CBSE Class 12-science Answered
what is the function of rochelle salt in fehling solution B???
Asked by Anushri | 05 Feb, 2014, 09:56: PM
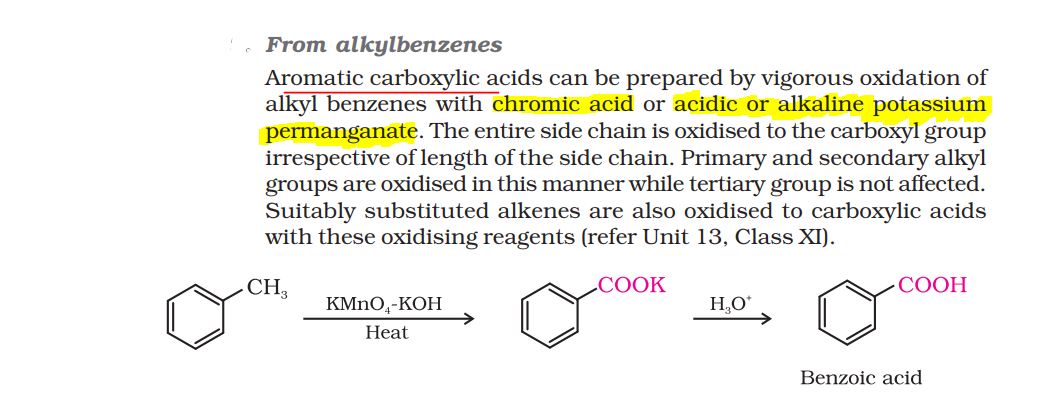
- Fehling's A is a blue aqueous solution of copper (II) sulphate, while Fehling's B is a clear solution of aqueous potassium sodium tartrate (also known as Rochelle salt) and a strong alkali (commonly sodium hydroxide).
- Equal volumes of the two mixtures are mixed together to get the final Fehling's solution, which is a deep blue colour.
- In this final mixture, aqueous tartrate ions from the dissolved Rochelle salt chelate to Cu2+ (aq) ions from the dissolved copper(II) sulphate, as bidentate ligands giving the bistartratocuprate(II)4- complex.
- The tartarate ions, by complexing copper prevent the formation of Cu (OH)2 from the reaction of CuSO4.2H2O and NaOH present in the solution.
Answered by | 06 Feb, 2014, 09:40: AM
Concept Videos
CBSE 12-science - Chemistry
Asked by ukg8612 | 15 Apr, 2024, 07:36: PM
CBSE 12-science - Chemistry
Asked by ajayarchi | 08 Feb, 2024, 03:43: AM
CBSE 12-science - Chemistry
Asked by pallasriramulu9 | 24 Dec, 2023, 06:05: AM
CBSE 12-science - Chemistry
Asked by bsaheliya | 22 Dec, 2023, 09:53: PM
CBSE 12-science - Chemistry
Asked by ygarg8323 | 18 Apr, 2022, 12:47: PM
CBSE 12-science - Chemistry
Asked by kaziryan.05 | 30 Jun, 2021, 04:52: PM
CBSE 12-science - Chemistry
Asked by kaziryan.05 | 29 Jun, 2021, 08:36: AM
CBSE 12-science - Chemistry
Asked by kaziryan.05 | 28 Jun, 2021, 02:34: PM
CBSE 12-science - Chemistry
Asked by saimerala007 | 22 May, 2021, 02:08: PM
CBSE 12-science - Chemistry
Asked by amitkumar.cis | 31 Dec, 2020, 10:45: AM