CBSE Class 12-science Answered
State Gauss's theorem ? Derive the expression for electric field due Spherical hollow conductor and infinitely charged sheet and linearly charged conductors.
Asked by avaneesh1162 | 13 Jun, 2021, 08:56: AM
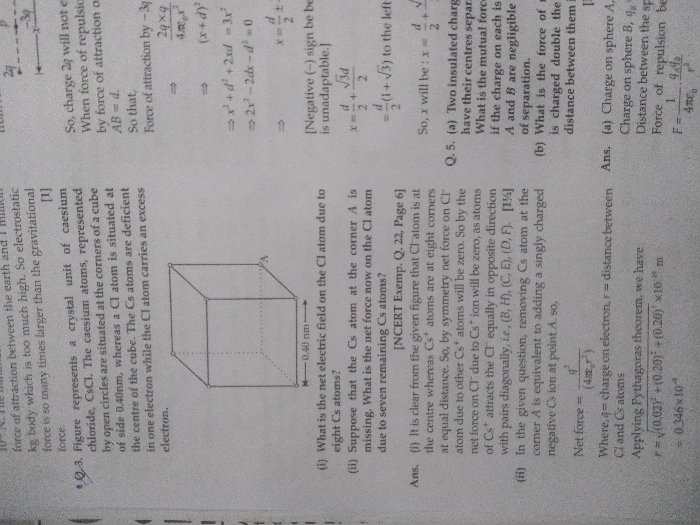
Gauss law states that electric flux φ through a closed surface equals ( q / εo ) , where q is total charge enclosed inside the closed surface
and εo is permittivity of free space .
------------------------------------------------------
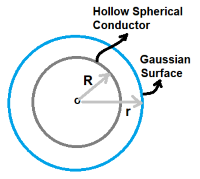
Let us consider a spherical hollow conductor of radius R that has surface charge so that total charge on the sphere is q .
If we need to find electric field at a distance r from centre of hollow sphere, we make a gaussian surface
using a concentric holow sphere of radius r as shown in figure.
Electric flux φ over the gaussian surface = Electric field × area
since electric field is uniform , electric flux φ = E × 4π r2
According to Gauss theorem , electric flux φ = E × 4π r2 = ( q / εo )
Hence E = q / ( 4πεo r2 )
when r < R , Gaussian surface will be inside the hollow sphere and enclosed charge is zero.
Hence electric field inside hollow sphere is zero.
-----------------------------------------------------------------
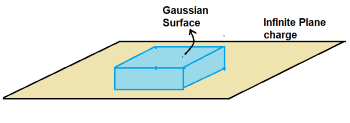
Let us consider an infinit plane that has surface charge density σ ( charge per unit area ) .
Electric field near to infinite plane is determined by making gaussian surface using a square box as shown in figure .
Let this square box enclose part of the charge of infinite plane within the area of box .
Also this square box intersects the plane so that top part of box is above the plane and bottom part of box is below the plane.
( part of the box below the plane is not visible in the figure ).
Hence a gaussian closed surface is formed that enclose part of the charge of infinite plane.
Let d be the height of top surface of gaussian surface above plane .
Then electric field at a distance d from plane is determined by gauss theorem .
E × 2A = ( σ × A ) / εo
LHS of above expression is total electric flux over the closed surface and RHS is the enclosed charge divided by εo.
Hence Electric field E = σ / ( 2 εo )
-----------------------------------------------------
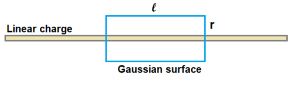
Let us consider a linearly charged thin rod of infinite length that has charge density λ ( charge per unit length ) .
To get electric field at distance r from rod , we form a gaussian closed surface by using a cylinder of length l
and radius r as shown in figure. Let the axis of cylinder coincide withe rod.
By Gauss theorem , E × ( 2 π r l ) = ( λ l ) / εo
LHS of above expression is total electric flux and RHS is enclosed charge divided by εo
Hence electric field E = λ / [ ( 2 π r ) εo ]
Answered by Thiyagarajan K | 13 Jun, 2021, 15:09: PM
Concept Videos
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by adityagalar2007 | 06 Apr, 2024, 13:06: PM
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by amlanmcob | 06 Apr, 2024, 12:27: PM
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by manishamunda787 | 02 Apr, 2024, 11:07: AM
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by kalsichaitanya | 30 Dec, 2023, 16:08: PM
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by glorialyanzaw | 13 Oct, 2023, 17:53: PM
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by srishtijha944 | 15 Jul, 2022, 21:55: PM
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by marshelojigas | 28 Jun, 2022, 06:46: AM
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by arjunsah797 | 01 Apr, 2022, 07:31: AM