JEE Class main Answered
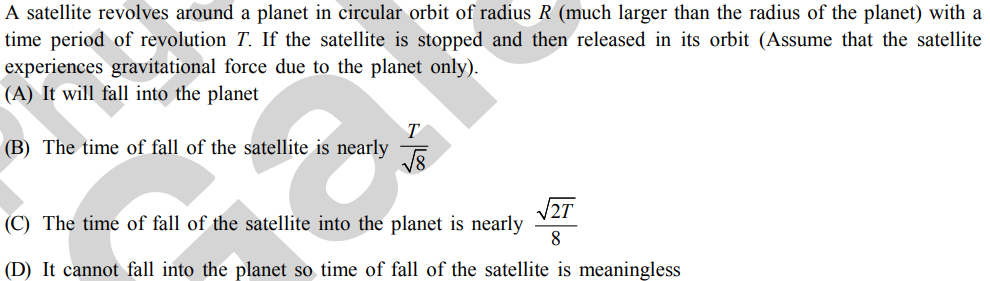
Four particles of equal masses are moving round a circle of radius r due to their mutual gravitation attraction. Find the angular velocity.
Asked by aadityakumar0603 | 05 Mar, 2023, 22:17: PM
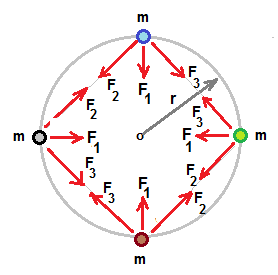
Figure shows four particles moving in a circular path due to gravitational force of attraction .
F1 is the force acting on each particle due to attraction by other particle that is diametrically opposite .
magnitude of F1 is
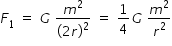
where G is universal gravitationla constant , m is mass of each particle and r is radius of circular path.
F2 and F3 are the forces acting on each particl due to left side and right side neighbour.
Magnitude of F2 and F3 are equal .
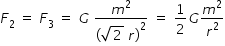
F2 and F3 each make angle 45o with F1 .
Hence resultant of F2 and F3 is in the same direction of F1 .
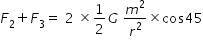
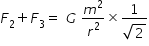
Magnitude of net force F acting on each particle is
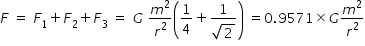
Above force F provides the centripetal force required for circular motion .
Centripetal force of circular motion equals gravitational force of attraction . Let ω be the angular speed of rotation of masses.
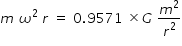

Answered by Thiyagarajan K | 06 Mar, 2023, 08:48: AM
JEE main - Physics
Asked by coolskrish | 13 Oct, 2024, 12:50: PM
JEE main - Physics
Asked by srkgb8018 | 15 May, 2024, 20:12: PM
JEE main - Physics
Asked by krajasekharnaidu13 | 04 Feb, 2024, 15:37: PM
JEE main - Physics
Asked by aadityakumar0603 | 05 Mar, 2023, 22:17: PM
JEE main - Physics
Asked by geethamehs08 | 15 Oct, 2022, 17:54: PM
JEE main - Physics
Asked by swayamagarwal2114 | 21 Jul, 2022, 17:18: PM
JEE main - Physics
Asked by das.atom1966 | 16 May, 2022, 17:34: PM