CBSE Class 9 Answered
Auditory parts of human ear
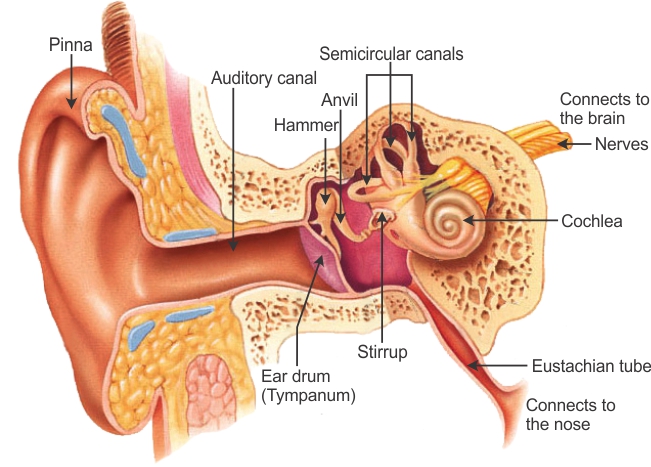
The outer ear is called 'pinna'. It collects the sound from the surroundings. The collected sound passes through the auditory canal. At the end of the auditory canal there is a thin membrane called the ear drum or tympanic membrane. When a compression of the medium reaches the eardrum, the pressure on the outside of the membrane increases and forces the eardrum inward. Similarly, the eardrum moves outward when a rarefaction reaches it. In this way the eardrum vibrates. The vibrations are amplified several times by three bones (the hammer, anvil and stirrup) in the middle ear. The middle ear transmits the amplified pressure variations received from the sound wave to the inner ear. In the inner ear, the pressure variations are turned into electrical signals by the cochlea. These electrical signals are sent to the brain via the auditory nerve, and the brain interprets them as sound.






