The Ultimate Guide to Building Financial Literacy for a Brighter Future

Teaching children and teenagers financial literacy is crucial for future success and lifelong learning. Financial literacy is essential for everyone and helps achieve financial goals and helps make better decisions in life.
By Topperlearning Expert 16th Aug, 2023 | 04:58 pm
ShareIntroduction to financial literacy
One needs cash to meet day-to-day expenses. Understanding and managing money has become necessary in today's fast-paced world. It should be a part of the curriculum from a very early stage. It is an essential skill for everyone, but it is essential for middle schoolers who are becoming more independent and making more financial decisions independently.
There can be different ways to deliver financial literacy to young learners. Some of these are listed below.
One should start with the basics. Do remember that too much information may overwhelm a learner. The basics may include topics like how to budget and save money.
Stay relevant and talk about ways finance is linked to their daily needs, education and opting for a future career choice with many real-life examples. Get children involved in day-to-day learning. Give them much exposure that they learn from real-life, practical experiences. While going for a monthly grocery visit, let them make the item list, pick the items from the store, provide opportunities to calculate the required bills and let them experience the checkout options. This can be done in stages per the child's age and the amount of information one wishes to transfer.
Moreover, CBSE has introduced financial literacy as a skill subject from class 6 onwards to let learners become financially literate from an early age. So, things will be more relatable at a learner's end.
Basics of Money Management
Money management is a process that has some basics like planning, organising, and controlling finances. It includes setting financial goals, budgeting, saving, investing, and managing debt. One may or may not be familiar with all these financial terms, but all these will depend mainly on how much one knows the art of money management.
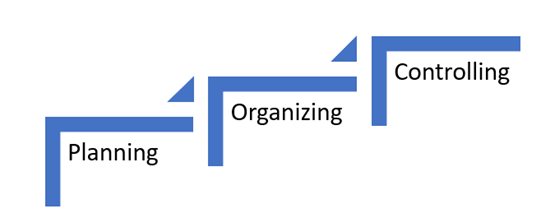
It is highly recommended that skills such as money management are introduced early for maximum benefits at later stages of one's life.
Managing money helps avoid unnecessary expenses and brings about a discipline around understanding how money works.
Here are some of the basics of money management:
Set financial goals. What does one want to achieve with their money? Buy a house, save for retirement, or pay for college? Once the goals are final, the plan can be reached basis the set goals.
Creating a budget is the first step. A budget is a plan for how money is spent. It helps track the income and expenses and whether one is going out of monthly expenses.
Saving money. To achieve the set financial goals, saving money is essential. There are different ways to save money. One can closely look at the budget and then allocate funds for monthly savings.
Investing. To grow the money, investing is the key. Many types of investment are available in the market to choose basis individual requirements.
Managing debt. It is crucial to manage debt very carefully. One should ensure that the bill payments are made on time.
Managing money is a crucial life skill that everyone should have. Below are some basic principles through which one can take control of the finances and achieve their goals.
Below are some more tips for managing money:
Track spending. Doing so will help to see where money is going and to identify areas where one can cut back.
Pay yourself first. Set aside money for savings or investing before paying any bills.
Live below means. Spend less money than earnings.
Be patient. It takes time to achieve financial goals. Do not get discouraged in case an immediate result is not visible.
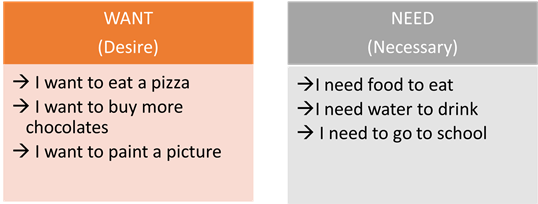
Needs vs wants.
It is very crucial to create discipline around needs and wants. Needs are necessities, and wants are the wish lists that never end.

One can live for days without luxury items but not food or water.

Food like Dal, Rice is a need for our body and considered as need. Pizza, burgers, etc., are wants that will never end. It is essential to distinguish between need and want from a very early age.

Ritu gets weekly pocket money of Rs 250. Her mother asked her to maintain an expense book to understand weekly expenses.
Below is a note from Ritu's expense book for the previous week.
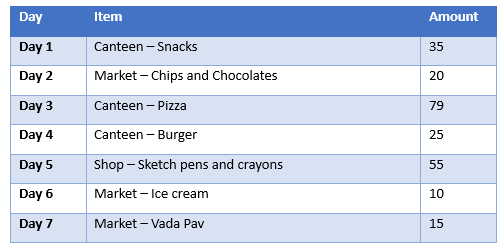
- What is the amount of money left with Ritu?
- Could Ritu have managed her expenses in a better way?
- Which all items from the list would one consider 'need' and 'want'?
- Weekly pocket money of Rs 250 results in approximately 12,000 yearly. What will be the amount if Ritu saves 50% of it?
- How would one have managed the 'want' expenses basis Ritu's expense book?
If you are a student, take your parent's help to try and answer the above problem.
Savings and investing
Savings is the act of keeping money aside for future use. It is a crucial part of financial planning as it helps to achieve short-term or long-term financial goals.
Money can be saved in various ways by opening a savings bank account, investing in the market, or buying a certificate of deposits like Fixed and recurring deposits.

With such financial instruments and advisory, a bank deposits one's money and provides interest on the sum invested.
Saving and investing are both important parts of financial planning. One can improve their financial literacy and achieve their financial goals by following the tips above.
Banking and financial services
Banking is accepting money from people termed as depositors and lending that money to other people or businesses in terms of loans.
Banks also invest some of the money depositors have deposited. People can withdraw their money from banks anytime via cheques, drafts, digital services such as UPI, Net Banking or ATMs, etc.
The Reserve Bank of India regulates this sector. The RBI plays a crucial role in ensuring the stability and soundness of the financial system.
There are different types of financial services available in India. Some of these are:
- Banking services: Savings accounts, loans, deposits and investments.
- Insurance services: such as term, life, health, property, and medical insurance.
- Investment services: mutual funds, SIPs, stocks, and bonds.
- Payment services: credit and debit cards, online payments.
- Financial planning services like the National pension scheme for retirement plans, tax planning, etc.

The Indian banking and financial services sector is an essential sector that boosts the economy. One can make informed financial decisions and achieve financial goals by understanding the different types of banking, financial services and insurance (BFSI services) and improving financial literacy.
One must also know that many things depend on financial attitude, behaviour and knowledge. A highly knowledgeable person may not have apt financial behaviour and attitude.
Protection of personal finance
It is crucial to stay updated with various malicious activities, especially with the rise of digital payments across banking and financial apps. It is recommended to install apps from trusted sources only.

Below are some steps to protect personal finance:
- Always create a strong login password. Do not share any such details with others.
- It is not recommended to share personal details online.
- Beware of online scams and fraud.
- Use updated software, apps and antivirus.
Some additional tips to protect personal finance:
- Keep a separate bank account for emergency funds. Maintain that account accordingly.
- Review insurance policies occasionally to ensure they still meet the needs.
- Set up transaction alerts for credit cards, debit cards, etc.
Early financial literacy: need of an hour.
Early financial literacy is understanding and managing money at a young age. Children need to learn about managing money at a young age to develop good financial habits that will last a lifetime. Involve them in daily learning on how money is earned, what expenses are, and how savings and investments are planned.
It is a concern for a developing country like India, where less than a third of the population is financially literate. In 2019, the National Centre for Financial Education (NCFE) was surveyed to assess and evaluate critical gaps in financial literacy. The survey included a sample of 75,000 individuals between 18 and 79. The survey was conducted in 14 national/ regional languages with household questionnaires. This survey revealed that only 27.18 % of the participants had achieved the minimum target score or were financially literate.

In one of his statements, the CEO of a well-known FinTech company emphasised the significance of early financial literacy at the school level, where the fundamentals of money management are taught alongside the formulae of physics, arithmetic, and chemistry. Although NEP 2020 seeks to impact the way education is delivered, the role of the parent remains crucial in laying the groundwork for their children's financial literacy. For instance, the lesson can be imparted by a fundamental weekly pocket money analysis. As a parent or guardian, one can request that their ward keep a diary of their expenses and savings from their weekly or monthly pocket money.
Allow young learners to learn through various real-life examples. Take them to shopping malls and markets and explain basic money management concepts.
It can help children
- take informed and better financial decisions.
- Avoid debt at a later stage in life.
- Achieve their financial goals.
Conclusion
Knowing the art of managing money and how money works from a very early age is crucial. It is the responsibility of parents, guardians and various institutions to make available resources and experiences to tackle money-related real-life applications. Moreover, financial literacy is included in the curriculum framework for adult education as a critical life skill under the national education policy 2020.
If you are a parent, teacher or guardian.
- Give children exposure to know how money works.
- Involve them while making the monthly budgets of essentials.
- Ask them to maintain trackers for the expenses made using their pocket money.
- Help them analyse their spending habits and categorise them as needs and wants.
- Create and build a habit of savings from an early age.
- As per their age, inform them about various savings instruments, uses and ways to manage money.
- There are various trusted online learning websites for self-referencing before delivering apt and accurate information to children. Go for it!
If you are a student.
- Start analysing the bills and various components associated with them. Bills can be of any grocery, food, shopping etc.
- Maintain a tracker or make notes on the expenses made daily. Doing so will help to understand where the money is going.
- Get involved with parents and guardians in understanding financial terms gradually.
- Avoid unnecessary expenses to help grow the savings.
Even TopperLearning experts are working on research-based blogs to provide supplementary inputs on basic financial literacy and updated resources for CBSE, ICSE and Maharashtra State Board.
FAQ's
Q 1. What is financial literacy?
Ans:Financial literacy is the ability to understand and use financial concepts and use these as skills to make informed decisions. It includes knowing how to manage money. How much money should one have for daily needs and in case of emergencies? What other options should one have to manage money effectively?
Q 2. Why is financial literacy important?
Ans: Financial literacy is essential, especially from an early age, as it shapes financial decision-making skills, which are very important to acquire.
It helps to
- take informed- decisions
- be financially independent
- stay less stressed
- protect from fraud and scams
- achieve various financial goals
- build wealth
Q 3. What are some essential financial literacy skills?
Ans: As we all know, managing money is a skill that helps make informed decisions. Apart from this, one should also know about budgeting, saving, investing, understanding credit, protecting assets, managing debts, tax planning, retirement planning, etc.
Q 4. Can children and teenagers benefit from financial literacy?
Ans: Absolutely! Being financially literate, they can
- learn how to budget and save money.
- Understand the difference between savings and investments.
- Learn about credit and how to use it responsibly.
- Learn about the importance of insurance.
- Know about the importance of saving for retirement.
Q 5. Can financial literacy help me achieve my financial goals?
Ans: Yes! Financially literate people can
- set realistic financial goals
- create an effective budget
- help to invest money wisely
- help to avoid debt traps
- protect their assets much better than others.
Q 6. What is CBSE Skill Education, and what are the books and support materials available for it?
Ans: As per NEP 2020, the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) introduced skill-based education in schools. The aim is to equip students with practical skills to help them in their careers.CBSE has published a range of books and support materials for this purpose, covering various subjects such as Retail, Information Technology, Beauty and Wellness, and more. Topperlearning strives to raiseawareness about the significance of such in-demand skills and topics throughthis blog series.
Important Resources
- Education Franchisee opportunity
- NCERT Solution
- CBSE Class 9 Mathematics
- NCERT Solutions for class 10 Science
- Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 9 Science
- NCERT Solutions for class 10 Maths
- Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 10 Hindi
- CBSE Class 10 English
- CBSE Class 10 English
- CBSE Class 10 Social Studies
- CBSE Class 10 Science
- CBSE Class 10 Mathematics
- Career In Science After 10
- Career In Commerce After 10
- Career In Humanities/Arts After 10
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11
- Business Studies Class 12 CBSE project