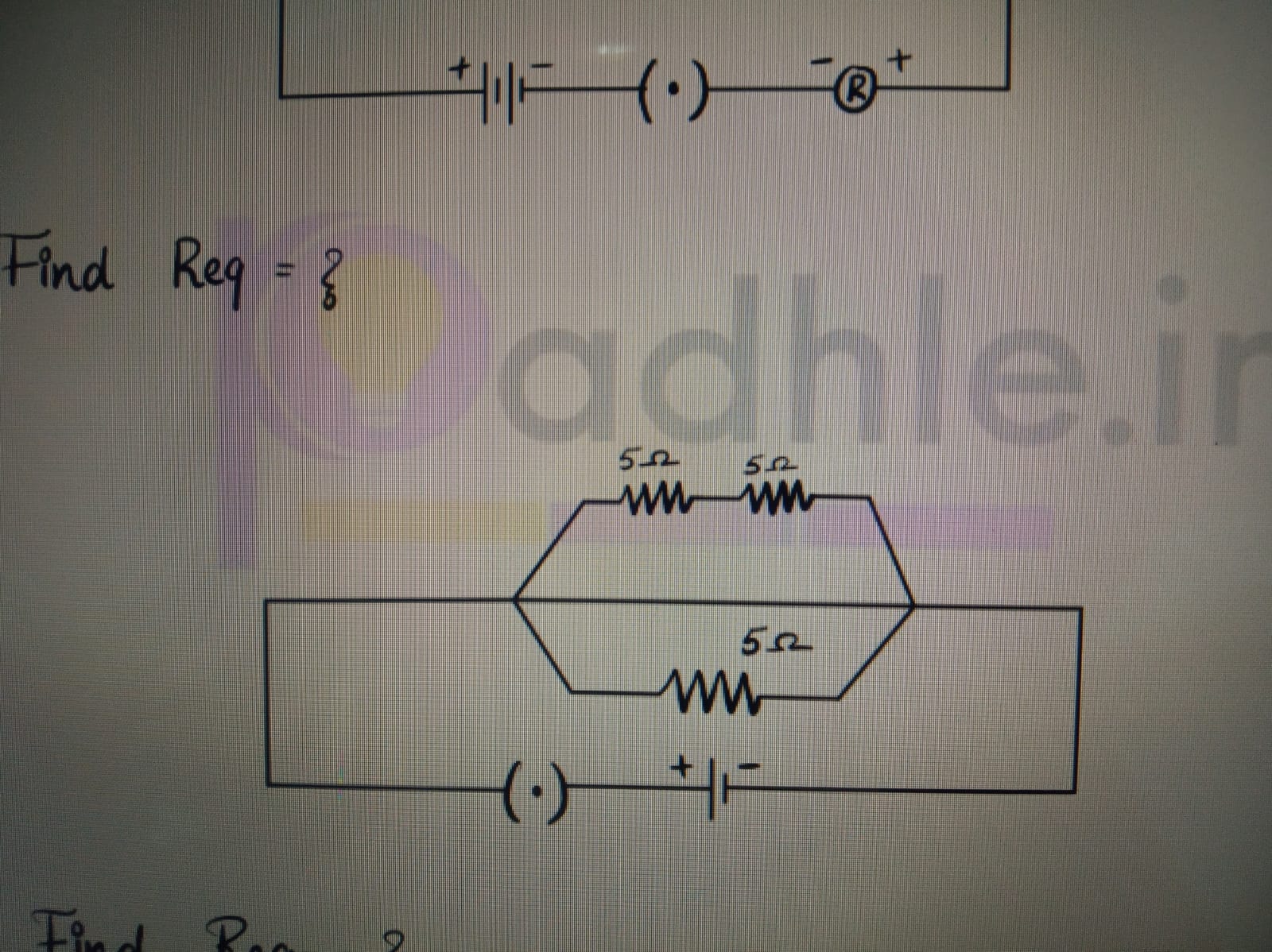
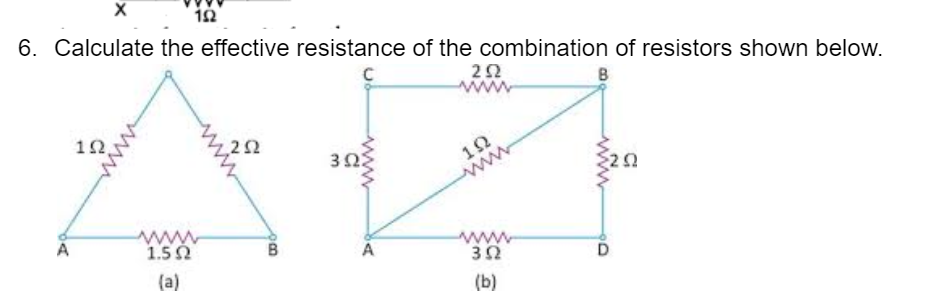
CBSE Class 10 Answered
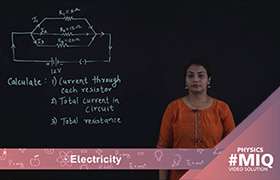
why is the combined resistance less when the resistors are connected in parallel and why is it more when they are in series?
Asked by snigdhaa138_461 | 11 Sep, 2010, 08:41: PM
Resistance = resistivity x (length / area)
When you put them in series, you increase the length of the resistor, keeping the cross sectional area same. Thus, resistance increases (Resistance is directly proportional to length of resistor).
When you connect them in parallel, you split the incoming current in multiple paths, decreasing the strength of the current. now, the voltage drop across the resistors is same, but the current flowing through the resultant resistance is higher than the individual resistances. to maintain the same voltage drop, resultant resistance has to be lower than individual resistances. (V = IR, if I increases then R decreases to maintain constant V)
[For your own understanding, you can understand it like this: in parallel, the corss sectional area of the net resistance increases, decreasing the resistance.]
Answered by | 11 Sep, 2010, 10:47: PM
Application Videos
Concept Videos
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by khajannirwan | 27 Feb, 2024, 10:20: PM
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by saanviyadla | 24 Jan, 2024, 07:06: PM
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by kamalaranjanmohantymohanty5 | 06 Jan, 2024, 10:05: AM
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by nandhikasugumar | 05 Oct, 2023, 04:01: PM
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by daniya062008 | 02 Oct, 2023, 08:25: PM
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by prassanna.j | 03 Sep, 2023, 12:28: PM
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by prassanna.j | 03 Sep, 2023, 12:21: PM
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by prassanna.j | 03 Sep, 2023, 12:13: PM
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by prassanna.j | 03 Sep, 2023, 12:11: PM