CBSE Class 10 Answered
Dear Student,
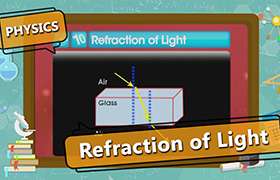
Refractive index, also called index of refraction, measure of the bending of a ray of light when passing from one medium into another. If i is the angle of incidence of a ray in vacuum (angle between the incoming ray and the perpendicular to the surface of a medium, called the normal), and r is the angle of refraction (angle between the ray in the medium and the normal), the refractive index n is defined as the ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction; i.e., n = sin i / sin r. Refractive index is also equal to the velocity c of light of a given wavelength in empty space divided by its velocity v in a substance, or n = c/v.
Some typical refractive indices for yellow light (wavelength equal to 589 nanometres [10-9 metre]) are the following: air, 1.0002; water, 1.333; crown glass, 1.517; dense flint glass, 1.655; and diamond, 2.417. The variation of refractive index with wavelength is the source of chromatic aberration in lenses