CBSE Class 10 - Problems on Pythagoras Theorem Videos
Problems on Pythagoras Theorem
This video explains how to solve problems on pythagoras theorem.
More videos from this chapter
View All-
equilateral triangle ABC , D is a point on side BC such that 3BD = BC. Prove that 9AD2 = 7AB2.
-
Question

- If A is the area of right triangle and b is one of the sides containing the right angle,then prove that the length of the altitude on the hypotenuse is 2Ab/√(b^4+4A^2)
- The height of a moving truck is 8 m. The distance from the bottom edge of the ramp on the ground to the truck is 15 m. What is the length of the ramp?
- In an equilateral triangle AD is the altitude drawn from A on side BC. Prove that 3AB2 =4AD2
- The area of a right triangle is 210 sq cm. If the smallest side is 12 cm, what is the hypotenuse?
- What is the value of a if a, a-1,a+8 are the lengths of the sides of a right triangle where a is a natural number?
-
In quadrilateral ABCD,
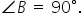 If AD2 = AB2 + BC2 + CD2. Prove that
If AD2 = AB2 + BC2 + CD2. Prove that 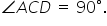
- The diagonals AC and BD of a rhombus ABCD are of length 6 cm and 8 cm respectively. What is the perimeter of the rhombus?
- Prove that if for a right triangle the sides containing the right angle have even numbers as their lengths, then the third side can"t be an odd number.