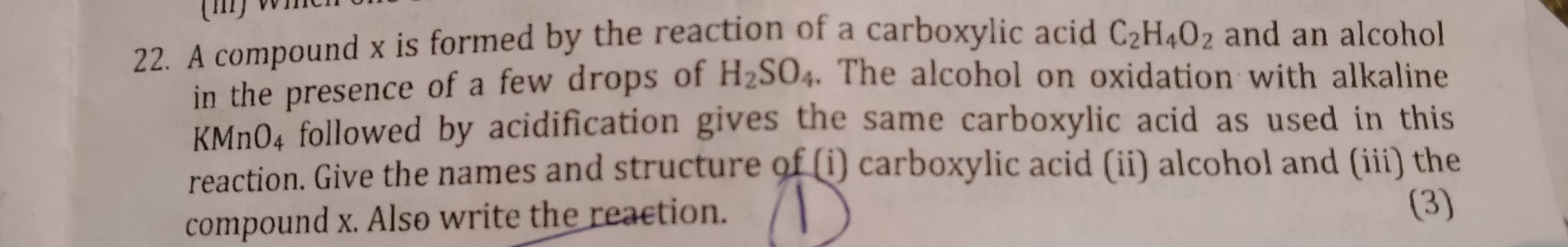CBSE Class 10 Answered
why soap is collidal in solution? how it does ion-ion repultion?
Asked by kamalnayansingh7 | 13 Jan, 2020, 08:35: AM
Colloidal state of matter: The state in which the size of the particle is such that it can pass through filter paper but not through the animal or vegetable membrane.
Consider the example of soap. Soap is the sodium salt of higher fatty acids and represented as RCOONa.
Examples: Sodium stearate, sodium palmitate
When soap is dissolved in water, it dissociates into RCOO− and Na+ ions.
The RCOO− consists of two parts—a non-polar, long hydrocarbon chain R (which is hydrophobic and called the tail) and the polar group COO− (which is hydrophilic and called the head).
The RCOO− ions are present on the surface with their polar group in water and their non-polar group away from water and remain at the surface.
At higher concentration, these ions do not remain on the surface but are pulled into the bulk of solution. Because of this, RCOO− ions coagulate to form a spherical shape with their hydrocarbon chains pointing towards the centre and the COO− part outwards on the surface of the sphere. This coagulate formed is called ionic micelle.
Each of these micelles contains up to 100 ions.

Answered by Ramandeep | 14 Jan, 2020, 12:32: PM
Application Videos
Concept Videos
CBSE 10 - Chemistry
Asked by sneh | 27 Mar, 2020, 10:11: AM
CBSE 10 - Chemistry
Asked by pranjaliinamdar2004 | 29 Feb, 2020, 19:20: PM
CBSE 10 - Chemistry
Asked by sweetykhatri99254 | 27 Feb, 2020, 15:40: PM
CBSE 10 - Chemistry
Asked by priyanshiishu | 30 Jan, 2020, 10:39: AM
CBSE 10 - Chemistry
Asked by kamalnayansingh7 | 13 Jan, 2020, 08:35: AM
CBSE 10 - Chemistry
Asked by Deepak | 22 Dec, 2019, 23:20: PM
CBSE 10 - Chemistry
Asked by ritikraghuwanshi6986 | 16 Dec, 2019, 20:42: PM
CBSE 10 - Chemistry
Asked by vedantsagrawal23 | 05 Dec, 2019, 08:34: AM
CBSE 10 - Chemistry
Asked by aryasaxena2003 | 25 Jul, 2019, 17:35: PM
CBSE 10 - Chemistry
Asked by rushabhjain.avv | 21 Mar, 2019, 22:07: PM