CBSE Class 12-science Answered
1.00 g of a non-electrolyte solute dissolved in 50 g of benzene lowered the freezing point of benzene by 0.40K. The freezing point depression constant of benzene is 5.12 K kg/mol. Find the molar mass of the solute
Asked by rockdeva663 | 17 Apr, 2019, 09:58: AM
Kf = 5.12 K k/mol
W1 = 50 g
W2 = 1.0 g
ΔTf = 0.4 K
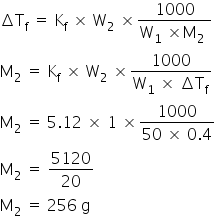
Answered by Ramandeep | 17 Apr, 2019, 10:41: AM
Concept Videos
CBSE 12-science - Chemistry
Asked by varinder2149 | 10 Dec, 2023, 08:21: PM
CBSE 12-science - Chemistry
Asked by vekariyaparth61 | 16 May, 2022, 04:33: PM
CBSE 12-science - Chemistry
Asked by goyalpavitarta | 03 May, 2021, 01:27: PM
CBSE 12-science - Chemistry
Asked by goyalpavitarta | 03 May, 2021, 01:25: PM
CBSE 12-science - Chemistry
Asked by goyalpavitarta | 03 May, 2021, 01:20: PM
CBSE 12-science - Chemistry
Asked by sshashu993 | 25 Jul, 2020, 08:02: AM
CBSE 12-science - Chemistry
Asked by anukritisingh8103.bmps | 15 Jul, 2020, 05:52: PM
CBSE 12-science - Chemistry
Asked by sharmasherryal | 25 May, 2020, 09:54: AM
CBSE 12-science - Chemistry
Asked by panthpreet0221 | 06 May, 2020, 10:41: AM