CBSE Class 12-science - Integrated Rate Equation Videos
Deriving integrated rate equation and calculate half life for zero order and first order reaction
Derive integrated rate equation and calculate half life for zero order and first order reaction. Define pseudo order reactions.
More videos from this chapter
View All-
Please ans both part

- Explain why the rate of a chemical reaction does not remain uniform throughout the reaction?
-
For a chemical reaction X
Y, The rate increases by the factor 2.25 when concentration of X is increased by 1.5. Derive or suggest the rate law equation and find the order of reaction.
- A gas phase decomposition of xy follows the rate law r = k[xy]n. what are the units of its rate constant?
-
The reaction A + 3B
 2C obeys the rate equation: Rate = k[A]1/3 [B]3/2. Find out the order of this reaction?
2C obeys the rate equation: Rate = k[A]1/3 [B]3/2. Find out the order of this reaction?
-
The experimental data for the reaction:
2A + B2 → 2AB is:
Write the rate equation for the reaction?
- The half-life of a first order decomposition of nitramide is 2.1 hour at 25o C. Determine the time taken for the compound to decompose 99% of its original amount, rate constant = 0.2303 per hour.
- The rate of reaction between A and B increases by a factor of 100. Calculate the order of the reaction when the concentration of A is increased 10 times.
-
Calculate the rate of reaction from the rate law:
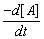 = k[A] [B]2, when the concentration of A and B are 0.01 M and 0.02 M respectively and k = 5.1 x 10-3 L2 mol-2 s-1.
= k[A] [B]2, when the concentration of A and B are 0.01 M and 0.02 M respectively and k = 5.1 x 10-3 L2 mol-2 s-1.
- Derive an equation for calculating the half life of a first order reaction






