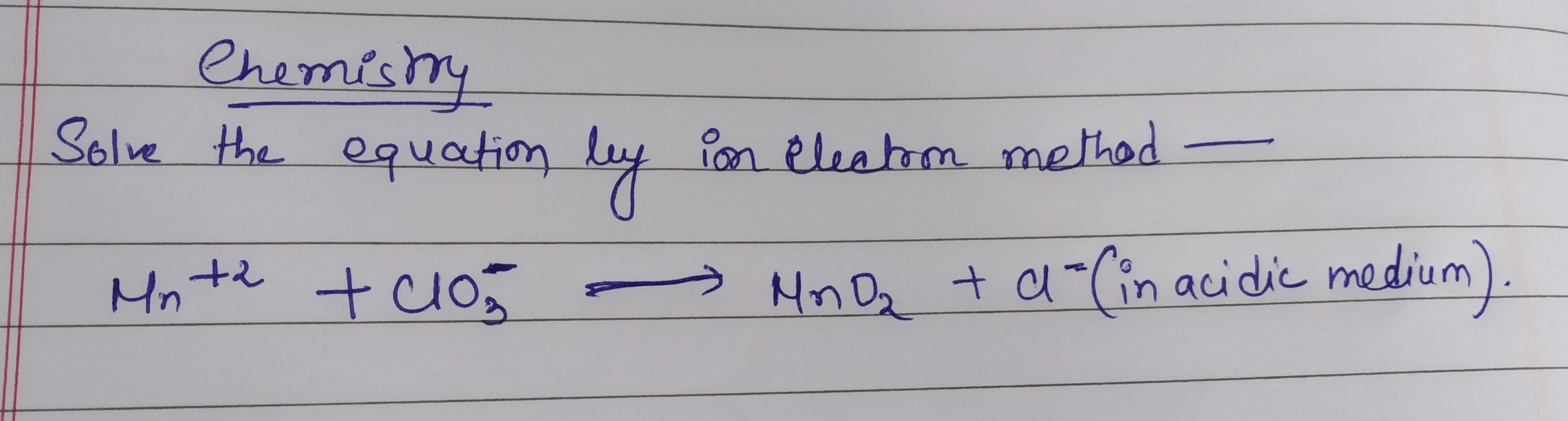
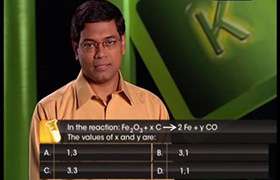CBSE Class 11-science Answered
The skeleton equation is:
MnO4- + I- → MnO2 + I2
Step 2
The oxidation number of various atoms involved in the reaction.
+7 -2 -1 +4 -2 0
Mn O4- + I- → Mn O2 + I2
Step 3
For Mn oxidation number changes from +7 to +4 so it is reduced. For I oxidation number changes from -1 to 0 so it is oxidised. No change in oxidation number of O.
Step 4
Determine the net increase in oxidation number for the element that is oxidized and the net decrease in oxidation number for the element that is reduced.
For I -1 to 0 Net change = +1
For Mn +7 to +4 Net change = -3
Step 5
Determine a ratio of oxidized to reduced atoms that would yield a net increase in oxidation number equal to the net decrease in oxidation number.
I atoms would yield a net increase in oxidation number of +3. (Three electrons would be lost by three I atoms.). 1 Mn atom would yield a net decrease of -3. (One Mn atom would gain three electrons.)
Thus the ratio of I atoms to Mn atoms is 3:1.
Step 6
To get the ratio identified in Step 5, add coefficients to the formulas which contain the elements whose oxidation number is changing.
MnO4- + 3I- → MnO2 + I2
Still, the equation is not balanced as the charge is different on both sides, so follow step 7.
Step 7
Balance the rest of the equation by inspection.
If we place a 3 in front of the I- and balance the iodine atoms with a 3/2 in front of the I2, both the atoms and the charge will be balanced.
MnO4- + 3I- → MnO2 + 3/2I2
Multiply by 2 to whole equation and we will get the balanced equation,
2MnO4- + 6I- → 2MnO2 + 3I2