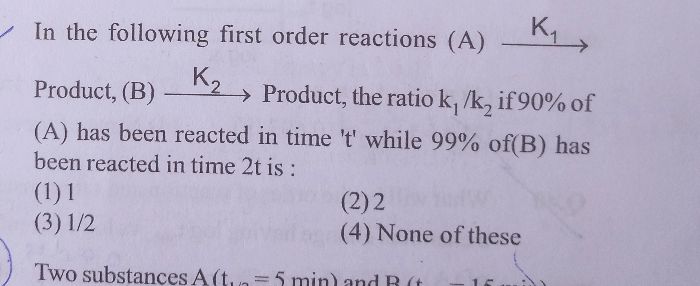CBSE Class 12-science Answered
integrated rate euqtion
Asked by sonu | 06 Feb, 2014, 09:44: PM
For the reaction A Products, which follows first order kinetics, the rate of the reaction is proportional to the concentration of A raised to power 1. i.e.,

Integration of the differential equation gives In [A] = - kt + constant
At t = 0, [A] = [A]o
ln [A]o = constant
On substitution, the integrated equation is transformed to

The rate constant k1, of a first order reaction can be determined from the expression, The integrated rate equation can also be written in the form,


Answered by | 07 Feb, 2014, 12:55: PM
Concept Videos
CBSE 12-science - Chemistry
Asked by bhadauriyax | 30 Nov, 2023, 06:23: PM
CBSE 12-science - Chemistry
Asked by rahulbiswal946 | 08 Nov, 2023, 07:01: PM
CBSE 12-science - Chemistry
Asked by mishraridhi2020 | 23 Jun, 2022, 09:16: AM
CBSE 12-science - Chemistry
Asked by cjam41665 | 10 Oct, 2021, 12:56: AM
CBSE 12-science - Chemistry
Asked by arshbhatia0809 | 22 Jul, 2021, 09:47: PM
CBSE 12-science - Chemistry
Asked by amitkumar.cis | 14 Jan, 2021, 12:40: PM
CBSE 12-science - Chemistry
Asked by Surendersingh0493 | 18 Oct, 2020, 02:05: PM
CBSE 12-science - Chemistry
Asked by khandarev3580 | 10 Oct, 2020, 10:54: AM
CBSE 12-science - Chemistry
Asked by rchaitra1204 | 07 Sep, 2020, 09:43: AM
CBSE 12-science - Chemistry
Asked by dr.akanksha0411 | 07 Aug, 2020, 11:56: AM