CBSE Class 10 - Spherical Mirrors Videos
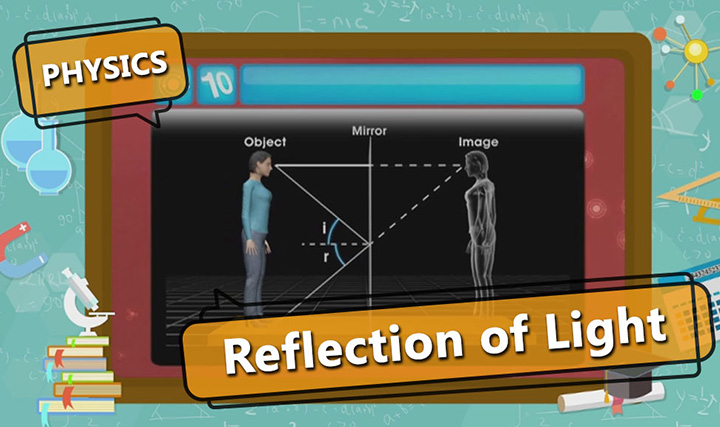
Reflection of Light
Define convex/concave mirror, pole, principal axis, radius/centre of curvature, aperture, and focal length for spherical/rear view mirrors.
More videos from this chapter
View All- Is object distance always negative in both lens and mirrors?
- The image of a candle flame placed at a distance of 30 cm from a spherical lens is formed on a screen placed at a distance of 60 cm from the lens. If the height of the flame is 2.4 cm,find the height of its image
- what is concave mirror?
- A concave mirror has focal length of 20cm. At what distance from the mirror a 5cm tall object be placed so that it forms an image at 15cm from the mirror? Also calculate the size of the image formed.
- An object is kept at a distance of 15 cm from a (a) Convex mirror (b) Plane mirror The focal length of the convex mirror and the concave lens are 10 cm each. Draw the appropriate ray diagrams, showing the formation of image, in each of the three cases.
- Very Short Answer Type Questions Name two mirrors used in this fair shop. Name the mirror in which the size of image is small.
- can a convex mirror ever form a real image? If yes, under what condition?
- how to draw a ray diagram for concave mirror (i) Parallel to pricipal axis (ii) Passing through center of curvature
-
if you placed an object at
(1) between 'C' and F and
(2) F then find the position of image, size and nature of image formed by a concave mirrors ( with ray diagrams)

- When an object is placed between pole and focus of a convex mirror, then what is the image formed?