CBSE Class 11-science Answered
The required reaction is:
6C(s) + 6H2(g) + 3O2(g) → C6H12O6(s)
We have to find out standard enthalpy of formation for glucose.
Enthalpy of combustion of glucose is -2802 kJ/mol.
C6H12O6 (s) + 6O2(g) → 6CO2(g) + 6H2O(l) ΔH = -2802 kJ/mol …(i)
Enthaply of formation of carbondioxide is 394 kJ/mol.
C(S) + O2(g) → CO2(g) ΔH = 394 kJ/mol …(ii)
Enthaply of formation of water is 386 kJ/mol.
H2 + ½ O2 → H2O ΔH = 386 kJ/mol …(iii)
Now, revert eq. (i), multiply eq. (ii) and (iii) by 6,
6CO2(g) + 6H2O(l) → C6H12O6 (s) + 6O2(g) ΔH = 2802 kJ/mol …(iv)
6C(S) + 6O2(g) → 6CO2(g) ΔH = 2364 kJ/mol …(v)
6H2 + 3O2 → 6H2O ΔH = 2316 kJ/mol …(vi)
Add eq.(iv), (v), (vi) we will get,
6C(s) + 6H2 (g) + 3O2(g) → C6H12O6 (s) ΔH = 2802 + 2364 + 2316 = 7482 kJ/mol
Enthalpy of formation of glucose = 7482 kJ/mol



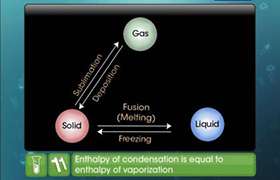
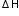 from: Enthalpy changes of formation and bond enthalpies.
from: Enthalpy changes of formation and bond enthalpies.