CBSE Class 10 Answered
derive relation between angular acceleration and linear acceleration
Asked by singhparansh | 18 Dec, 2021, 05:15: PM
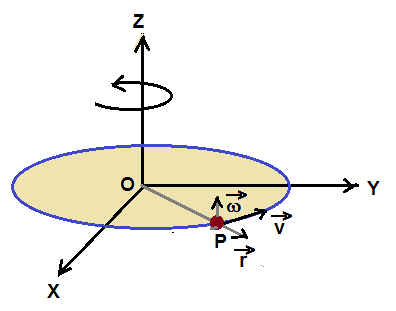
Let us consider a circular lemma as shown in fifure that rotates about an axis passing through centre of mass.
Let z-axis coincide with the axis of rotation so that lemma is in x-y plane.
At a point P , we see that tangential velocity vector  is mutually perpendicular to angular velocity vector
is mutually perpendicular to angular velocity vector 
 is mutually perpendicular to angular velocity vector
is mutually perpendicular to angular velocity vector 
and radial position vector  .
.
 .
.If the lemma makes one complete rotation in T seconds , then linear displacement made by point P in tangential direction is ( 2π r )
Hence velocity v in tangential direction , v = ( 2π r ) / T
But angular velocity ω = 2π / T
Hence from above two expressions, we get , v = ω r
Since magnitude of velocity v in tangential direction is produt of magnitude of angular velocity and radial distance
and also direction of velocity v is mutually perpendicular to vector 

and vector  , then we get velocity vector
, then we get velocity vector  in terms of vector product as
in terms of vector product as
 , then we get velocity vector
, then we get velocity vector  in terms of vector product as
in terms of vector product as =
=  ×
× 
Acceleration  = ( d
= ( d  / dt ) in tangential direction is determined by differentiating abvove expression .
/ dt ) in tangential direction is determined by differentiating abvove expression .
 = ( d
= ( d  / dt ) in tangential direction is determined by differentiating abvove expression .
/ dt ) in tangential direction is determined by differentiating abvove expression .
since ( d / dt )= 0 , we get
/ dt )= 0 , we get 
 / dt )= 0 , we get
/ dt )= 0 , we get 
where  = ( d
= ( d / dt ) is angular acceleration.
/ dt ) is angular acceleration.
 = ( d
= ( d / dt ) is angular acceleration.
/ dt ) is angular acceleration.Hence by magnitude , a = α r is the relation between angular acceleration and acceleration in tangential direction .
Answered by Thiyagarajan K | 19 Dec, 2021, 09:47: AM
Application Videos
Concept Videos
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by agankitgupta938 | 18 Apr, 2024, 04:29: PM
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by infinityupgraded | 13 Apr, 2024, 08:17: AM
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by suryamr2019 | 08 Mar, 2024, 04:32: PM
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by sheetal.kolte | 04 Mar, 2024, 12:38: PM
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by shrilakshmimunoli | 01 Mar, 2024, 01:15: AM
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by khajannirwan | 27 Feb, 2024, 10:20: PM
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by sailakshmi.avinesh | 13 Feb, 2024, 07:03: AM
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by saurabhjd527 | 30 Jan, 2024, 07:55: PM
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by saanviyadla | 24 Jan, 2024, 07:06: PM