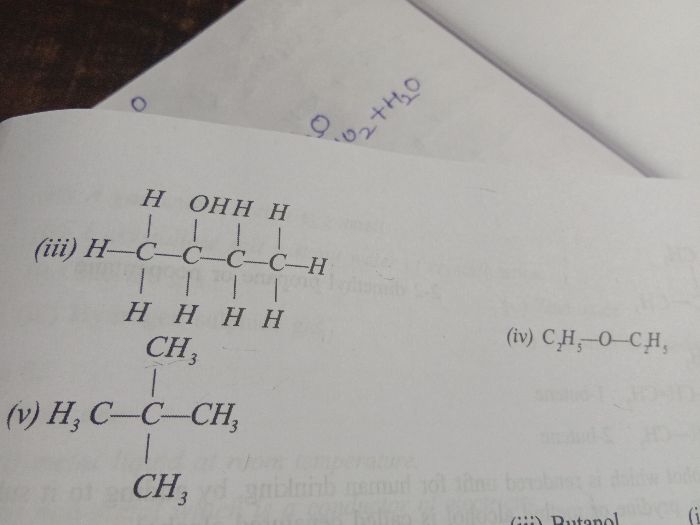ICSE Class 10 Answered
Explain functional group with examples.
Asked by jaiswalsindhuli717 | 12 Nov, 2018, 20:18: PM
Functional Groups:
All organic compounds are derivatives of hydrocarbons.
The derivatives are obtained by replacing one or more hydrogen atoms with some other atom or a group
of atoms.
The new set of compounds formed after replacement has functions different from the parent hydrocarbon.
Functional group:
An atom or a group of atoms present in the molecules, which determines the characteristics property of the organic compounds, is called the functional group.

|
Organic compound |
Functional group |
General formulae |
|
Haloalkanes |
Halide-X (F,Cl,Br,I) |
R-X |
|
Alcohols |
Hydroxyl-OH |
R-OH |
|
Aldehydes |
Aldehyde-CHO |
|
|
Carboxylic acids |
Carboxyl-COOH |
|
|
Ketones |
Keto |
|
|
Ethers |
Ethers
|
R-O-R’ |
Answered by Varsha | 13 Nov, 2018, 10:04: AM
Application Videos
Concept Videos
ICSE 10 - Chemistry
Asked by anshpatel6307 | 18 Mar, 2022, 21:32: PM
ICSE 10 - Chemistry
Asked by pritijpjain | 13 Feb, 2021, 07:44: AM
ICSE 10 - Chemistry
Asked by Kanwaranita10 | 16 Feb, 2020, 09:23: AM
ICSE 10 - Chemistry
Asked by arpitt682 | 01 Oct, 2019, 15:44: PM
ICSE 10 - Chemistry
Asked by vijay.prag | 14 Jul, 2019, 09:35: AM
ICSE 10 - Chemistry
Asked by jaiswalsindhuli717 | 16 Dec, 2018, 17:20: PM
ICSE 10 - Chemistry
Asked by hy666333 | 12 Dec, 2018, 20:04: PM
ICSE 10 - Chemistry
Asked by jaiswalsindhuli717 | 12 Nov, 2018, 20:29: PM
ICSE 10 - Chemistry
Asked by jaiswalsindhuli717 | 12 Nov, 2018, 20:18: PM
ICSE 10 - Chemistry
Asked by dr_pradip27121972 | 03 Jun, 2018, 12:55: PM