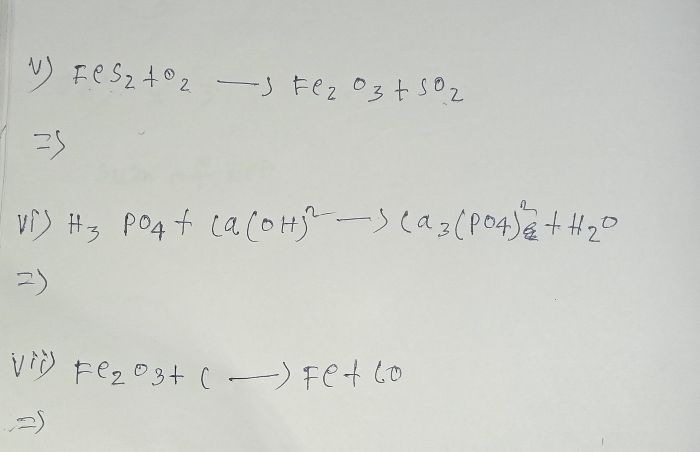CBSE Class 10 Answered
When iron and sulphur are heated together, they combine to form a single product, iron sulphide.
2Fe(s) + S(s) → FeS (s)
Iron Sulphur Iron sulphide
When lead dioxide reacts with sulphur dioxide, both these compounds combine to form lead sulphate.
PbO2(s) + SO2(s) → PbSO4(s)
Lead dioxide Sulphur dioxide Lead sulphate
2) Decomposition reaction
When mercuric oxide is heated in a crucible, the orange-red powder begins to darken and a silver mirror begins to deposit on the cooler parts of the crucible. This is mercury. If we hold a glowing splint near the crucible, it can relight. This shows that the gas evolved during the reaction is oxygen.
2HgO(s) → 2Hg(s) + O2 ↑
Mercuric oxide Mercury Oxygen
Electrolysis of water produces two volumes of hydrogen gas and one volume of oxygen gas on passing an electric current through acidulated water.
2H2O(l) → 2H2 (g) + O2(g)
Thermal decomposition
During thermal decomposition a chemical compound breaks into simpler compounds. The simpler compounds do not reunite to form the original compound on cooling.
Example:
2 KClO3 → 2KCl + 3O2
2NaNO3 → 2NaNO2 + O2
Photochemical reaction: The chemical reactions which proceed with the absorption of light energy are called photochemical reactions.
Example:
Photosynthesis in plants.
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O2
Example:
Silver chloride turns grey in the sunlight. This is due to the decomposition of silver chloride into silver and chlorine by sunlight.
2AgCl → 2 Ag + Cl2
Electrochemical reaction: The chemical reactions which proceed with the absorption of electric energy are called electrochemical reactions.
Example:
Fused potassium chloride on passing electric current through it breaks (decomposes) into its charged particles (ions).
KCl → K+ + Cl-
3) Double decomposition
Precipitation reactions
The insoluble solid formed during the double displacement reactions is called a precipitate. Reactions in which a precipitate is formed as one of the products are also called precipitation reactions.
Sodium sulphate reacts with barium chloride to form barium sulphate and sodium chloride solution.
Na2SO4 (aq) + BaCl2 → BaSO4(s) + 2NaCl(aq)
Sodium Barium Barium Sodium
sulphate chloride sulphate chlorideNeutralisation reactions
The reaction between an acid and a base to form a salt and water is called as neutralisation reaction.
NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
Sodium Hydrochloric Sodium Water
hydroxide acid chloride
3) Oxidation and Reduction reactions (Redox)
Oxidation reactions
Hydrogen sulphide reacts with chlorine gas to form hydrogen chloride and sulphur. In this reaction, the chlorine acts as an oxidising agent and removes hydrogen from hydrogen sulphide to form sulphur.
H2S + Cl2 → 2HCl + S
Hydrogen Chlorine Hydrogen Sulphur
sulphide chloride
Ferrous chloride reacts with chlorine gas to form ferric chloride. In this reaction, ferrous chloride gains the electronegative radical chlorine and is therefore oxidised to ferric chloride.
2FeCl2 + Cl2 → 2FeCl3
Ferrous Chlorine Ferric
chloride chloride
Reduction reactions
Ferric oxide reacts with carbon monoxide to form iron and carbon dioxide. In this reaction, carbon monoxide acts as a reducing agent and removes oxygen from ferric oxide to form iron.
Fe2O3 + 3CO → 2Fe + 3CO2↑
Ferric oxide Carbon monoxide Iron Carbon dioxide
Chlorine gas reacts with hydrogen sulphide to form hydrogen chloride and sulphur. In this reaction, hydrogen sulphide acts as a reducing agent and supplies hydrogen to chlorine to form hydrogen chloride.
H2S + Cl2 → 2HCl + S
Hydrogen Chlorine Hydrogen Sulphur
sulphide chlorideRedox reactions:
Consider the redox reaction between hydrogen sulphide and chlorine.
In the reaction between hydrogen sulphide and chlorine, the products formed are hydrogen chloride and sulphur.
H2S + Cl2 → 2HCl + S
Hydrogen Chlorine Hydrogen Sulphur
sulphide chloride
When an atom or a group of atoms loses electrons, oxidation takes place. In this reaction, hydrogen sulphide is oxidised to sulphur.
H2S → S
S-2 - 2 e- → S
Sulphide ion Sulphur
Since, hydrogen sulphide loses electrons; it is called a reducing agent.
When an atom or a group of atoms gains electrons, reduction takes place. In this reaction, chlorine is reduced to hydrogen chloride.
Cl2 → HCl
2Cl + 2 e ̶ → 2Cl ̶
Chlorine Chloride ion
Since, chlorine accepts electrons it is called an oxidising agent.
4) Displacement reaction
Zinc displaces copper in copper sulphate to form zinc sulphate.
Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
Zinc Copper sulphate Zinc sulphate Copper
Chlorine, being more electronegative than potassium displaces it from potassium bromide to form potassium chloride and bromine gas.
Cl2 + 2KBr → 2KCl + Br2
Chlorine Potassium Potassium Bromine
bromide chloride5) Double displacement reaction
Sodium hydroxide reacts with hydrochloric acid to form sodium chloride and water.
NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
Sodium Hydrochloric Sodium Water
hydroxide Acid chloride