CBSE Class 11-science - Equilibrium of Rigid Body Videos
Systems of Particles and Rotational Motion
This video explains the principle of moments and the example of locating the centre of gravity.
More videos from this chapter
View All- What do you understand by mechanical equilibrium of a rigid body?
- When will you say that a body is in partial equilibrium?
- For a rigid body to be in rotational equilibrium, prove that the sum of all the external torques acting on it is zero.
- Define couple and moment of couple.
- A cap of pen can be easily opened with the help of two fingers than one finger. Why?
- What do you understand by Mechanical Advantage?
- The mechanical advantage for a lever is greater than one. Comment on the statement.
-
A uniform beam of length L meters and weight M kg supports two unequal masses each of mass m1 and m2 respectively, balanced at the opposite ends of the seesaw. Calculate the normal force N exerted on the beam by the support, and develop the equations for net force and net torque for the system using equilibrium conditions for a rigid body.
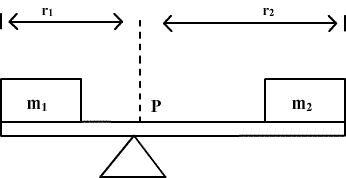
- Prove that the moment of a couple does not depend upon the point about which moments are taken.
- Distinguish between centre of gravity of a body and its centre of mass.






