CBSE Class 12-science Answered
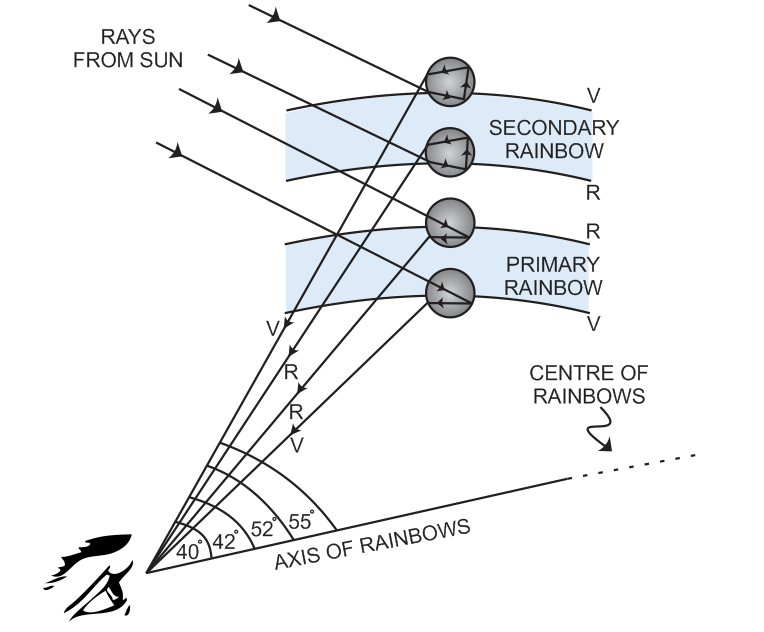
When sunlight enters a raindrop, it gets refracted, which causes separation of white light in different wavelengths or colours. Red light has a longer wavelength gets bent least while the violet light has shorter wavelength gets bent the most. Generally two kinds of rainbows are formed.
The inner of the two bows seen is the primary rainbow. It is found that violet light found on inside, emerges at an angle 40⁰ and red light found on the outside, emerges at an angle 42⁰. The outer of two bows is called secondary rainbow. It shows solar spectrum in reverse order. The red light on inner edge makes an angle of 52⁰ and violet light on the outer edge makes an angle 54⁰. The intensity of the light is reduced at second reflection and hence it is not brighter as the primary one.
If we look at a raindrop with different direction, it looks different colours. We get a circular rainbow exactly opposite the sun. If the sun is high in the sky, we are able to see the top of the circle and the shape of the rainbow looks flat. If the sun is low, we can see a full semicircle and at a plane, we are able to see a full circular rainbow.