CBSE Class 12-science Answered
What deflection is produced in the galvanometer when there is a relative motion between the coil and the magnet?
Asked by Aditya Great | 07 Dec, 2014, 01:14: PM
The figure below shows a coil of few turns of conducting material insulated from one another. It is connected to a galvanometer.
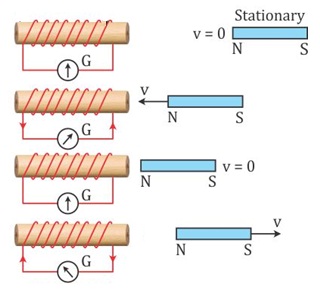
When the magnet is held stationary, the galvanometer shows no deflection.
When the north pole of the magnet is brought towards the coil, the galvanometer shows a sudden deflection indicating that a current is induced in the coil.
The galvanometer deflection is temporary and it lasts as long as the bar magnet is in motion. There won't be any deflection when the bar magnet is held stationary anywhere.
When the magnet is moved away from the coil, the galvanometer shows deflection in the opposite direction indicating the direction of induced current in the reversed direction.
When the south pole of the bar magnet is moved towards or away from the coil, the deflection in the galvanometer will be opposite to that observed with the north pole for similar movements.
The deflection in the galvanometer will be larger when the magnet is pushed or pulled away from the coil faster.
This indicates that when there is a relative motion between the coil and the magnet a current gets induced in the coil. This current gets detected with the help of galvanometer.
This experiment shows that a current flows in the coil only when there is a relative motion between the coil and the magnet due to which the galvanometer connected with the coil shows deflection.The direction of deflection in a galvanometer is reversed if the direction of motion (or polarity of the magnet) is reversed.
This indicate that whenever there is a change in the magnetic flux linked with a coil, an emf is induced. The induced emf lasts so long as there is a change in the magnetic flux linked with the coil.This phenomenon in which an electric current is induced in a conductor because of a changing magnetic field is called electromagnetic induction.
Answered by Jyothi Nair | 08 Dec, 2014, 10:05: AM
Concept Videos
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by Topperlearning User | 20 May, 2015, 02:09: PM
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by Topperlearning User | 28 Apr, 2015, 02:05: PM
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by Topperlearning User | 20 May, 2015, 02:11: PM
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by Topperlearning User | 20 May, 2015, 02:14: PM
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by Topperlearning User | 20 May, 2015, 02:33: PM
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by Topperlearning User | 28 Apr, 2015, 01:54: PM
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by Topperlearning User | 20 May, 2015, 02:36: PM
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by Topperlearning User | 20 May, 2015, 02:50: PM
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by Topperlearning User | 20 May, 2015, 02:56: PM
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by Topperlearning User | 20 May, 2015, 03:06: PM