n - (x - y)n = 2[nC1xn-1y1 + nC3xn-3y3 + nC5xn-5y5 + ...]
• If n is odd, then {(x + y)n + (x - y)n} and {(x + y)n - (x - y)n} both have the same number of terms equal to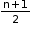
• If n is even, then {(x + y)n + (x - y)n} has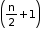 terms and {(x + y)n - (x - y)n} has
terms and {(x + y)n - (x - y)n} has 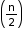 terms.
terms. - General and Middle Terms
• General Term
i. General term in the expansion of (x + y)n is Tk+1 = nCkxn-kyk
ii. General term in the expansion of (x - y)n is Tk+1 = nCk(-1)kxn-kyk
• Term from the end
In the binomial expansion of (x + y)n, the kth term from the end is ((n + 1) - k + 1) = (n - k + 2)th term from the beginning.
• Middle Term(s)
i. If n is even, there is only one middle term in the expansion of (x + y)n and it will be the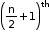 term.
term.
ii. If n is odd, there are two middle terms in the expansion of (x + y)n, i.e. the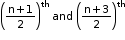 term.
term.
iii. In the expansion of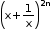 , where x ≠ 0, the middle term is
, where x ≠ 0, the middle term is 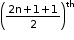 i.e., (n + 1)th term, as 2n is even.
i.e., (n + 1)th term, as 2n is even. - Binomial Coefficients
• The coefficients, the number of combinations of n objects taken r at a time, occurring in the binomial expansion, are known as binomial coefficients.
• The coefficients nCr of terms equidistant from the beginning and end are equal. These coefficients are known as binomial coefficients.
i.e. nCr = nCn-r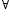 r = 0, 1, 2, ..., n
r = 0, 1, 2, ..., n
• Coefficient of (k + 1)th term in the binomial expansion of (1 + x)n is nCk.
• Coefficient of Xk term in the binomial expansion of (1 + x)n is nCk.
• Coefficient of Xk term in the binomial expansion of (1 - x)n is (-1)k nCk.
• Coefficient of (k + 1)th term in the binomial expansion of (1 - x)n is (-1)k nCk. - Binomial theorem for negative or fractional index
• Let n be a negative integer or a fraction (+ve or –ve) and x be a real number such that | x | < 1, then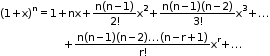
• General Term
General term in the expansion of (1 + x)n when n is negative or fractional is given by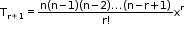
- Some special expansions
• (1 - x)-1 = 1 + x + x2 + ... + xr + ...
• (1 + x)-1 = 1 - x + x2 - ... + (-1)rxr + ...
Download complete content for FREE 

