ICSE Class 10 Answered
WHAT IS THE CAUSE FOR THE CENTRIPETAL FORCE ACTING ON A CAR MOVING IN CIRCULAR PATH
Asked by Chris | 11 Feb, 2016, 08:25: PM
When a rigid body moves along a circular path with uniform speed; its direction changes continuously. Due to inertia, at every point of the circular path; the body tends to move along tangent to the circular path at that point. According to Newton's second law of motion, a change in the direction of motion of the body can take place only if some external force acts on the body. Thus to move a body along a circular path; an external force is required, which will deflect the body from its straight path to the circular path at every point of the path.
An external force required to make a body move along circular path with uniform speed is called centripetal force.
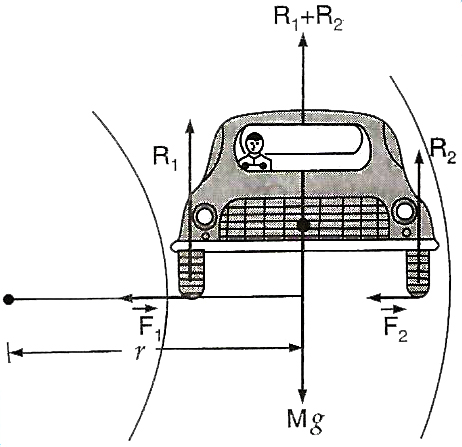
Consider a car of weight Mg going around a circular path of radius r with velocity v on a level road. While taking the round, the tyres of the vehicles try to leave the road and go away from the centre of curve. Due to this the forces of friction, F1 and F2 act inward at the inner and outer tyres respectively. If R1 and R2 are the normal reactions of the ground on the inner and outre tyres respectively, then
F1 = μ R1 and F2 = μ R2;
where μ is the coefficient of friction between the tyre and the road.
The total force of friction provides the necessary force i.e.,
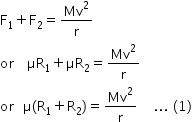
As there can be no motion of the car along vertical,, the total normal reaction on the car balances its weight i.e.,
R1 + R2 = Mg ... (2)
From eqn (1) and (2),
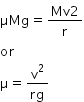
Answered by Faiza Lambe | 12 Feb, 2016, 09:11: AM
Application Videos
Concept Videos
ICSE 10 - Physics
Asked by praggya.srivastava.g1972 | 13 Oct, 2023, 10:51: AM
ICSE 10 - Physics
Asked by roopan249 | 04 Jun, 2022, 05:58: PM
ICSE 10 - Physics
Asked by roopan249 | 04 Jun, 2022, 05:57: PM
ICSE 10 - Physics
Asked by prachivanave21.10spicertl | 13 May, 2020, 12:28: PM
ICSE 10 - Physics
Asked by shambhavikesarwani11 | 07 Apr, 2020, 10:01: PM
ICSE 10 - Physics
Asked by saibaba1069 | 25 Mar, 2020, 01:14: PM
ICSE 10 - Physics
Asked by rouhin06ganguly | 25 Mar, 2020, 12:26: PM
ICSE 10 - Physics
Asked by saibaba1069 | 23 Mar, 2020, 10:58: PM
ICSE 10 - Physics
Asked by amrutiyavishwa | 04 Mar, 2019, 12:23: PM





